
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
In this subpart one must identify the functional group that is present in each molecule and thereby indicate the family of organic compounds to which the compound specifically belongs to.
Concept Introduction:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry-IUPAC has developed a method for systematically naming organic compounds. The name given to a compound according to the
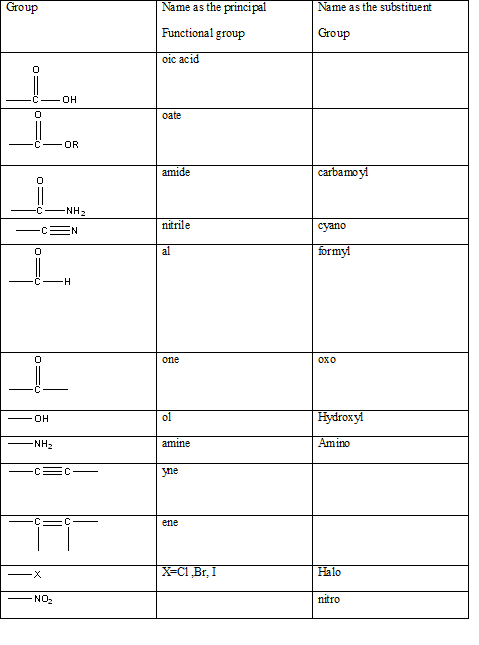
Table 1: The series of functional groups arranged in the decreasing order of the priority.
Answer to Problem 57QAP
Explanation of Solution
- The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts.
- The suffix that is used to indicate the main functional group of the structure.
- Name of the chain that is used to identify the main carbon chain of the compound.
- The prefixes that are used to indicate the substituent groups.
- The numbers that are used to indicate the places at which the substituent groups, additional groups and the main functional groups are attached to the chain.
The IUPAC name of an aliphatic compound can easily be developed by following the steps stated below in the given order.
- The main functional group should be identified first.
- The root name for the principal chain should be selected.
- In the name of the chain, the suffix for the double or triple bond in the parent chain should be added.
- The substituent groups should be named.
- The name of the substituent groups should be added in the name of chain.
- The carbon atoms in the chain should be numbered.
- The minimum possible number is given to the main functional group present as a substituent in the chain.
| Number of carbon atoms | Root name | Name of the corresponding |
| 1 | meth | Methane |
| 2 | eth | Ethane |
| 3 | prop | Propane |
| 4 | but | Butane |
| 5 | pent | Pentane |
| 6 | hex | Hexane |
Table 2: The root names used for the compounds according to the number of carbon atoms and the names of the corresponding hydrocarbons.
According to this explanation-NH2 is the functional group of
(b)
Interpretation:
In this subpart one must identify the functional group that is present in each molecule and thereby indicate the family of organic compounds to which the compound specifically belongs to.
Concept Introduction:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry-IUPAC has developed a method for systematically naming organic compounds. The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts the critical or the first part is to identify the main functional group present in a molecule in order to name it correctly. It allows the identification of the class of the compound easily possible without any ambiguity. The table indicating the main functional groups present in organic molecules can be summarized in the table below.
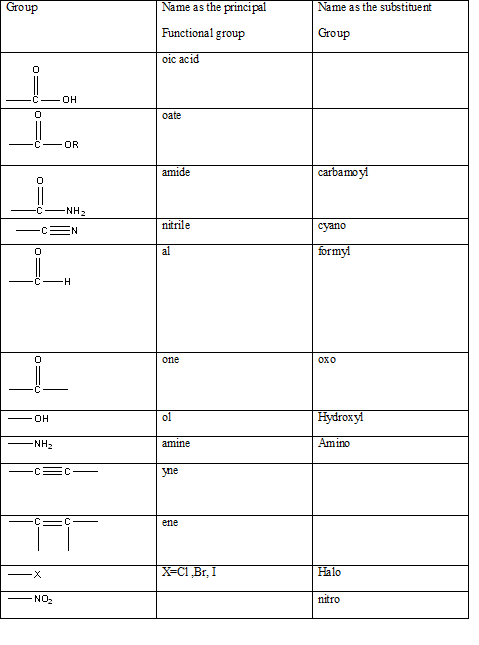
Table 1: The series of functional groups arranged in the decreasing order of the priority.
