
Concept explainers
For each amino acid: [1] draw the L enantiomer in a Fischer projection; [2] classify the amino acid as neutral, acidic, or basic; [3] give the three-letter symbol; [4] give the one-letter symbol.
- leucine
- tryptophan
- lysine
- aspartic acid
(a)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of leucine in Fisher projection needs to be drawn and should be identified as acidic, basic or neutral. The three letter and one symbol for it needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
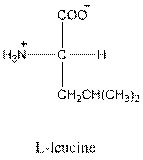
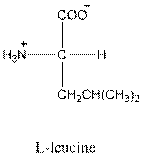
Answer to Problem 25P
- L-isomer of leucine is as follows:
- Leucine is neutral.
- Three-letter symbol for leucine is Leu.
- One-letter symbol for leucine is L.
Explanation of Solution
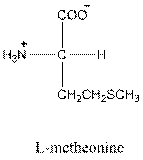
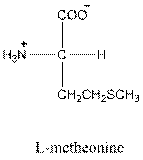
For leucine the R group is
The amino acid leucine has one positive charge on amino group
One letter symbol for leucine is L and three-letter symbol for leucine is Leu.
(b)
Interpretation:
To draw L-isomer of tryptophan (amino acid) in Fisher projection, to identify it is acidic, basic or neutral and to give three letter and one symbol for it
Concept Introduction : :
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
Answer to Problem 25P
- L-isomer of tryptophan is as follows:
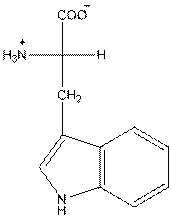
- Amino acid tryptophan is neutral.
Explanation of Solution
For tryptophan the R group is as follows:
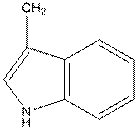
And in L-isomer the amino group
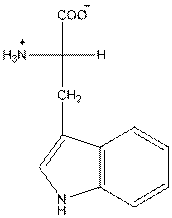
The amino acid tryptophan has one positive charge on amino group
One letter symbol for tryptophan is W and three-letter symbol for tryptophan is Trp.
(c)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of lysine in Fisher projection needs to be drawn, whether it is acidic, basic or neutral needs to be determined and the three-letter and one symbol for it needs to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
Answer to Problem 25P
- L-isomer of lysine is as follows:
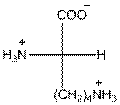
- The amino acid lysine is basic in nature.
- The three letter symbol for lysine is Lys.
- The one letter symbol for lysine is K.
Explanation of Solution
For lysine the R group is
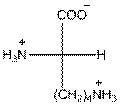
The amino acid lysine has one positive charge on amino group
The three letter symbol for lysine is Lys and one letter symbol for lysine is K.
(d)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of aspartic acid in Fisher projection needs to be drawn, whether it is acidic, basic or neutral needs to be determined and the three-letter and one symbol for it needs to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
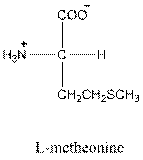
Answer to Problem 25P
- L-isomer of aspartic acid is as follows:
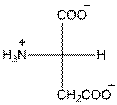
- The aspartic acid is acidic in nature.
- The three letter symbol for aspartic acid is Asp.
- The one letter symbol for aspartic acid is D.
Explanation of Solution
For aspartic acid the R group is
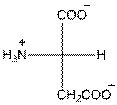
The aspartic acid has one positive charge on amino group
The three letter symbol for aspartic acid is Asp and the one letter symbol for aspartic acid is D.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- 4. Propose a synthesis of the target molecules from the respective starting materials. a) b) LUCH C Br OHarrow_forwardThe following mechanism for the gas phase reaction of H2 and ICI that is consistent with the observed rate law is: step 1 step 2 slow: H2(g) +ICI(g) → HCl(g) + HI(g) fast: ICI(g) + HI(g) → HCl(g) + |2(g) (1) What is the equation for the overall reaction? Use the smallest integer coefficients possible. If a box is not needed, leave it blank. + → + (2) Which species acts as a catalyst? Enter formula. If none, leave box blank: (3) Which species acts as a reaction intermediate? Enter formula. If none, leave box blank: (4) Complete the rate law for the overall reaction that is consistent with this mechanism. (Use the form k[A][B]"..., where '1' is understood (so don't write it) for m, n etc.) Rate =arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand rating and don't use Ai solutionarrow_forward
- 1. For each of the following statements, indicate whether they are true of false. ⚫ the terms primary, secondary and tertiary have different meanings when applied to amines than they do when applied to alcohols. • a tertiary amine is one that is bonded to a tertiary carbon atom (one with three C atoms bonded to it). • simple five-membered heteroaromatic compounds (e.g. pyrrole) are typically more electron rich than benzene. ⚫ simple six-membered heteroaromatic compounds (e.g. pyridine) are typically more electron rich than benzene. • pyrrole is very weakly basic because protonation anywhere on the ring disrupts the aromaticity. • thiophene is more reactive than benzene toward electrophilic aromatic substitution. • pyridine is more reactive than nitrobenzene toward electrophilic aromatic substitution. • the lone pair on the nitrogen atom of pyridine is part of the pi system.arrow_forwardThe following reactions are NOT ordered in the way in which they occur. Reaction 1 PhO-OPh Reaction 2 Ph-O -CH₂ heat 2 *OPh Pho -CH2 Reaction 3 Ph-O ⚫OPh + -CH₂ Reaction 4 Pho Pho + H₂C OPh + CHOPh H₂C -CH₂ Reactions 1 and 3 Reaction 2 O Reaction 3 ○ Reactions 3 and 4 ○ Reactions 1 and 2 Reaction 4 ○ Reaction 1arrow_forwardSelect all possible products from the following reaction: NaOH H₂O a) b) ОН HO O HO HO e) ОН f) O HO g) h) + OHarrow_forward
- 3. Draw diagrams to represent the conjugation in these molecules. Draw two types of diagram: a. Show curly arrows linking at least two different ways of representing the molecule b. Indicate with dotted lines and partial charges (where necessary) the partial double bond (and charge) distribution H₂N* H₂N -NH2arrow_forwardQuestion 2 of 25 point Question Attempt 3 of Ulimited Draw the structure for 3-chloro-4-ethylheptane. Part 2 of 3 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Draw the structure for 1-chloro-4-ethyl-3-lodooctane. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X G X B c Part 3 of 30 Draw the structure for (R)-2-chlorobutane. Include the stereochemistry at all stereogenic centers. Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G X A 。 MacBook Pro G P Save For Later Submit Assignment Privacyarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- In a silicon and aluminum alloy, with 12.6% silicon, what are the approximate percentages of the phases present in the constituent that is formed at the end of solidification? Temperature (°C) 1500 1000 L B+L 1415- α+L 577' 500 1.65 12.6 99.83 α+B B 0 Al 20 40 60 Weight percent silicon 80 Siarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





