
Concept explainers
a. How many amide bonds join the amino acids in the peptide chain?
b.Give the name of the N-terminal amino acid.
c.Give the name of the C-terminal amino acid. 
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of amide bonds that join the amino acids in the: IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP peptide chain.
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. The amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha-amino acids.
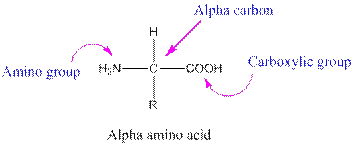
Answer to Problem 38P
There are
Explanation of Solution
When amino acids joined to one another by amide bonds to form large molecules are called peptides. The amide bonds present in peptides are called peptides bonds.
To make a dipeptide, the amino group
To calculate the number of amide bonds present in any sequence will be one less the number of amino acids present in the sequence.
For example, there are two amino acids present in a dipeptide. Then, the number of amide bonds will be one.
The given sequence is as follows:
IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
There are total
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the N-terminal amino acid of the given amino acid sequence present in the bee venom should be determined.
IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. The amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha-amino acids.
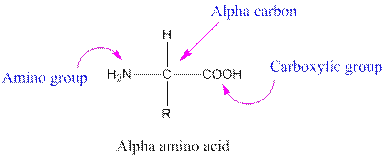
Answer to Problem 38P
Isoleucine (I) will be the N-terminal amino acid present in the given sequence IRCFITPDIT-51amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acid having a free
The name, one-letter and three-letter abbreviation of the amino acids are mentioned in the table given below:
| Name of Amino Acid | Three-letter abbreviation | One-letter abbreviation |
| Alanine | Ala | A |
| Asparagine | Asn | N |
| Cysteine | Cys | C |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I |
| Leucine | Leu | L |
| Methionine | Met | M |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F |
| Proline | Pro | P |
| Serine | Ser | S |
| Threonine | Thr | T |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y |
| Valine | Val | V |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E |
| Arginine | Arg | R |
| Histidine | His | H |
| Lysine | Lys | K |
The given sequence is as follows:
IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
From the table, 'I' will be the amino acid present at the N-terminal. And 'I' is the 'Isoleucine' amino acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the C-terminal amino acid of the given amino acid sequence present in the bee venom should be determined.
IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. The amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha-amino acids.
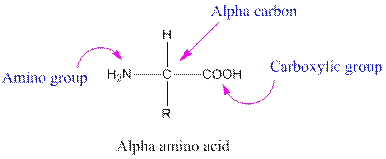
Answer to Problem 38P
Proline (P) will be the C-terminal amino acid present in the given sequence IRCFITPDIT-51amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acid having a free
The name, one-letter and three-letter abbreviation of the amino acids are mentioned in the table given below:
| Name of Amino Acid | Three-letter abbreviation | One-letter abbreviation |
| Alanine | Ala | A |
| Asparagine | Asn | N |
| Cysteine | Cys | C |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I |
| Leucine | Leu | L |
| Methionine | Met | M |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F |
| Proline | Pro | P |
| Serine | Ser | S |
| Threonine | Thr | T |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y |
| Valine | Val | V |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E |
| Arginine | Arg | R |
| Histidine | His | H |
| Lysine | Lys | K |
The given sequence is as follows:
IRCFITPDIT-51amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
From the table, 'P' will be the amino acid present at the C-terminal. And 'P' is the 'Proline' amino acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- Nonearrow_forward3. A molecular form of "dicarbon", C2, can be generated in gas phase. Its bond dissociation energy has been determined at 599 kJ/mol. Use molecular orbital theory to explain why energy of dissociation for C₂+ is 513 kJ/mol, and that for C2² is 818 kJ/mol. (10 points)arrow_forward9.73 g of lead(IV) chloride contains enough Cl- ions to make ____ g of magnesium chloride.arrow_forward
- 6. a) C2's. Phosphorus pentafluoride PF5 belongs to D3h symmetry group. Draw the structure of the molecule, identify principal axis of rotation and perpendicular (4 points) b) assume that the principal axis of rotation is aligned with z axis, assign symmetry labels (such as a1, b2, etc.) to the following atomic orbitals of the P atom. (character table for this group is included in the Supplemental material). 3s 3pz (6 points) 3dz²arrow_forward2. Construct Lewis-dot structures, and draw VESPR models for the ions listed below. a) SiF5 (4 points) b) IOF4 (4 points)arrow_forward5. Complex anion [AuCl2]¯ belongs to Doh symmetry point group. What is the shape of this ion? (4 points)arrow_forward
- 4. Assign the following molecules to proper point groups: Pyridine N 1,3,5-triazine N Narrow_forward7. a) Under normal conditions (room temperature & atmospheric pressure) potassium assumes bcc lattice. Atomic radius for 12-coordinate K atom is listed as 235 pm. What is the radius of potassium atom under normal conditions? (3 points) b) Titanium metal crystallyzes in hcp lattice. Under proper conditions nitrogen can be absorbed into the lattice of titanium resulting in an alloy of stoichiometry TiNo.2. Is this compound likely to be a substitutional or an interstitial alloy? (Radius of Ti (12-coordinate) is 147 pm; radius of N atom is 75 pm. (3 points)arrow_forwardcan someone answer the questions and draw out the complete mechanismarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





