
Physics for Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781133953982
Author: SERWAY, Raymond A./
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 23P
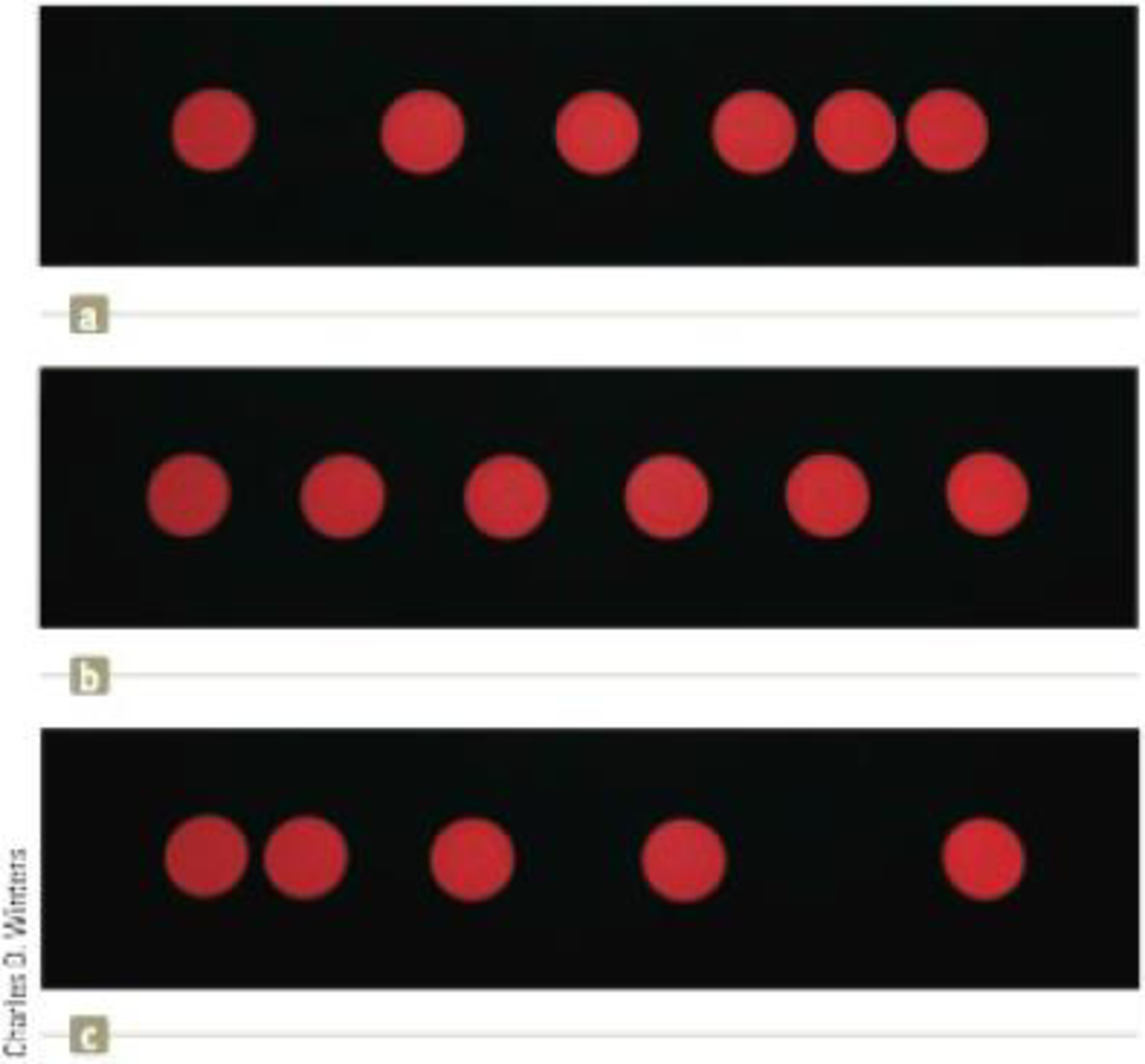
Each of the strobe photographs (a), (b), and (c) in Figure P2.13 was taken of a single disk moving toward the right, which we take as the positive direction. Within each photograph the time interval between images is constant. For each photograph, prepare graphs of x versus t, vx versus t, and ax versus t, vertically aligned with their time axes identical, to show the motion of the disk. You will not be able to place numbers other than zero on the axes, but show the correct shapes for the graph lines.
