
Concept explainers
Draw the products of each reaction.
a. 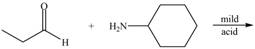 e.
e. 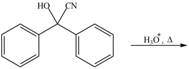
b. 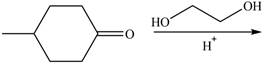 f.
f. 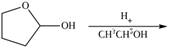
c. 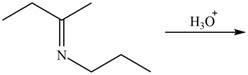 g.
g. 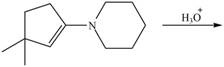
d. 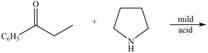 h.
h. 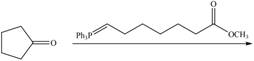
(a)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) reacts with
Answer to Problem 21.46P
The product of the given reaction isdrawn in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves the treatment of an aldehyde with a
A carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) reacts with
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,
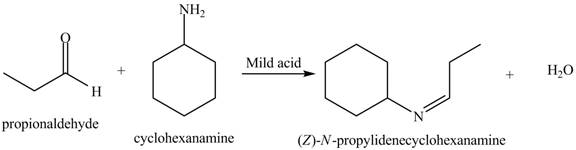
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Acetals are the groups in which carbon atom is bonded with two
Answer to Problem 21.46P
The product of the given reaction isdrawn in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves the treatment of a ketone with a diol.
Acetals are the groups in which carbon atom is bonded with two
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,
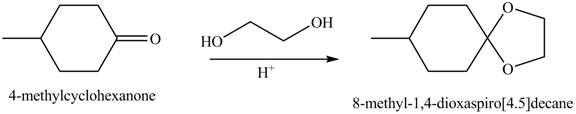
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The hydrolysis of both enamines and imines yield aldehydes or ketones. The mechanisms of both reactions are exactly opposite to their formations, as they are formed from the treatment of aldehyde/ketones with amines.
Answer to Problem 21.46P
The product of the given reaction isdrawn in Figure 3.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves the hydrolysis of an imine.
The hydrolysis of both enamines and imines yield aldehydes orketones along with primary (imine) or secondary amine (enamine). The mechanisms of both reactions are exactly opposite to their formations, as they are formed from the treatment of aldehyde/ketones with amines.
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,
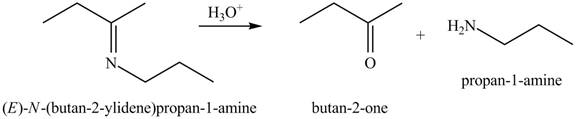
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) reacts with
Answer to Problem 21.46P
The product of the given reaction isdrawn in Figure 4.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves the treatment of ketone with
A carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) reacts with
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,
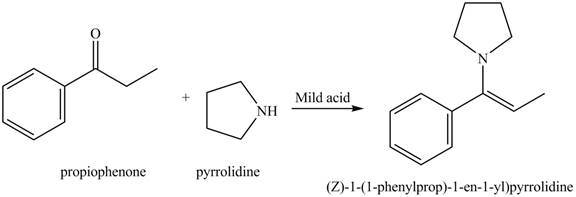
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Cyanohydrins are the nucleophilic addition product of carbonyl compounds in which
Answer to Problem 21.46P
The product of the given reaction isdrawn in Figure 5.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves the hydrolysis of cyanohydrin compound.
Cyanohydrins are the nucleophilic addition product of carbonyl compounds in which
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,
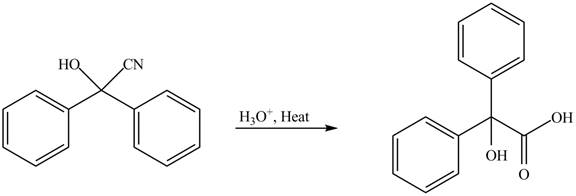
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Hemiacetals are the groups in which carbon atom is bonded to one
Answer to Problem 21.46P
The product of given reaction isdrawn in Figure 6.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves the treatment of cyclic hemiacetal with ethanol in the presence of acid.
Hemiacetals are the groups in which carbon atom is bonded to one
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,
<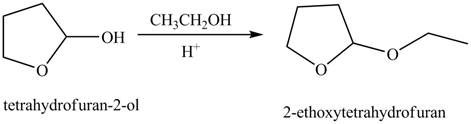
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The hydrolysis of both enamines and imines yield aldehydes or ketones along with primary (imine) or secondary amine (enamine). The mechanisms of both reactions are exactly opposite to their formations, as they are formed from the treatment of aldehyde/ketones with amines.
Answer to Problem 21.46P
The product of the given reaction isdrawn in Figure 7.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves the hydrolysis of an enamine.
