
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to derive the structure of an
Answer to Problem 21.4P
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is,
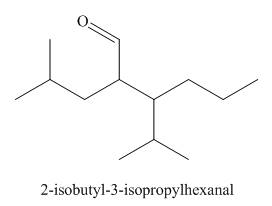
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
One should follow the given steps to derive the structure of an aldehyde from its IUPAC name. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
The given IUPAC name suggests the presence of
Thus, the structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is,

Figure 1
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to derive the structure of an aldehyde from its IUPAC name. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
Answer to Problem 21.4P
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is,
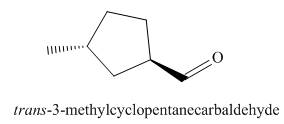
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
One should follow the given steps to derive the structure of an aldehyde from its IUPAC name. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
The given IUPAC name suggests the presence of

Figure 2
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to derive the structure of an aldehyde from its IUPAC name. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
Answer to Problem 21.4P
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is,
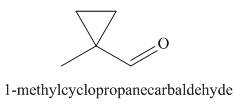
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
One should follow the given steps to derive the structure of an aldehyde from its IUPAC name. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
The given IUPAC name suggests the presence of

Figure 3
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to derive the structure of an aldehyde from its IUPAC name. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
Answer to Problem 21.4P
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is,
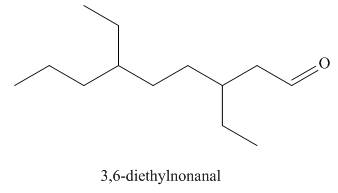
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC name of the given compound is
One should follow the given steps to derive the structure of an aldehyde from its IUPAC name. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
The given IUPAC name suggests the presence of
Thus, the structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is,

Figure 4
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name is shown in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- In the following reaction, what quantity in moles of CH₃OH are required to give off 4111 kJ of heat? 2 CH₃OH (l) + 3 O₂ (g) → 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂O(g) ∆H° = -1280. kJarrow_forwardIndicate the processes in the dismutation of Cu2O.arrow_forward1. Consider these three reactions as the elementary steps in the mechanism for a chemical reaction. 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 Potential Energy (kJ) 600 400 200 0 -200- -400 -600- -800 (i) Cl₂ (g) + Pt(s) → 2Cl (g) + Pt(s) (ii) Cl (g)+ CO (g) + Pt (s) → CICO (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 1550 kJ Ea = 2240 kJ (iii) Cl (g) + CICO (g) → Cl₂CO (g) Ea = 2350 kJ AH=-950 kJ ΔΗ = 575 ΚΙ AH=-825 kJ a. Draw the potential energy diagram for the reaction. Label the data points for clarity. The potential energy of the reactants is 600 kJ Reaction Progress b. What is the overall chemical equation? c. What is the overall change in enthalpy for the above chemical reaction? d. What is the overall amount of activation energy for the above chemical reaction? e. Which reaction intermediate would be considered a catalyst (if any) and why? f. If you were to add 2700kJ of energy to the reaction (e.g. 2700 kl of heat or electricity), would you be able to make the reaction reverse itself (i.e. have…arrow_forward
- draw the enolate anion and the carbonyl that would be needed to make this product through an aldol addition reaction.arrow_forwardDraw the Michael Adduct and the final product of the Robinson annulation reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw the Michael adduct and final product of the Robinson annulation reaction. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forward
- Post Lab Questions. 1) Draw the mechanism of your Diels-Alder cycloaddition. 2) Only one isomer of product is formed in the Diels-Alder cycloaddition. Why? 3) Imagine that you used isoprene as diene - in that case you don't have to worry about assigning endo vs exo. Draw the "endo" and "exo" products of the Diels-Alder reaction between isoprene and maleic anhydride, and explain why the distinction is irrelevant here. 4) This does not hold for other dienes. Draw the exo and endo products of the reaction of cyclohexadiene with maleic anhydride. Make sure you label your answers properly as endo or exo. 100 °C Xylenes ??? 5) Calculate the process mass intensity for your specific reaction (make sure to use your actual amounts of reagent).arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) A, B C and D that are formed in the reaction: H + NH-NH-CH [A+B] [C+D] hydrazonesarrow_forwardHow can you prepare a 6 mL solution of 6% H2O2, if we have a bottle of 30% H2O2?arrow_forward
- How many mL of H2O2 from the 30% bottle must be collected to prepare 6 mL of 6% H2O2.arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) B and C that are formed in the reaction: HN' OCH HC1 B + mayoritario C minoritario OCH3arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) that are formed in the reaction: NH-NH, OCH3 -H₂O OCH3arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
