
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications, Student Value Edition Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134702193
Author: Allan R. Hambley
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.80P
Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits for the two-terminal circuit shown in Figure P2.80. 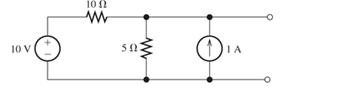
Figure P2.80
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule08:14
Students have asked these similar questions
A singl core cable of voltage 30 kv.
The diameter of Conductor is 3 cm.
The diameter of cable is 25 cm. This
cable has Two layer of insulator having
arelative permittivity 5-3 respectively
of
The ratio of
maximum electric stress
of
maximum electric stress
8
First layer to the
of second layer is 10 Find &
1- The thickness of each layers.
3-
The voltage of each
layers. §.
Layers
The saving in radius of cable if
another ungrading cable has the
Same maximum electric stress, Total
village, Conductor diameter of
grading cable.
66 KV sing care Cable has
a drameter of conductor of 3 cm.
The radius of cable is 10 cm.
This Cable house Two relative permmitivity
of insulation 6 and 4 respectively.
If The ratio of maximum electric stress
of first layer to the maximum eledric
streep & second layer is s
1- find the village & each layers.
2- Min- electric stress J Cable
3- Compare the voltage of ungrading
Cable has the same distance and
relectric stresses.
Prelab Information
1. Laboratory Preliminary Discussion
First-order Low-pass RC Filter Analysis
The first-order low-pass RC filter shown in figure 1 below represents all voltages and currents in the time domain. It is of course
possible to solve for all circuit voltages using time domain differential equation techniques, but it is more efficient to convert the
circuit to its s-domain equivalent as shown in figure 2 and apply Laplace transform techniques.
vs(t)
i₁(t)
+
R₁
ww
V₁(t)
12(t)
Lic(t)
Vout(t)
=
V2(t)
R₂
Vc(t)
C
Vc(t)
VR2(t)
= V2(t)
+
Vs(s)
Figure 1: A first-order low-pass RC filter represented in the time domain.
I₁(s)
R1
W
+
V₁(s)
V₂(s)
12(s)
Ic(s)
+
Vout(S)
==
Vc(s)
Vc(s)
Zc(s)
=
=
VR2(S)
V2(s)
Figure 2: A first-order low-pass RC filter represented in the s-domain.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications, Student Value Edition Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (7th Edition)
Ch. 2 - Reduce each of the networks shown in Figure P2.1...Ch. 2 - A 4- resistance is in series with the parallel...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Suppose that we need a resistance of 1.5 k and...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance between terminals a...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance between terminals a...Ch. 2 - What resistance in parallel with 120 results in...Ch. 2 - Determine the resistance between terminals a and b...Ch. 2 - Two resistances having values of R and 2R are in...Ch. 2 - A network connected between terminals a and b...
Ch. 2 - Two resistances R1 and R2 are connected in...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance for the infinite...Ch. 2 - If we connect n 1000- resistances in parallel,...Ch. 2 - The heating element of an electric cook top has...Ch. 2 - We are designing an electric space heater to...Ch. 2 - Sometimes, we can use symmetry considerations to...Ch. 2 - The equivalent resistance between terminals a and...Ch. 2 - Three conductances G1 G2, and G3 are in series....Ch. 2 - Most sources of electrical power behave as...Ch. 2 - The resistance for the network shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Often, we encounter delta-connected loads such as...Ch. 2 - What are the steps in solving a circuit by network...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.23....Ch. 2 - Find the voltages v1 and v2 for the circuit shown...Ch. 2 - Find the values of v and i in Figure P2.25. Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.24....Ch. 2 - Find the voltage v and the currents i1 and 12 for...Ch. 2 - Find the values of vs, v1, and i2 in Figure P2.28....Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.29....Ch. 2 - Consider the cirrcuit shown in Figure P2.30 Find...Ch. 2 - Solve for the values of i1, i2, and the powers for...Ch. 2 - The 12-V source in Figure P2.32 is delivering 36...Ch. 2 - Refer to the circuit shown in Figure P2.33. With...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.34. Find...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.35...Ch. 2 - Use the voltage-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Use the current-division principle to calculate i1...Ch. 2 - Use the voltage-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Use the current-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Suppose we need to design a voltage-divider...Ch. 2 - A source supplies 120 V to the series combination...Ch. 2 - We have a 60- resistance, a 20- resistance, and...Ch. 2 - A worker is standing on a wet concrete floor,...Ch. 2 - Suppose we have a load that absorbs power and...Ch. 2 - We have a load resistance of 50 that we wish to...Ch. 2 - We have a load resistance of 1 k that we wish to...Ch. 2 - The circuit of Figure P2.47 is similar to networks...Ch. 2 - Write equations and solve for the node voltages...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.49....Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.50....Ch. 2 - Given R1=4 , R2=5 , R2=8 , R4=10 , R5=2 , and...Ch. 2 - Determine the value of i1 in Figure P2.52 using...Ch. 2 - Given R1=15 , R5=5 , R3=20 , R4=10 , R5=8 , R6=4 ,...Ch. 2 - In solving a network, what rule must you observe...Ch. 2 - Use the symbolic features of MATLAB to find an...Ch. 2 - Solve for the values of the node voltages shown in...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.57....Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered to the 8- ...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.59....Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.62 shows an unusual voltage-divider...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages in the circuit of...Ch. 2 - We have a cube with 1- resistances along each...Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered to the 15- resistor...Ch. 2 - Determine the value of v2 and the power delivered...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of i1...Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered by the voltage...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of v...