
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The number of stereogenic centers present in
Concept introduction: Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds. Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy
Answer to Problem 21.39P
There are five stereogenic centers present in
Explanation of Solution
The stereogenic centers in
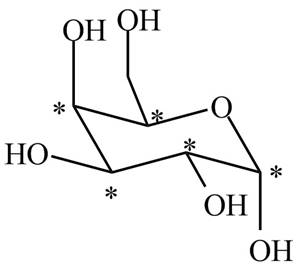
Figure 1
The stereogenic centers are marked by star. There are five stereogenic centers present in
There are five stereogenic centers present in
(b)
Interpretation: The hemiacetal carbon in
Concept introduction: Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds. Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Galactose is a aldohexose as it contains six carbon atoms as well as an aldehyde functional group. The molecular formula of galactose
Aldehydes or ketones on reaction with one equivalent of alcohol form hemiacetal and on reaction with two equivalents of alcohol it forms acetals. This is nucleophilic addition reaction. These reactions takes place in presence of acids, commonly
Ethers contain only one alkoxy group on a carbon atom while acetals contain two alkoxy groups on a single carbon atom.
Hemiacetals contains one alkoxy group and one hydroxyl group attached to same carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 21.39P
The hemiacetal carbon in
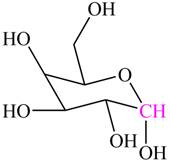
Explanation of Solution
The hemiacetal carbon in
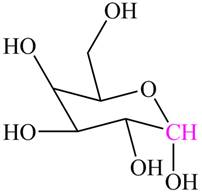
Figure 2
The highlighted carbon contains alkoxy group and hydroxyl group. Hence, this carbon is labeled as hemiacetal carbon.
The hemiacetal carbon in
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of
Concept introduction: Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds. Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Galactose is a aldohexose as it contains six carbon atoms as well as an aldehyde functional group. The molecular formula of galactose
Answer to Problem 21.39P
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
In
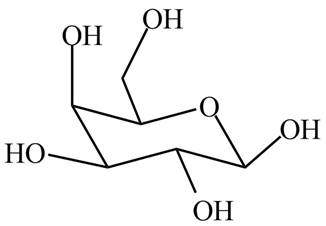
Figure 3
The structure of
(d)
Interpretation: The structure of poly hydroxy aldehyde that cyclizes to
Concept introduction: Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds. Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Galactose is a aldohexose as it contains six carbon atoms as well as an aldehyde functional group. The molecular formula of galactose
Aldehydes or ketones on reaction with one equivalent of alcohol form hemiacetal and on reaction with two equivalents of alcohol it forms acetals. This is nucleophilic addition reaction. These reactions takes place in presence of acids, commonly
In
Answer to Problem 21.39P
The structure of poly hydroxy aldehyde that cyclizes to
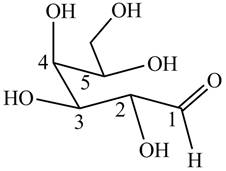
Explanation of Solution
The cyclization of poly hydroxy aldehyde results in the formation of hemiacetal. The hydroxyl group on

Figure 4
The structure of poly hydroxy aldehyde that cyclizes to
(e)
Interpretation: The products formed when
Concept introduction: Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds. Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Galactose is a aldohexose as it contains six carbon atoms as well as an aldehyde functional group. The molecular formula of galactose
Aldehydes or ketones on reaction with one equivalent of alcohol form hemiacetal and on reaction with two equivalents of alcohol it forms acetals. This is nucleophilic addition reaction. These reactions takes place in presence of acids, commonly
Answer to Problem 21.39P
The products formed when
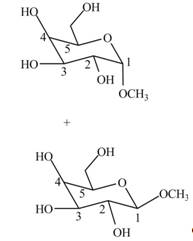
Explanation of Solution
Cyclic hemiacetals can be converted to acetals by treatment with alcohol in presence of acid. The hydroxyl group of hemiacetal is converted to alkoxy group. The
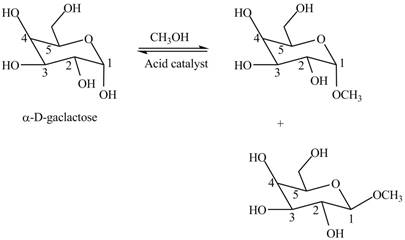
Figure 5
The products formed when
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- One step of glycolysis is a retro-aldol reaction (aldolase) to produce ATP.Below is the aldol reaction of the equilibrium. Show the mechanism for the base catalyzed reaction. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardWhy does the following reaction lead to poor yields? Correct the reaction. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardDraw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardI have a bottle of butanal that has been improperly used by lab workers. They allowed a traceamount NaOH (aq) to contaminate the bottle. What is now in my bottle of “butanal? What is the molecular name and functional group name? Draw the structure.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