Answer to Problem 57QAP
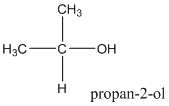
Explanation of Solution
- The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts.
- The suffix that is used to indicate the main functional group of the structure.
- Name of the chain that is used to identify the main carbon chain of the compound.
- The prefixes that are used to indicate the substituent groups.
- The numbers that are used to indicate the places at which the substituent groups, additional groups and the main functional groups are attached to the chain.
- The IUPAC name of an aliphatic compound can easily be developed by following the steps stated below in the given order.
- Identifying the principal functional group.
- Selecting the main chain.
- Selecting the root name for the principal chain.
- Addition of the suffix for the double/triple bond in the main carbon chain to the name of the chain.
- Addition of the suffix used to indicate the principal functional group to the name of the chain.
- Naming the substituent groups.
- Adding the names of the substituent groups to the name of the chain.
- Numbering the carbon chain.
- Writing the numbers that are used to indicate the positions of the main functional group and the substituent groups in front of these groups.
| Number of carbon atoms | Root name | Name of the corresponding |
| 1 | meth | Methane |
| 2 | eth | Ethane |
| 3 | prop | Propane |
| 4 | but | Butane |
| 5 | pent | Pentane |
| 6 | hex | Hexane |
Table 2: The root names used for the compounds according to the number of carbon atoms and the names of the corresponding hydrocarbons.
According to this explanation-OH is the functional group of an alcohol. This functional group is present in the main carbon chain of the example compound and hence resulting in absence of any substituent groups. Since there are only three carbon atoms in the main chain one should use the root name −prop in naming the compound. Also the −OH functional group is connected to the second carbon of the main chain and hence one must also indicate the position of −OH by using 2- as well.
(c)
Interpretation:
In this subpart one must identify the functional group that is present in each molecule and thereby indicate the family of organic compounds to which the compound specifically belongs to.
Concept Introduction:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry-IUPAC has developed a method for systematically naming organic compounds. The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts the critical or the first part is to identify the main functional group present in a molecule in order to name it correctly. It allows the identification of the class of the compound easily possible without any ambiguity. The table indicating the main functional groups present in organic molecules can be summarized in the table below.
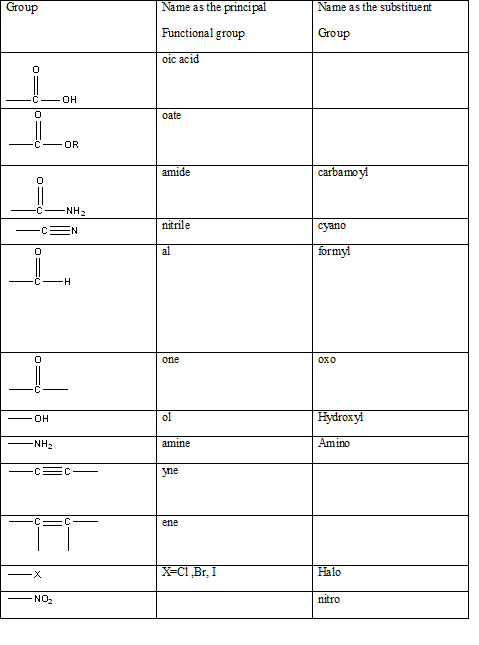
Table 1: The series of functional groups arranged in the decreasing order of the priority.
Answer to Problem 57QAP
Explanation of Solution
- The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts.
- The suffix that is used to indicate the main functional group of the structure.
- Name of the chain that is used to identify the main carbon chain of the compound.
- The prefixes that are used to indicate the substituent groups.
- The numbers that are used to indicate the places at which the substituent groups, additional groups and the main functional groups are attached to the chain. The IUPAC name of an aliphatic compound can easily be developed by following the steps stated below in the given order.
