
(a)
Interpretation:
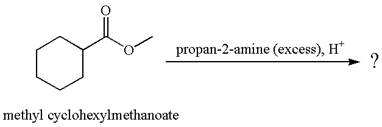
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The esters in acidic condition undergo hydrolysis and form the corresponding
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
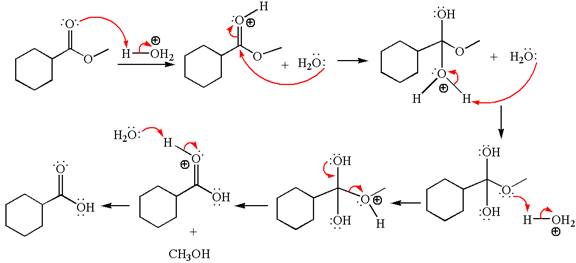
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in an acidic condition, it undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and alcohol. The ester is activated by protonation of carbonyl oxygen. The water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of protonated ester and removes methanol as the leaving group. The product with detailed mechanism is as follows:
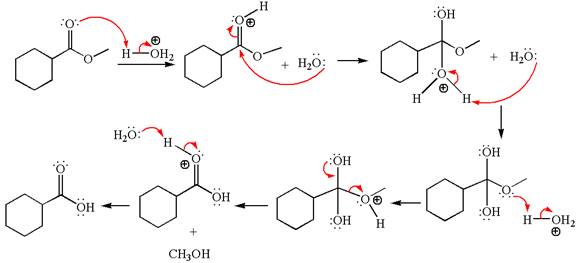
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester in an acidic condition.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The ester can be hydrolyzed in basic condition and forms corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol. As hydrolysis occurs in basic condition, it deprotonates carboxylic acid to carboxylate ion. Thus, to recover, it must then be treated with an acid.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
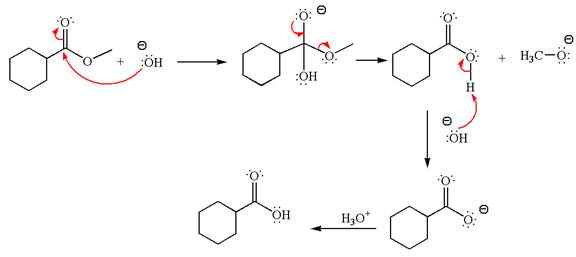
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
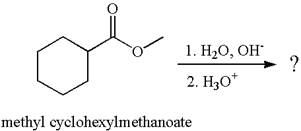
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in a basic condition, it undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and alcohol. The hydroxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks ester carbonyl to form an intermediate having negatively charged oxygen. The intermediate undergoes elimination of methoxide by delocalization of lone pair of negatively charged oxygen and forms carboxylic acid. The carboxylic acid further undergoes deprotonated to carboxylate ion due to basic reaction condition. Therefore, the carboxylic acid is recovered by addition of
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester in a basic condition.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The alcohols are weak nucleophiles and thus cannot react with an ester under normal condition. Thus, on addition of base, the alcohol is converted to alkoxide ion, which acts as a good nucleophile and undergoes transesterification when reacted with an ester.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
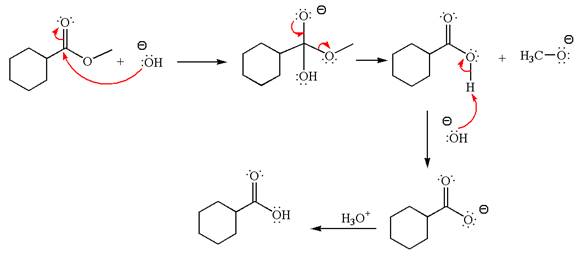
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; on reaction with
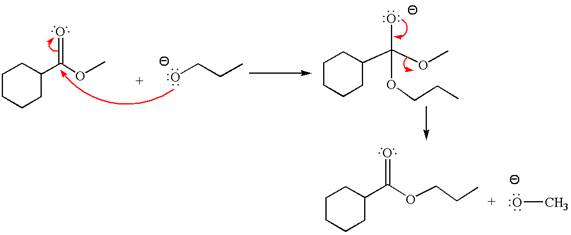
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with alkoxide ion.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
Alcohols are weak nucleophiles and cannot react with an ester under normal condition. Thus, for the reaction to carry out, it can be catalyzed by addition of an acid. The ester, on acid-catalyzed reaction with alcohol, undergoes transesterification, called acid-catalyzed transesterification.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
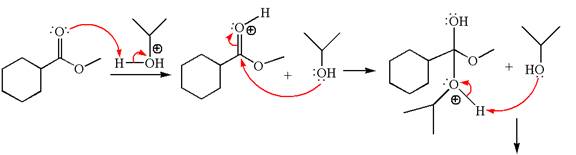
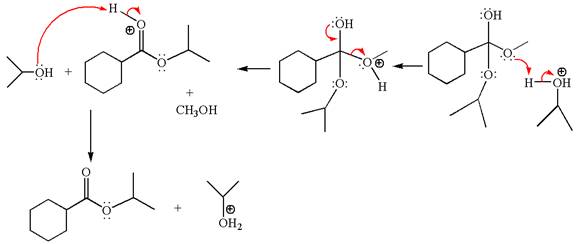
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
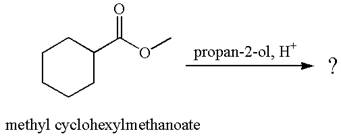
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; on reaction with


The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with alcohol in an acidic condition.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The ester, on reaction with an excess of
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
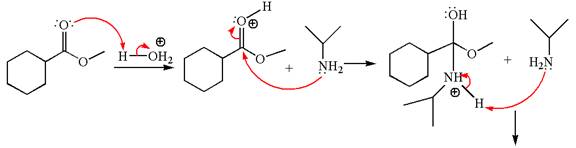
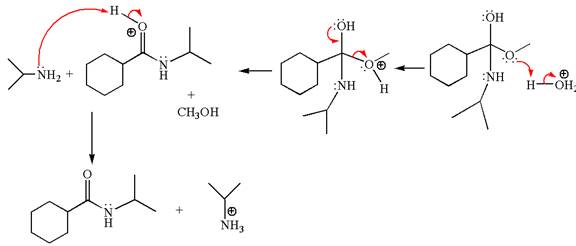
