
Concept explainers
Decide if the side chains of the amino acid residues in the following peptides are nonpolar or polar, and label the hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of each peptide.
- VLLFGEDEK
- RKVSFLGAA
(a)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the side chains of the amino acid residue in the given peptide should be determined and also label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends of the given peptide.
VLLFGEDEK
Concept Introduction:
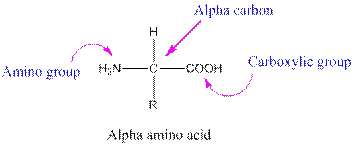
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. Amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha amino acids.
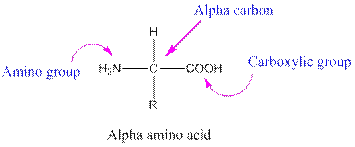
This table gives information about the polarity of the side chains:
| Name of Amino Acid | One-letter abbreviation | Structure | Side chain Polarity | Side chain |
| Alanine | A | 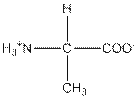 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Asparagine | N | 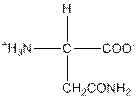 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Cysteine | C | 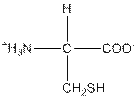 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Glutamine | Q | 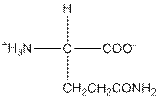 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Glycine | G | 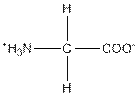 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Isoleucine | I | 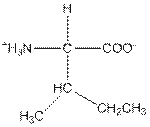 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Leucine | L | 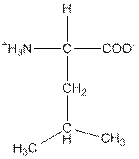 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Methionine | M | 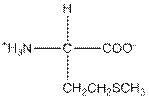 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Phenylalanine | F | 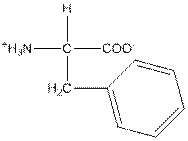 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Proline | P | 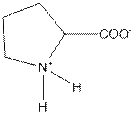 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Serine | S | 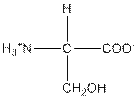 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Threonine | T | 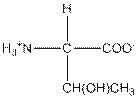 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Tryptophan | W | 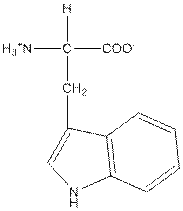 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Tyrosine | Y | 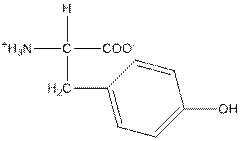 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Valine | V | 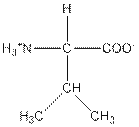 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Aspartic acid | D | 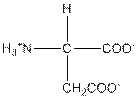 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Glutamic acid | E | 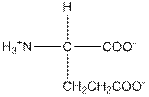 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Arginine | R | 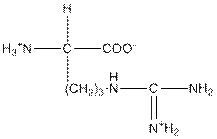 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Histidine | H | 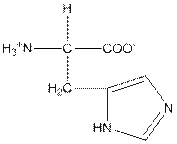 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Lysine | K | 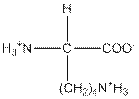 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
Answer to Problem 56P
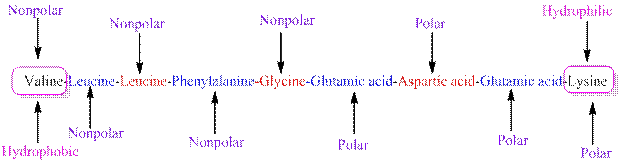
The polarity of the side chains of amino acids are shown along with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of the given peptide 'VLLFGEDEK' as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Side chains of amino acids are non-polar because only carbon and hydrogen atoms are present having very small dipole moment and tends to repel water. That's why non-polar amino acids are hydrophobic in nature.
Side chains of amino acids are polar because these proteins have those toms which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds have very high dipole moment and tends to attract water. That's why polar amino acids are hydrophilic in nature.
From the table, the sequence of peptide contains the following amino acids:
V = Valine is a non-polar amino acid.
L = Leucine is a non-polar amino acid.
F = Phenylalanine is a non-polar amino acid.
G = Glycine is a non-polar amino acid.
E = Glutamic acid is a polar amino acid.
D = Aspartic acid is a polar amino acid.
K = Lysine is a polar amino acid.
From the given peptide sequence 'VLLFGEDEK', Valine present at the right end and Lysine present at the left end of the sequence.
Valine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophobic in nature.
Lysine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophilic in nature.
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends along with polar and non-polar amino acids are indicated in the given sequence as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the side chains of the amino acid residue in the given peptide should be determined and also label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends of the given peptide.
RKYSFLGAA
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. Amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha amino acids.