- The main functional group should be identified first.
| Number of carbon atoms | Root name | Name of the corresponding |
| 1 | meth | Methane |
| 2 | eth | Ethane |
| 3 | prop | Propane |
| 4 | but | Butane |
| 5 | pent | Pentane |
| 6 | hex | Hexane |
Table 2: The root names used for the compounds according to the number of carbon atoms and the names of the corresponding hydrocarbons.
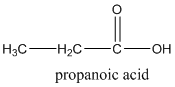
According to this explanation-COOH is the functional group of a
(d)
Interpretation:
In this subpart one must identify the functional group that is present in each molecule and thereby indicate the family of organic compounds to which the compound specifically belongs to.
Concept Introduction:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry-IUPAC has developed a method for systematically naming organic compounds. The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts the critical or the first part is to identify the main functional group present in a molecule in order to name it correctly. It allows the identification of the class of the compound easily possible without any ambiguity. The table indicating the main functional groups present in organic molecules can be summarized in the table below.
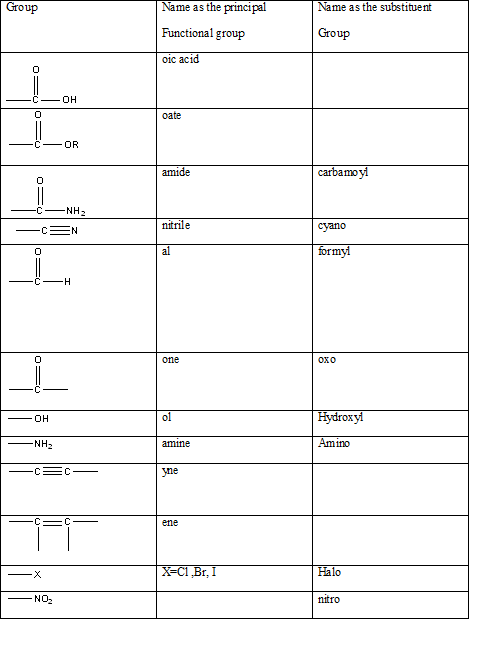
Table 1: The series of functional groups arranged in the decreasing order of the priority.
Answer to Problem 57QAP
Explanation of Solution
- The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts.
- The suffix that is used to indicate the main functional group of the structure.
- Name of the chain that is used to identify the main carbon chain of the compound.
- The prefixes that are used to indicate the substituent groups.
- The numbers that are used to indicate the places at which the substituent groups, additional groups and the main functional groups are attached to the chain.
The IUPAC name of an aliphatic compound can easily be developed by following the steps stated below in the given order.
- The main functional group should be identified first.
- The root name for the principal chain should be selected.
- In the name of the chain, the suffix for the double or triple bond in the parent chain should be added.
- The substituent groups should be named.
- The name of the substituent groups should be added in the name of chain.
- The carbon atoms in the chain should be numbered.
- The minimum possible number is given to the main functional group present as a substituent in the chain.
| Number of carbon atoms | Root name | Name of the corresponding |
| 1 | meth | Methane |
| 2 | eth | Ethane |
| 3 | prop | Propane |
| 4 | but | Butane |
| 5 | pent | Pentane |
| 6 | hex | Hexane |
Table 2: The root names used for the compounds according to the number of carbon atoms and the names of the corresponding hydrocarbons.
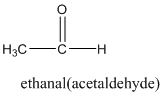
According to this explanation- CHO is the functional group of a carboxylic acid. This functional group is present in the main carbon chain of the example compound and hence resulting in absence of any substituent groups. Since there are only two carbon atoms in the main chain one should use the root name −eth in naming the compound. Also, the −CHO functional group is named as −al in the IUPAC name.
(e)
Interpretation:
In this subpart one must identify the functional group that is present in each molecule and thereby indicate the family of organic compounds to which the compound specifically belongs to.
Concept Introduction:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry-IUPAC has developed a method for systematically naming organic compounds. The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts the critical or the first part is to identify the main functional group present in a molecule in order to name it correctly. It allows the identification of the class of the compound easily possible without any ambiguity. The table indicating the main functional groups present in organic molecules can be summarized in the table below.
