
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The VSEPR formula and shape for
Concept Introduction:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model predicts shape by inclusion of bond angles and most distant arrangement of atoms that leads to minimum repulsion. For the molecules that have no lone pairs around the central atom the bonded-atom unshared -pair arrangement is decided by the table as follows:
In order to determine the shape the steps to be followed are indicated as follows:
- 1. Lewis structure of molecule should be written.
- 2. The type electron arrangement around the central atom should be identified around the central atom. This essentially refers to determination of bond pairs and unshared or lone pairs around central atoms.
- 3. Then bonded-atom unshared -pair arrangement that can maximize the distance of electron pairs about central atom determines the shape.
For molecules that have lone pairs around central atom, lone pairs influence shape, because there are no atoms at the positions occupied by these lone pairs. The key rule that governs the molecular shape, in this case, is the extent of lone –lone pair repulsions are far greater than lone bond pair or bond pair-bond pair repulsions. The table that summarized the molecular shapes possible for various combinations of bonded and lone pairs are given as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 2E.12E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom along with uni-negative charge in
The skeleton structure in
These 13 electron pairs are assigned as lone pairs of each of the
Hence, the Lewis structure
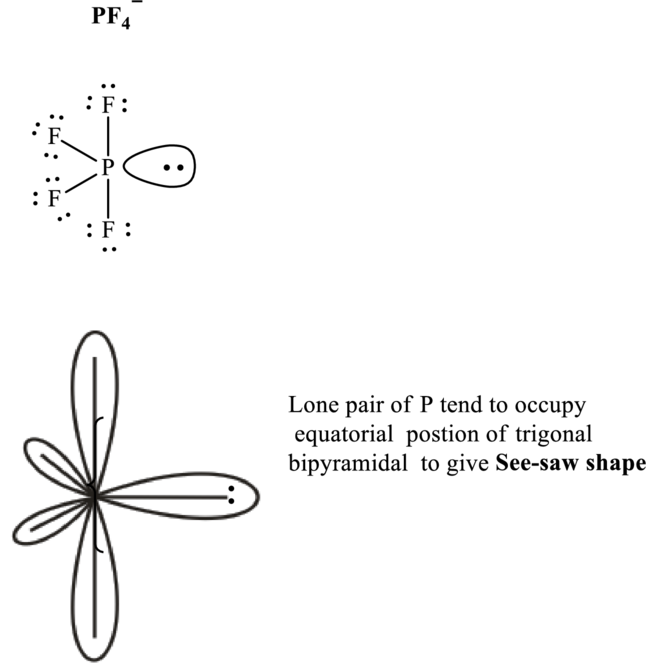
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bon pairs by X, then for any see-saw species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
It is evident that in
(b)
Interpretation:
The VSEPR formula and shape for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 2E.12E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each chlorine and central iodine in