The hydrolysis of both enamines and imines yield aldehydes or ketones along with primary (imine) or secondary amine (enamine). The mechanisms of both reactions are exactly opposite to their formations, as they are formed from the treatment of aldehyde/ketones with amines.
Thus, the Product of the given reaction is,
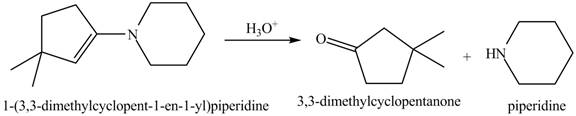
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation: The product of given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The Wittig reaction utilizes carbon nucleophile from the Wittig reagent to yield alkenes. When a carbonyl compound is treated with a Wittig reagent, the
Answer to Problem 21.46P
The product of the given reaction isdrawn in Figure 8.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves the hydrolysis of an enamine.
The Wittig reaction utilizes carbon nucleophile from the Wittig reagent to yield alkenes. When a carbonyl compound is treated with a Wittig reagent, the
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,
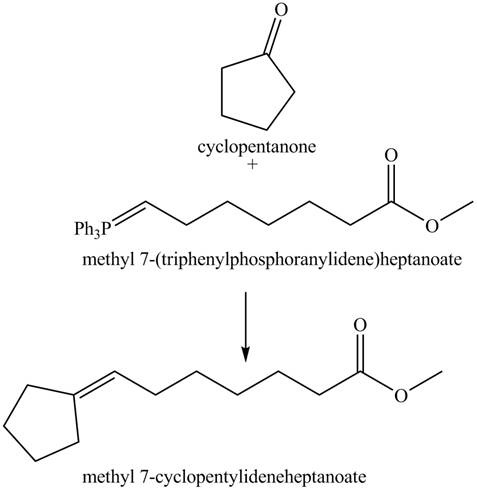
Figure 8
(a) The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 1.
(b) The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 2.
(c) The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 3.
(d) The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 4.
(e) The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 5.
(f) The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 6.
(g) The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 7.
(h) The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 8.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- 2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); Reagents: H₂O (B); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI OH - α-α Br + enant Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardBased on concepts from Lecture 3-5, which of the following ionic compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices MgO BeO CaO BaOarrow_forwardFrom an energy standpoint, which two process - in the correct order - are involved in the dissolving of an ionic compound crystal? Group of answer choices Water coordination to the ions followed by sublimation into the gas phase Sublimation of the crystal into gas-phase ions followed by water coordination to the ions Ion dissociation from the crystal followed by water coordination to the ions Water coordination to the ions followed by ion dissociation from the crystalarrow_forward
- For which Group 2 metal (M), is this process the most exothermic? M2+(g) + O2−(g) + CO2(g) → MO(s) + CO2(g) Group of answer choices M = Sr M = Mg M = Ca M = Baarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); R₂BH (6); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s) HO OHarrow_forwardFor which of the following ionic compounds would you expect the smallest difference between its theoretical and experimental lattice enthalpies? (You may assume these all have the same unit cell structure.) Electronegativities: Ca (1.0), Fe (1.8), Mg (1.2), O (3.5), S (2.5), Zn (1.6) Group of answer choices ZnO MgS CaO FeSarrow_forward
- In the Born-Haber cycle for KCl crystal formation, what enthalpy component must be divided by two? Group of answer choices KCl(s) enthalpy of formation Ionization energy for K(g) K(s) sublimation enthalpy Cl2 bond dissociation enthalpyarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); H₂O₂ / HO (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI хот Br Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardWhat is the correct chemical equation for the lattice formation reaction for CaBr2? Group of answer choices Ca2+(g) + 2 Br−(g) → CaBr2(s) ½ Ca2+(g) + Br−(g) → ½ CaBr2(s) Ca(s) + Br2(l) → CaBr2(s) Ca(s) + 2 Br−(g) → CaBr2(s)arrow_forward
- PLEASE ANSWER THE QUESTION!!!arrow_forward3. SYNTHESIS. Propose a sequence of synthetic steps (FGI) that convert the starting material (SM) into the Target molecule. For each FGI in your proposed synthesis, specify the reagents / conditions, and draw the product(s) of that FGI. DO NOT INCLUDE the FGI mxn in the answer you submit. If an FGI requires two reagent sets, specify the order in which the reagent sets are added, e.g., i) Hg(OAc)2 / H₂O; ii) NaBH4/MeOH. Indicate the stereochemistry (if any) of the products of each FGI. FGI 1. Me Starting Material Source of all carbons in the Target molecule (can use multiple copies) Me Me Target molecule + enantiomerarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction mechanism stepsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





