
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
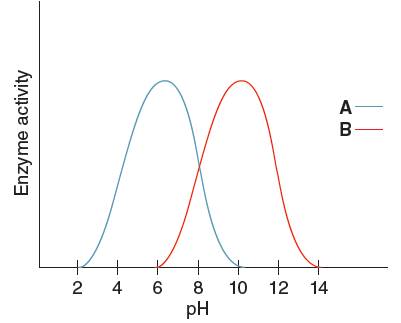
The optimum pH for enzyme 'A' needs to be determined, using the given pH versus enzyme activity graph for enzyme A and B.
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the
Answer to Problem 21.83P
Optimum pH for enzyme 'A' is
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. By increasing temperature, rate of reaction also increases until its maximum activity occurs that is at
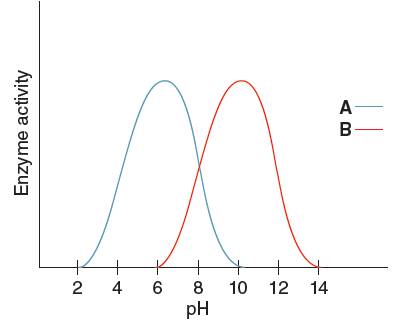
Optimum pH is the pH at which the activity of an enzyme is maximum. So, from the given graph, the activity of enzyme A is maximum at pH 6. Hence the optimum pH of enzyme A is 6.
(b)
Interpretation:
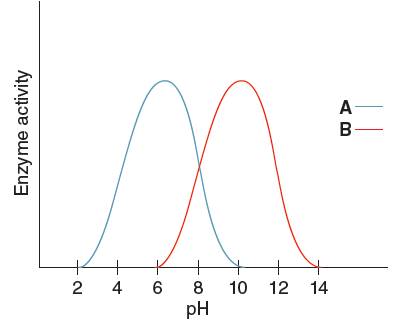
The optimum pH for enzyme 'B' needs to be determined, using the given pH versus enzyme activity graph for enzyme A and B.
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 21.83P
Optimum pH for enzyme 'B' is
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. By increasing temperature, rate of reaction also increases until its maximum activity occurs that is at
Optimum pH is the pH at which the activity of an enzyme is maximum. So, from the given graph, the activity of enzyme B is maximum at pH 10.
Hence, the optimum pH of enzyme B is 10.
(c)
Interpretation:
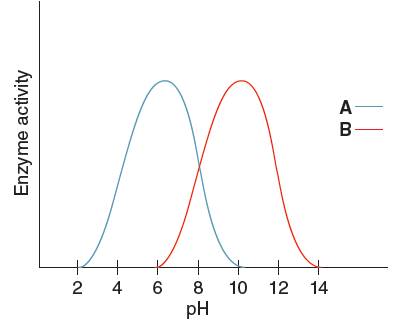
The enzyme having the higher activity when pH is
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 21.83P
Enzyme 'A' will have higher pH at
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. Optimum pH is the pH value at which the enzyme is most active. The rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction is maximum at optimum pH
The graph shown below clearly explains the activity of an enzyme with change in pH values:
From the given graph, it can be seen that the activity of enzyme B starts from pH 6 onwards and activity of enzyme A starts from pH 2 onwards. So, before pH 2 enzyme A is inactive and before pH 6 enzyme B is inactive. Therefore, at pH 4 the activity of enzyme A is higher than that of enzyme B.
(d)
Interpretation:
The enzyme having the higher activity at pH
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 21.83P
Enzyme 'B' will have the higher activity at pH
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. Optimum pH is the pH value at which the enzyme is most active. The rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction is maximum at optimum pH
The graph shown below clearly explains the activity of an enzyme with change in pH values:
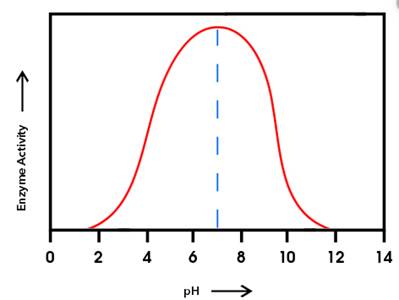
From the given graph, it can be seen that the activity of enzyme B starts from pH 6 onwards and becomes maximum at pH 10and then activity of enzyme starts decreasing. And activity of enzyme A starts from pH 2 onwards and becomes maximum at pH 6 and then starts decreasing.
At pH 9, activity of enzyme A is decreasing and that of enzyme B is increasing. Hence, at pH 9 activity of enzyme B is higher than that of enzyme A.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
- Identify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
- in the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