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in an acidic condition, it undergoes aminolysis to form amide and alcohol. The ester is activated by protonation of carbonyl oxygen. The amine molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of protonated ester and removes methanol as the leaving group. The product with detailed mechanism is as follows:

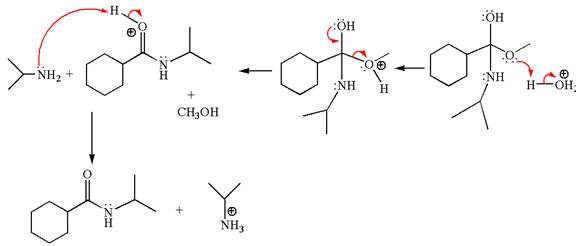
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with amine in an acidic condition.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The alcohols are weak nucleophiles; in an acidic or basic condition, they undergo transesterification with an ester, but under normal condition, the reaction does not occur.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
No reaction takes place between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
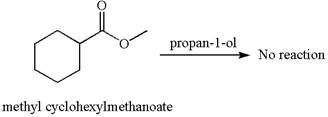
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
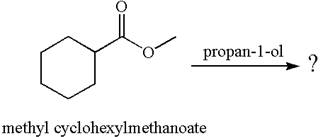
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester, and the given reagent
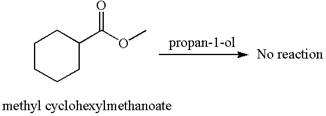
It is determined that there is no reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Identifying electron-donating and electron-withdrawing effects on benzene For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density Molecule CF3 O donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene CH3 O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects O donating O withdrawing Ono resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Explanation Check Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward* Hint: Think back to Chem 1 solubility rules. Follow Up Questions for Part B 12. What impact do the following disturbances to a system at equilibrium have on k, the rate constant for the forward reaction? Explain. (4 pts) a) Changing the concentration of a reactant or product. (2 pts) b) Changing the temperature of an exothermic reaction. (2 pts) ofarrow_forwardDraw TWO general chemical equation to prepare Symmetrical and non-Symmetrical ethers Draw 1 chemical reaction of an etherarrow_forward
- Give the chemical equation for the preparation of: -Any aldehyde -Any keytonearrow_forward+ C8H16O2 (Fatty acid) + 11 02 → 8 CO2 a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? H2o CO₂ c. Which reactant is the electron donor? Futty acid d. Which reactant is the electron acceptor? e. Which of the product is now reduced? f. Which of the products is now oxidized? 02 #20 102 8 H₂O g. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? 2 h. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forward→ Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + 1FAD + 1ADP 2CO2 + CoA + 3NADH + 1FADH2 + 1ATP a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? c. Which reactant is the electron donor? d. Which reactants are the electron acceptors? e. Which of the products are now reduced? f. Which product is now oxidized? g. Which process was used to produce the ATP? h. Where was the energy initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? i. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? j. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forward
- Rank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. OCH 3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) Br (Choose one) Explanation Check NO2 (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Aarrow_forwardFor each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