Answer to Problem 56P
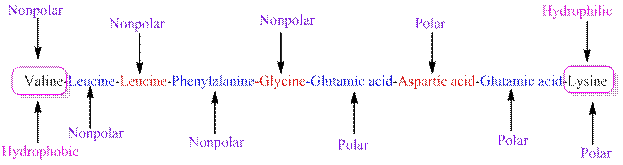
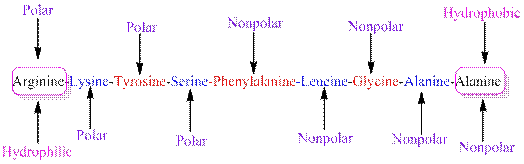
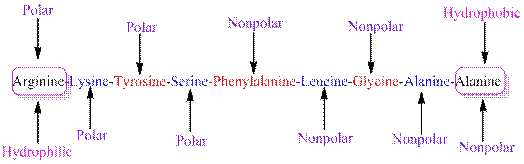
The polarity of the side chains of amino acids are shown along with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of the given peptide 'RKYSFLGAA' as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Side chains of amino acids are non-polar because only carbon and hydrogen atoms are present having very small dipole moment and tends to repel water. That's why non-polar amino acids are hydrophobic in nature.
Side chains of amino acids are polar because these proteins have those toms which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds have very high dipole moment and tends to attract water. That's why polar amino acids are hydrophilic in nature.
From the table, the sequence of peptide 'RKYSFLGAA' contains the following amino acids:
R = Arginine is a polar amino acid.
K = Lysine is a polar amino acid.
Y = Tyrosine is a polar amino acid.
S = Serine acid is a polar amino acid.
F = Phenylalanine is a non-polar amino acid.
L = Leucine is a non-polar amino acid.
G = Glycine is a non-polar amino acid.
A = Alanine is a non-polar amino acid.
From the given peptide sequence 'RKYSFLGAA', Arginine present at the right end and Alanine present at the left end of the sequence.
Arginine is a polar amino acid and hydrophilic in nature.
Alanine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophobic in nature.
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends along with polar and non-polar amino acids are indicated in the given sequence as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B Bond A Bond C a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. Weakest Bond Strongest Bond b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. c. (5pts) Use principles discussed in lecture, supported by relevant structures, to succinctly explain the why your part b (i) radical is more stable than your part b(ii) radical. Written explanation can be no more than one-two succinct sentence(s)!arrow_forward. 3°C with TH 12. (10pts total) Provide the major product for each reaction depicted below. If no reaction occurs write NR. Assume heat dissipation is carefully controlled in the fluorine reaction. 3H 24 total (30) 24 21 2h • 6H total ● 8H total 34 래 Br2 hv major product will be most Substituted 12 hv Br NR I too weak of a participate in P-1 F₂ hv Statistically most favored product will be major = most subst = thermo favored hydrogen atom abstractor to LL Farrow_forwardFive chemistry project topic that does not involve practicalarrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardQ2. Consider the hydrogenation of ethylene C2H4 + H2 = C2H6 The heats of combustion and molar entropies for the three gases at 298 K are given by: C2H4 C2H6 H2 AH comb/kJ mol¹ -1395 -1550 -243 Sº / J K¹ mol-1 220.7 230.4 131.1 The average heat capacity change, ACP, for the reaction over the temperature range 298-1000 K is 10.9 J K¹ mol¹. Using these data, determine: (a) the standard enthalpy change at 800 K (b) the standard entropy change at 800 K (c) the equilibrium constant at 800 K.arrow_forward13. (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B Bond A Bond C a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. Weakest Bond Strongest Bond b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. c. (5pts) Use principles discussed in lecture, supported by relevant structures, to succinctly explain the why your part b (i) radical is more stable than your part b(ii) radical. Written explanation can be no more than one-two succinct sentence(s)! Googlearrow_forward
- Print Last Name, First Name Initial Statifically more chances to abstract one of these 6H 11. (10pts total) Consider the radical chlorination of 1,3-diethylcyclohexane depicted below. 4 4th total • 6H total 래 • 4H total 21 total ZH 2H Statistical H < 3° C-H weakest - product abstraction here bund leads to thermo favored a) (6pts) How many unique mono-chlorinated products can be formed and what are the structures for the thermodynamically and statistically favored products? Product 6 Number of Unique Mono-Chlorinated Products Thermodynamically Favored Product Statistically Favored Product b) (4pts) Draw the arrow pushing mechanism for the FIRST propagation step (p-1) for the formation of the thermodynamically favored product. Only draw the p-1 step. You do not need to include lone pairs of electrons. No enthalpy calculation necessary H H-Cl Waterfoxarrow_forward10. (5pts) Provide the complete arrow pushing mechanism for the chemical transformation → depicted below Use proper curved arrow notation that explicitly illustrates all bonds being broken, and all bonds formed in the transformation. Also, be sure to include all lone pairs and formal charges on all atoms involved in the flow of electrons. CH3O II HA H CH3O-H H ①arrow_forwardDo the Lone Pairs get added bc its valence e's are a total of 6 for oxygen and that completes it or due to other reasons. How do we know the particular indication of such.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