Figure P2.13
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A block of mass 1.4 kg is attached to a horizontal spring that has a force constant 900 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is compressed 2.0 cm and is then released from rest.
a
x = 0
x
b
(a) A constant friction force of 4.4 N retards the block's motion from the moment it is released. Using an energy approach, find the position x of the block at which its speed is a maximum.
cm
(b) Explore the effect of an increased friction force of 13.0 N. At what position of the block does its maximum speed occur in this situation?
cm
A block of mass m = 3.00 kg situated on a rough incline at an angle of 0 = 37.0° is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (see the figure below). The pulley is frictionelss. The block is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. The block
moves 11.0 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline.
k=100 N/m
Ө
m
23.
What is the velocity of a beam of electrons that goes undeflected when passing through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields of magnitude 8.8 X 103 V/m and 7.5 X 10-3 T. respectively? What is the radius of the electron orbit if the electric field is turned off?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics
Ch. 2.1 - Under which of the following conditions is the...Ch. 2.2 - Are officers in the highway patrol more interested...Ch. 2.4 - Make a velocitytime graph for the car in Figure...Ch. 2.4 - If a car is traveling eastward and slowing down,...Ch. 2.5 - Which one of the following statements is true? (a)...Ch. 2.6 - In Figure 2.12, match each vxt graph on the top...Ch. 2.7 - Consider the following choices: (a) increases, (b)...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1OQCh. 2 - A racing car starts from rest at t = 0 and reaches...Ch. 2 - Prob. 3OQ
Ch. 2 - When applying the equations of kinematics for an...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5OQCh. 2 - Prob. 6OQCh. 2 - When the pilot reverses the propeller in a boat...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8OQCh. 2 - A skateboarder starts from rest and moves down a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 10OQCh. 2 - Prob. 11OQCh. 2 - A pebble is dropped from rest from the top of a...Ch. 2 - A student at the top of a building of height h...Ch. 2 - You drop a ball from a window located on an upper...Ch. 2 - A pebble is released from rest at a certain height...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown straight up in the air. For which...Ch. 2 - Prob. 17OQCh. 2 - Each of the strobe photographs (a), (b), and (c)...Ch. 2 - If the average velocity of an object is zero in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2CQCh. 2 - If a car is traveling eastward, can its...Ch. 2 - Prob. 4CQCh. 2 - Prob. 5CQCh. 2 - You throw a ball vertically upward so that it...Ch. 2 - (a) Can the equations of kinematics (Eqs....Ch. 2 - (a) Can the velocity of an object at an instant of...Ch. 2 - Two cars are moving in the same direction in...Ch. 2 - Position, Velocity, and Speed The position versus...Ch. 2 - The speed of a nerve impulse in the human body is...Ch. 2 - A person walks first at a constant speed of 5.00...Ch. 2 - A particle moves according to the equation x =...Ch. 2 - The position of a pinewood derby car was observed...Ch. 2 - Prob. 6PCh. 2 - A positiontime graph for a particle moving along...Ch. 2 - An athlete leaves one end of a pool of length L at...Ch. 2 - Find the instantaneous velocity of the particle...Ch. 2 - Prob. 10PCh. 2 - Prob. 11PCh. 2 - A car travels along a straight line at a constant...Ch. 2 - A person takes a trip, driving with a constant...Ch. 2 - Prob. 14PCh. 2 - Prob. 15PCh. 2 - A child rolls a marble on a bent track that is 100...