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of i3...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - Find the power delivered by the source and the...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - The circuit shown in Figure P2.75 is the dc...Ch. 2 - Use MATLAB and mesh-current analysis to determine...Ch. 2 - Connect a 1-V voltage source across terminals a...Ch. 2 - Connect a 1-V voltage source across the terminals...Ch. 2 - Use MATLAB to solve for the mesh currents in...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - We can model a certain battery as a voltage source...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin arid Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - An automotive battery has an open-circuit voltage...Ch. 2 - A certain two-terminal circuit has an open-circuit...Ch. 2 - If we measure the voltage at the terminals of a...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the maximum power that can be delivered to a...Ch. 2 - Find the maximum power that can be delivered to a...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.91 shows a resistive load RL connected...Ch. 2 - Starling from the Norton equivalent circuit with a...Ch. 2 - A battery can be modeled by a voltage source Vt in...Ch. 2 - Use superposition to find the current i in Figure...Ch. 2 - Solve for is in Figure P2.49 by using...Ch. 2 - Solve the circuit shown in Figure P2.48 by using...Ch. 2 - Solve for i1 in Figure P2.34 by using...Ch. 2 - Another method of solving the circuit of Figure...Ch. 2 - Use the method of Problem P2.98 for the circuit of...Ch. 2 - Solve for the actual value of i6 for the circuit...Ch. 2 - Device A shown in Figure P2.101 has v=3i2 for i 0...Ch. 2 - The Wheatstone bridge shown in Figure 2.66 is...Ch. 2 - The Wheatstone bridge shown in Figure 2.66has...Ch. 2 - In theory, any values can be used for R1 and R3 in...Ch. 2 - Derive expressions for the Thévenin voltage and...Ch. 2 - Derive Equation 2.93 for the bridge circuit of...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.107PCh. 2 - Explain what would happen if, in wiring the bridge...Ch. 2 - Match each entry in Table T2.1(a) with the best...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit of Figure T2.2 with vs=96V ,...Ch. 2 - Write MATLAB code to solve for the node voltages...Ch. 2 - Write a set of equations that can be used to solve...Ch. 2 - Determine the Thévenin and Norton equivalent...Ch. 2 - According to the superposition principle, what...Ch. 2 - Determine the equivalent resistance between...Ch. 2 - Transform the 2-A current source and 6- ...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is the general problem with static scoping?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
#inc1ude iostream; using namespace std; int main() { char name, go; cout Enter your name: ; getline name; cou...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
What is an object? What is a control?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
2-1 List the five types of measurements that form the
basis of traditional ptane surveying-
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Summarize the steps performed by the CPU when an interrupt occurs.
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Method fahrenheit returns the Fahrenheit equivalent of a Celsius temperature, using the calculation fahrenheit ...
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve it in a different way than the previous solution that I searched forarrow_forwardA lossless uncharged transmission line of length L = 0.45 cm has a characteristic impedance of 60 ohms. It is driven by an ideal voltage generator producing a pulse of amplitude 10V and width 2 nS. If the transmission line is connected to a load of 200 ohms, sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for the interval 0 < t < 20 nS. You may assume that the propagation velocity of the transmission is c/2. Answered now answer number 2. Repeat Q.1 but now assume the width of the pulse produced by the generator is 4 nS. Sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for 0 < t < 20 nS.arrow_forwardSolve this experiment with an accurate solution, please. Thank you.arrow_forward
- A lossless uncharged transmission line of characteristic impedance Zo = 600 and length T = 1us is connected to a 180 load. If this transmission line is connected at t = 0 to a 90 V dc source with an internal resistance of 900, from a bounce diagram of this system sketch (a) the voltage at z=0, z=L, and z = L/2 for up to 7.25μs and (b) calculate the load voltage after an infinite amount of time.arrow_forwardA lossless uncharged transmission line of length L = 0.45 cm has a characteristic impedance of 60 ohms. It is driven by an ideal voltage generator producing a pulse of amplitude 10V and width 2 nS. If the transmission line is connected to a load of 200 ohms, sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for the interval 0 < t < 20 nS. You may assume that the propagation velocity of the transmission is c/2.arrow_forwardThe VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) is measured to be 2 on a transmission line. Find two values of the reflection coefficient with one corresponding to Z > Zo and the other to Zarrow_forwardA dc voltage of unknown value Vand internal resistance Reis connected through a switch to a lossless transmission line of Zo = 1000. If the first 5 μS of the voltages at z = 0 and z = L are observed to be as shown below, calculate Vo, RG, the load resistanceR,, and the transit time T. 100 + [V]:-0. V 90 [V]:-V 100 75 I, Տ 1,μs 2 4 6 0 2 4 6arrow_forwardA lossless open circuited transmission line behaves as an equivalent capacitance of Ceq = Tan (BL) Show for BL << 1 that Ceq = C'L where L is the length of the transmission line and wZo C' is the lumped parameter capacitance per unit length of the transmission line. Hint: For x small, Tan(x) = x.arrow_forward= A generator with VG 300V and R = 50 is connected to a load R = 750 through a 50 lossless transmission line of length L = 0.15 m. (a) Compute Zin, the input impedance of the line at the generator end. (b) Compute and V. (c) Compute the time-average power Pin delivered to the line. (d) Compute VL, IL, and the time-average power delivered to the load, PL (e) How does Pin compare to PL? Explain.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Norton's Theorem and Thevenin's Theorem - Electrical Circuit Analysis; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-kkvqr1wSwA;License: Standard Youtube License