
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Hybridization of underlined
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the hypothetical concept of mixing of atomic orbital into hybrid orbitals that are of dissimilar shapes, energies and are appropriate for combination of electrons to form bonds in
Hybridization is calculated by the hybrid orbitals and to calculate hybrid orbitals we need to know the steric number that is given by,
The table that relates the steric number with hybridization is as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 2F.8E
The molecule
Explanation of Solution
The molecule
The symbol for carbon is
The symbol for hydrogen is
Its Lewis structure is as follows:
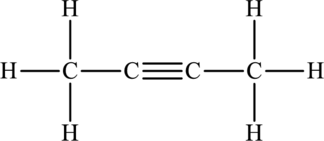
As from the structure above, 2 atoms are bonded to the underlined atom and 0 lone pair on it.
Substitute 2 for number of atoms bonded to the central atom and 0 for a number of lone pair on the central atom in equation (1) to find out the steric number.
Hence, the hybridization of
(b)
Interpretation:
Hybridization of underlined
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 2F.8E
The molecule
Explanation of Solution
The molecule
The symbol for carbon is
The symbol for hydrogen is
The symbol for nitrogen is
Its Lewis structure is as follows:
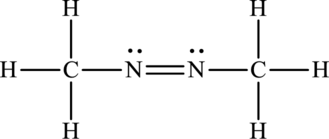
As from the structure above, 2 atoms are bonded to the underlined nitrogen atom and 1 lone pair on it.
Substitute 2 for a number of atoms bonded to the central atom and 1 for a number of lone pairs on the central atom in equation (1) to find out the steric number.
Hence, the hybridization of
(c)
Interpretation:
Hybridization of underlined
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 2F.8E
The molecule
Explanation of Solution
The molecule
The symbol for carbon is
The symbol for hydrogen is
Its Lewis structure is as follows:
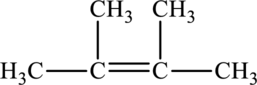
As from the structure above, 3 atoms are bonded to the underlined carbon atom and 0 lone pair on the same atom.
Substitute 3 for a number of atoms bonded to the central atom and 0 for a number of lone pair on the central atom in equation (1) to find out the steric number.
Hence, the hybridization of
(d)
Interpretation:
Hybridization of underlined
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 2F.8E
The molecule
Explanation of Solution
The molecule
The symbol for carbon is
The symbol for hydrogen is
The symbol for nitrogen is
Its Lewis structure is as follows:
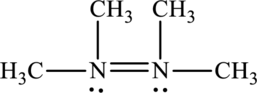
As from the structure above, 3 atoms are bonded to the underlined nitrogen atom and 1 lone pair on the same atom.
Substitute 3 for a number of atoms bonded to central atom and 1 for a number of lone pair on the central atom in equation (1) to find out the steric number.
Hence, the hybridization of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ACHIEVE/CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES ACCESS 1TERM
- What type of interaction would you expect between the following R groups in the tertiary structure of a protein? O -CH2-CO and -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH3+ a. disulfide bonds b. salt bridges c. hydrogen bonds HO abios vist anisinoo tedt bigil s ai loistaslor sale! 10 OUT d. hydrophobic interactions e. peptide bondsarrow_forward4. True or false: This skeletal structure represents a saturated fatty acid. Ini to 0 fale) me OH faistong starrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 5-Methyl-2-hexanone (with the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the first photo attached*arrow_forwardDraw the formula for 3-chlorobenzoic acetic anhydride.arrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 2-methylbutanoic acid (indicate the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forward
- Obtain 2-methylbutanoic acid by malonic or acetylacetic synthesis (indicate the formulas of the compounds involved).arrow_forwardEFFICIENTS SAMPLE READINGS CONCENTRATIONS Pigiadient) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) 58 6.274 3.898 301.7 151.2 14150 5.277 3.865 348.9 254.8 B 5.136 3.639 193.7 85.9 605 4.655 3.041 308.6 199.6 05 5.135 3.664 339.5 241.4 0139 4.676 3.662 160.6 87.6 90148 5.086 3.677 337.7 242.5 0092 6.348 3.775 464.7 186.4 PART3 5.081 3.908 223.5 155.8 5.558 3.861 370.5 257.1 4.922 3.66 326.6 242.9 4.752 3.641 327.5 253.3 50 5.018 3.815 336.1 256.0 84 4.959 3.605 317.9 216.6 38 4.96 3.652 203.8 108.7 $3 5.052 3.664 329.8 239.0 17 5.043 3.767 221.9 149.7 052 5.058 3.614 331.7 236.4 5.051 4.005 211.7 152.1 62 5.047 3.637 309.6 222.7 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 995 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 04 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 16 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 0.011 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 AVERAGE STDEV COUNT 95% CI Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH₃COCH₃) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH), applying heat to them produces an aldol condensation of the two compounds. If this is correct, draw the formula for the final product.arrow_forward
- If we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A), what product(s) are obtained?arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardYou need to make a buffer by dissolving benzoic acid and sodium benzoate in water. What is the mass of benzoic acid that you would weigh out, in mg, to create 50 mL of a buffer at pH = 4.7 that will change pH no more than 0.10 units with the addition of 0.001 moles of acid or base? Enter just the answer without the units (mg) - just the number will do!arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





