
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Base and monosaccharide used to form a given nucleoside needs to be identified and the name of the nucleoside needs to be stated.
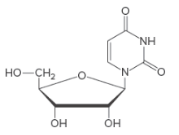
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA are
A
Only the base and the sugar portion of a nucleotide is called a nucleoside.
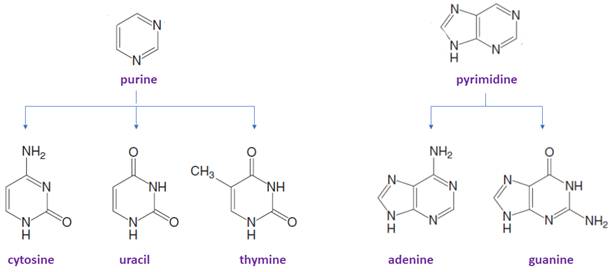
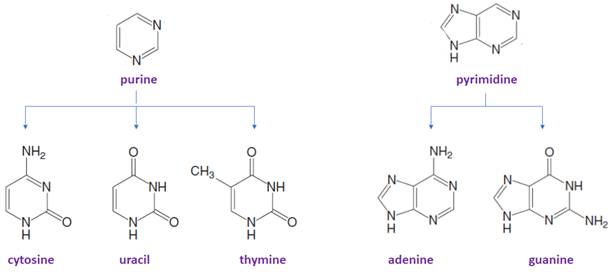
Bases in DNA/RNA:
There are only five common nitrogen-containing bases are present in DNA/RNA, which are derived either from pyrimidine or purine.
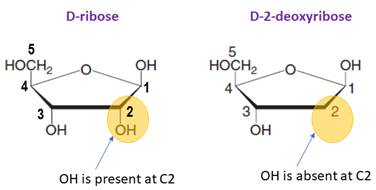
Sugar in DNA/RNA:
The monosaccharide in RNA is D-ribose.
In DNA, the monosaccharide is D-2-deoxyribose (lacks a hydroxylgroup at C2).
Naming Nucleosides:
The suffix −idine is used to name a nucleoside derived from a pyrimidine base.
The suffix -osine is used to name a nucleoside derived from a purine base.
The prefix deoxy- is used if hydroxyl group is missing at C-2 position of the sugar.
(b)
Interpretation:
Base and monosaccharide used to form a given nucleosideneed to be identified and the name of the nucleoside needs to be stated.
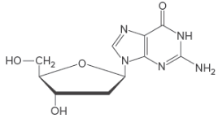
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA are linear
A nucleotide has three components; a five-membered sugar ring (monosaccharide), a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group.
Only the base and the sugar portion of a nucleotide is called a nucleoside.
Bases in DNA/RNA:
There are only five common nitrogen-containing bases are present in DNA/RNA, which are derived either from pyrimidine or purine.
Sugar in DNA/RNA:
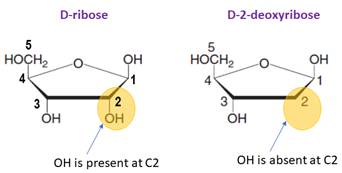
The monosaccharide in RNA is D-ribose.
In DNA, the monosaccharide is D-2-deoxyribose (lacks a hydroxyl group at C2).
Naming Nucleosides:
The suffix −idine is used to name a nucleoside derived from a pyrimidine base.
The suffix -osine is used to name a nucleoside derived from a purine base.
The prefix deoxy- is used if hydroxyl group is missing at C-2 position of the sugar.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following molecules and assign charges where appropriate. The order in which the atoms are connected is given in parentheses. a. CIFCIF b. BrCNBrCN 0 c. SOCI2 × (CISCIO) SOC₁₂ (CISCI) You can draw both an octet and a valence shell expanded structure. Considering the following structural information, which is the better one: The measured S-OS-O bond length in SOC12SOCl2 is 1.43 Å. For comparison, that in SO2SO2 is 1.43 Å [Exercise 1-9, part (b)], that in CHзSOHCH3 SOH d. CH3NH2CH3NH2 (methanesulfenic acid) is 1.66 A. e. CH3OCH3 CH3 OCH3 NH2 f. N2H2× (HNNH) N2 H2 (HNNH) g. CH2COCH₂ CO h. HN3× (HNNN) HN3 (HNNN) i. N20 × (NNO) N2O (NNO)arrow_forwardbre The reaction sequence shown in Scheme 5 demonstrates the synthesis of a substituted benzene derivative Q. wolsd works 2 NH2 NaNO2, HCI (apexe) 13× (1 HNO3, H2SO4 C6H5CIN2 0°C HOTE CHINO₂ N O *O₂H ( PO Q Я Scheme 5 2 bag abouoqmics to sounde odi WEIC (i) Draw the structure of intermediate O. [2 marks] to noitsmot od: tot meinedogm, noit so oft listsb ni zaupaib bas wa (ii) Draw the mechanism for the transformation of aniline N to intermediate O. Spoilage (b) [6 marks] (iii) Identify the reagent X used to convert compound O to the iodinated compound [tom E P. vueimado oilovonsa ni moitos nolisbnolov ayd toes ai tedw nisiqx (iv) Identify the possible structures of compound Q. [2 marks] [2 marks] [shom 2] (v) bus noires goiribbeolovo xnivollot adj to subora sidab Draw the mechanism for the transformation of intermediate P to compound Q. [5 marks] vi (vi) Account for the regiochemical outcome observed in the reaction forming compound Q. [3 marks]arrow_forwardPROBLEM 4 Solved Show how 1-butanol can be converted into the following compounds: a. PROBLEM 5+ b. d. -C= Narrow_forward
- The vibrational contribution isa) temperature independent for internal energy and heat capacityb) temperature dependent for internal energy and heat capacityc) temperature independent for heat capacityd) temperature independent for internal energyarrow_forwardQuantum mechanics. Explain the basis of approximating the summation to an integral in translational motion.arrow_forwardQuantum mechanics. In translational motion, the summation is replaced by an integral when evaluating the partition function. This is correct becausea) the spacing of the translational energy levels is very small compared to the product kTb) the spacing of the translational energy levels is comparable to the product kTc) the spacing of the translational energy levels is very large compared to the product kTarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning  Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