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.9 shows a graph of vx versus t for the...Ch. 2 - (a) Use the data in Problem 3 to construct a...Ch. 2 - A particle starts from rest and accelerates as...Ch. 2 - An object moves along the x axis according to the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 21PCh. 2 - Draw motion diagrams for (a) an object moving to...Ch. 2 - Each of the strobe photographs (a), (b), and (c)...Ch. 2 - Prob. 24PCh. 2 - An electron in a cathode-ray tube accelerates...Ch. 2 - Prob. 26PCh. 2 - A parcel of air moving in a straight tube with a...Ch. 2 - A truck covers 40.0 m in 8.50 s while smoothly...Ch. 2 - An object moving with uniform acceleration has a...Ch. 2 - In Example 2.7, we investigated a jet landing on...Ch. 2 - Prob. 31PCh. 2 - Solve Example 2.8 by a graphical method. On the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 33PCh. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible?...Ch. 2 - Prob. 35PCh. 2 - Prob. 36PCh. 2 - Prob. 37PCh. 2 - Prob. 38PCh. 2 - A glider of length moves through a stationary...Ch. 2 - A glider of length 12.4 cm moves on an air track...Ch. 2 - Prob. 41PCh. 2 - At t = 0, one toy car is set rolling on a straight...Ch. 2 - Prob. 43PCh. 2 - Prob. 44PCh. 2 - Prob. 45PCh. 2 - An attacker at the base of a castle wall 3.65 m...Ch. 2 - Prob. 47PCh. 2 - Prob. 48PCh. 2 - Prob. 49PCh. 2 - The height of a helicopter above the ground is...Ch. 2 - Prob. 51PCh. 2 - Prob. 52PCh. 2 - Prob. 53PCh. 2 - At time t = 0, a student throws a set of keys...Ch. 2 - Prob. 55PCh. 2 - Prob. 56PCh. 2 - Prob. 57PCh. 2 - A student drives a moped along a straight road as...Ch. 2 - The speed of a bullet as it travels down the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 60APCh. 2 - The froghopper Philaenus spumarius is supposedly...Ch. 2 - Prob. 62APCh. 2 - Prob. 63APCh. 2 - In Figure 2.11b, the area under the velocitytime...Ch. 2 - Prob. 65APCh. 2 - A woman is reported to have fallen 144 ft from the...Ch. 2 - An elevator moves downward in a tall building at a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 68APCh. 2 - Prob. 69APCh. 2 - Prob. 70APCh. 2 - At t = 0, one athlete in a race running on a long,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 72APCh. 2 - Prob. 73APCh. 2 - Prob. 74APCh. 2 - Two objects, A and B, are connected by hinges to a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 76APCh. 2 - Prob. 77APCh. 2 - Prob. 78APCh. 2 - Prob. 79APCh. 2 - Prob. 80APCh. 2 - Prob. 81CPCh. 2 - Prob. 82CPCh. 2 - In a womens 100-m race, accelerating uniformly,...Ch. 2 - Two thin rods are fastened to the inside of a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 85CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 10. A light bulb emits 25.00 W of power as visible light. What are the average electric and magnetic fields from the light at a distance of 2.0 m?arrow_forward9. Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .15 seconds. Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.arrow_forwardIn the movie Fast X, a 10100 kg round bomb is set rolling in Rome. The bomb gets up to 17.6 m/s. To try to stop the bomb, the protagonist Dom swings the counterweight of a crane, which has a mass of 354000 kg into the bomb at 3.61 m/s in the opposite direction. Directly after the collision the crane counterweight continues in the same direction it was going at 2.13 m/s. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the bomb right after the collision?arrow_forward
- Ultimate Byleth and Little Mac fight. Little Mac, who is a boxer, dashes forward at 26.6 m/s, fist first. Byleth moves in the opposite direction at 3.79 m/s, where they collide with Little Mac’s fist. After the punch Byleth flies backwards at 11.1 m/s. How fast, and in what direction, is Little Mac now moving? Little Mac has a mass of 48.5 kg and Byleth has a mass of 72.0 kg.arrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale as wellarrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY