
Concept explainers
SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY
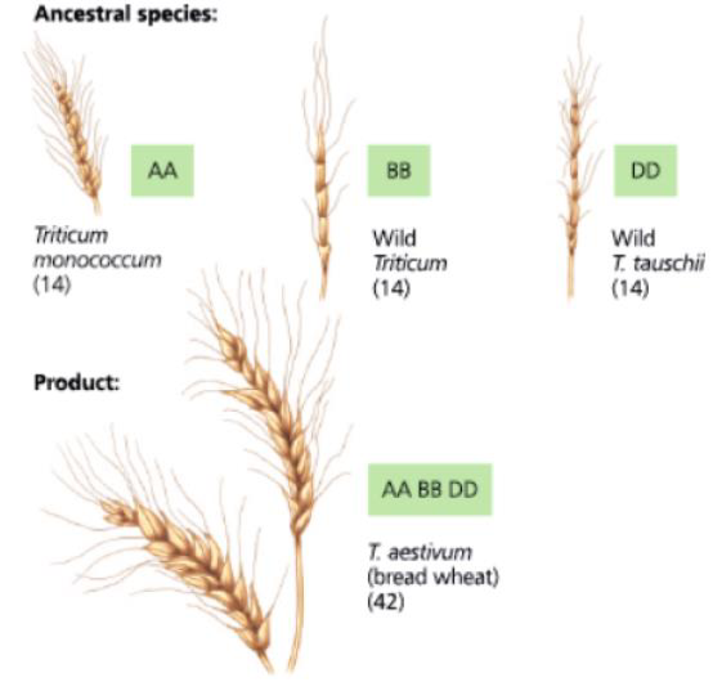
DRAW IT In this chapter, you read that bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) is an allohexaploid, containing two sets of chromosomes from each of three different parent species. Genetic analysis suggests that the three species pictured following this question each contributed chromosome sets to T. aestivum. (The capital letters here represent sets of chromosomes rather than individual genes.) Evidence also indicates that the first polyploidy event was a spontaneous hybridization of the early cultivated wheat species T. monococcum and a wild Triticum grass species. Based on this information, draw a diagram of one possible chain of events that could have produced the allohexaploid T. aestivum.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus, Books a la Carte Edition; Modified Mastering Biology with Pearson eText - ValuePack Access Card - for Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physical Science
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
- ethical considerations in medical imagingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward2. In one of the reactions of the citric acid cycle, malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate. When this reaction is considered in isolation, a small amount of malate remains and is not oxidized. The best term to explain this is a. enthalpy b. entropy c. equilibrium d. free energy e. loss of energyarrow_forward
- 18. The citric acid cycle takes place in a. the chloroplasts b. the cytosol c. the inner mitochondrial membrane d. between the two mitochondrial membranes e. the mitochondrial matrix 40 WILarrow_forward8. Most reactions of anaerobic respiration are similar to a. aerobic respiration b. photosynthesis c. lactic acid fermentation d. alcoholic fermentation e. both c and darrow_forward12. Which of the following molecules can absorb light? a. Pigments b. Chlorophyll c. Rhodopsin d. Carotenoids e. All of the abovearrow_forward
- Which of the following proteins or protein complexes is directly required for the targeting of mitochondrial inner membrane multipass proteins, such as metabolite transporters, whose signal sequence is normally not cleaved after import? OA. TIM22 OB. TIM23 C. OXA OD. Mia40 OE SAMarrow_forwardQUESTION 9 An animal cell has been wounded and has a small rupture in its plasma membrane. Which of the following is more likely to happen next? OA. The cell rapidly cleaves by cytokinesis. OB. The rate of receptor-mediati endocytosis is increased. OC. The rate of exocytosis is increased. OD. The rate of pinocytosis is increased.arrow_forwardFor the a subunit of a trimeric G protein, A. a G-protein-coupled receptor GPCR) acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), whereas a regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) can act as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). B. a GPCR acts as a GAP, whereas an RGS can act as a GEF. C. both a GPCR and an RGS can act as a GEF. O D. both a GPCR and an RGS can act as a GAP OE. None of the above.arrow_forward
- A cell expresses a transmembrane protein that is cleaved at the plasma membrane to release an extracellular fragment. The fragment binds to receptor proteins on nearby cells and activates signaling pathways resulting in altered gene expression patterns in the cells. What form of intercellular signaling does this represent? OA. Contact-dependent signaling B. Paracrine signaling OC. Synaptic signaling D. Endocrine signaling E. Autocrine signalingarrow_forwardWhich of the following drive nuclearly encoded proteins import into the mitochondrial matrix? OA. ATP hydrolysis OB. Membrane Potential OC. K+ Ions OD. A and B OE. None of the abovearrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true regarding Cholesterol import into the cell? OA. It is transported within LDL B. Receptor mediated endocytosis is involved OC. Release of cholesterol occurs in the Lysosome D. All of the above are true statements OE. None of the above are true statementsarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