The skeleton structure in
These 13 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs of each of the chlorine atoms and central iodine to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure and corresponding VSPER geometry in
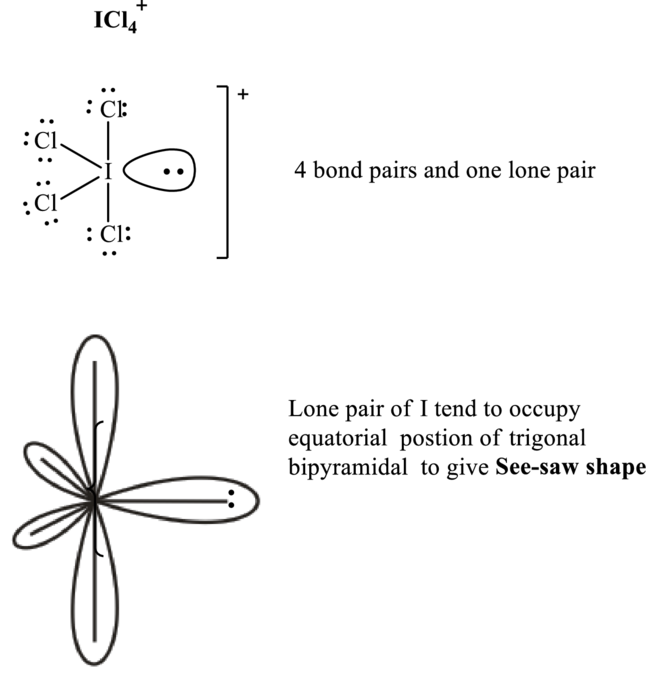
It is evident that in
Lone pairs tend to occupy the equatorial locations of trigonal plane in trigonal bi-pyramidal arrangement so as to have minimum repulsions in accordance with VSPER model. This results in see-saw shaped
(c)
Interpretation:
The VSEPR formula and shape for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 2E.12E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom along with uni-negative charge in
The skeleton structure in
These 15 electron pairs are assigned as lone pairs of each of the
Hence, Lewis structure of
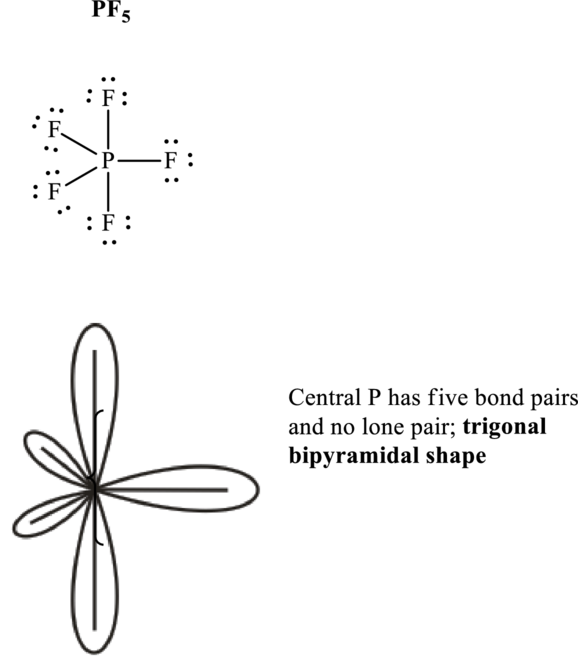
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any trigonal pyramidal geometry the VSEPR formula is predicted as
It is evident that in
(d)
Interpretation:
The VSEPR formula and shape for xenon terafluoride molecule has to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 2E.12E
The shape for xenon terafluoride molecule is square planar and corresponding VSEPR formula is
Explanation of Solution
Xenon terafluoride has
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each oxygen atom and central
The skeleton structure in
These 14 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs of each of the fluorine atoms and central xenon to satisfy respective octets. Thus, the Lewis structure and corresponding VSEPR geometry
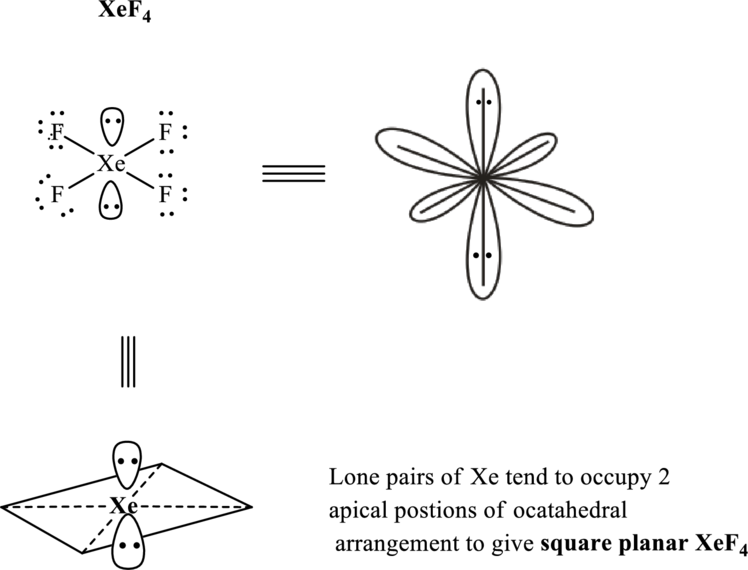
It is evident that in
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for square planar any species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ACHIEVE/CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES ACCESS 1TERM
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