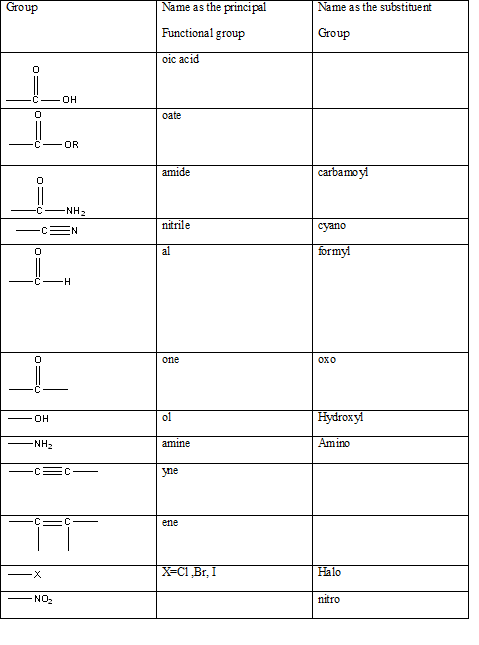
Table 1: The series of functional groups arranged in the decreasing order of the priority.
Answer to Problem 57QAP
Explanation of Solution
- The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts.
- The suffix that is used to indicate the main functional group of the structure.
- Name of the chain that is used to identify the main carbon chain of the compound.
- The prefixes that are used to indicate the substituent groups.
- The numbers that are used to indicate the places at which the substituent groups, additional groups and the main functional groups are attached to the chain.
The IUPAC name of an aliphatic compound can easily be developed by following the steps stated below in the given order.
- The main functional group should be identified first.
- The root name for the principal chain should be selected.
- In the name of the chain, the suffix for the double or triple bond in the parent chain should be added.
- The substituent groups should be named.
- The name of the substituent groups should be added in the name of chain.
- The carbon atoms in the chain should be numbered.
- The minimum possible number is given to the main functional group present as a substituent in the chain.
| Number of carbon atoms | Root name | Name of the corresponding |
| 1 | meth | Methane |
| 2 | eth | Ethane |
| 3 | prop | Propane |
| 4 | but | Butane |
| 5 | pent | Pentane |
| 6 | hex | Hexane |
Table 2: The root names used for the compounds according to the number of carbon atoms and the names of the corresponding hydrocarbons.
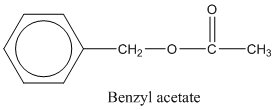
In this case the main functionality is −COOR group. In this particular example the −R group is the benzyl group which has a CH2 group attached to the benzene group.
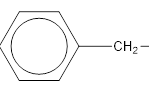
benzyl group.
(f)
Interpretation:
In this subpart one must identify the functional group that is present in each molecule and thereby indicate the family of organic compounds to which the compound specifically belongs to.
Concept Introduction:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry-IUPAC has developed a method for systematically naming organic compounds. The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts the critical or the first part is to identify the main functional group present in a molecule in order to name it correctly. It allows the identification of the class of the compound easily possible without any ambiguity. The table indicating the main functional groups present in organic molecules can be summarized in the table below.
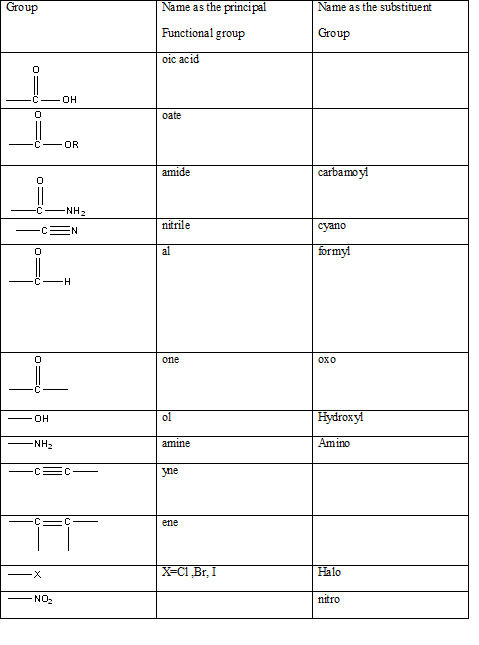
Table 1: The series of functional groups arranged in the decreasing order of the priority.
Answer to Problem 57QAP
Explanation of Solution
- The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts.
- The suffix that is used to indicate the main functional group of the structure.
- Name of the chain that is used to identify the main carbon chain of the compound.
- The prefixes that are used to indicate the substituent groups.
- The numbers that are used to indicate the places at which the substituent groups, additional groups and the main functional groups are attached to the chain. The IUPAC name of an aliphatic compound can easily be developed by following the steps stated below in the given order.
- The main functional group should be identified first.
| Number of carbon atoms | Root name | Name of the corresponding |
| 1 | meth | Methane |
| 2 | eth | Ethane |
| 3 | prop | Propane |
| 4 | but | Butane |
| 5 | pent | Pentane |
| 6 | hex | Hexane |
Table 2: The root names used for the compounds according to the number of carbon atoms and the names of the corresponding hydrocarbons.
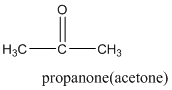
According to this explanation C=O is the functional group of a carboxylic acid. This functional group is present in the main carbon chain of the example compound and hence resulting in absence of any substituent groups. Since there are only three carbon atoms in the main chain one should use the root name −prop in naming the compound. Also, the −C=O functional group is named as −one in the IUPAC name.
(g)
Interpretation:
In this subpart one must identify the functional group that is present in each molecule and thereby indicate the family of organic compounds to which the compound specifically belongs to.
Concept Introduction:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry-IUPAC has developed a method for systematically naming organic compounds. The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts the critical or the first part is to identify the main functional group present in a molecule in order to name it correctly. It allows the identification of the class of the compound easily possible without any ambiguity. The table indicating the main functional groups present in organic molecules can be summarized in the table below.
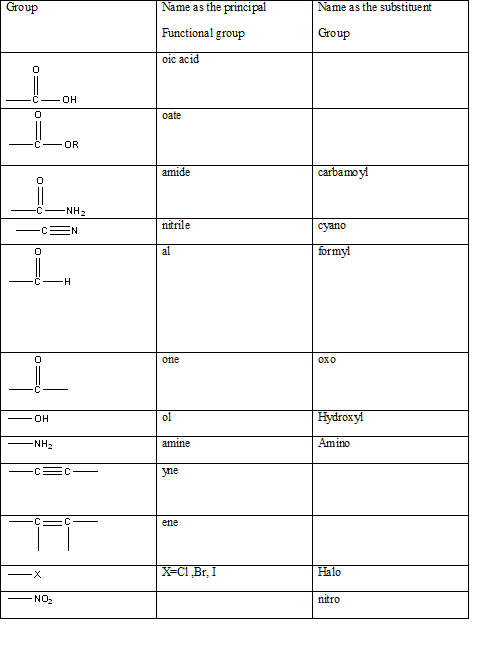
Table 1: The series of functional groups arranged in the decreasing order of the priority.
Answer to Problem 57QAP
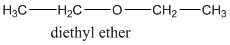
Explanation of Solution
- The name given to a compound according to the IUPAC nomenclature consists of several parts.
- The suffix that is used to indicate the main functional group of the structure.
- Name of the chain that is used to identify the main carbon chain of the compound.
- The prefixes that are used to indicate the substituent groups.
- The numbers that are used to indicate the places at which the substituent groups, additional groups and the main functional groups are attached to the chain. The IUPAC name of an aliphatic compound can easily be developed by following the steps stated below in the given order.
- The main functional group should be identified first.
| Number of carbon atoms | Root name | Name of the corresponding |
| 1 | meth | Methane |
| 2 | eth | Ethane |
| 3 | prop | Propane |
| 4 | but | Butane |
| 5 | pent | Pentane |
| 6 | hex | Hexane |
Table 2: The root names used for the compounds according to the number of carbon atoms and the names of the corresponding hydrocarbons.
A compound belonging to the class ether has the general form of R-O-R1 where R, R1 are the alkyl groups. R and R1 groups can be the same like in this example where R- group is the ethyl group containing two carbons in the alkyl chain.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: Foundation - Text (Looseleaf)
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning  Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





