
(a)
The formula for the pressure difference
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The following figure shows the two containers with water and oil.
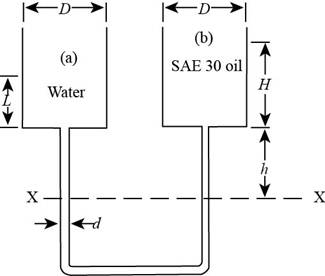
Figure-(1)
The height of oil in container is
Write the hydrostatic equation for the left limb.
Here, the pressure at
Write the hydrostatic equation for the right limb.
Here, the pressure at
The pressure of the right limb and the left limb is same at the datum
Substitute
The figure below shows the rise in limb
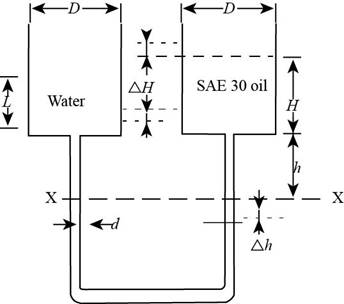
Figure-(2)
Both the containers are of equal diameter hence, the change in height of limb is
The volume rise and fall in both the containers is same.
Write the expression for balance the volume in both containers.
Here, the diameter of the limb is
Write the hydrostatic equation for the left limb at the datum
Write the hydrostatic equation for the right limb at the datum
The pressure at both the limbs is same at the datum.
Substitute
From Equation (IV) and Equation (II).
Substitute
When
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the formula for the pressure difference
(b)
The formula for the pressure difference
The percentage change in pressure difference.
(b)
Answer to Problem 2.34P
The formula for the pressure difference
The percentage change in pressure difference is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for diameter of limb.
Substitute
Write the percentage change in pressure.
Here, the change in pressure in case 1 is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the formula for the pressure difference
Substitute
Thus, the percentage change in pressure difference is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics
- B C 3.0 E F G 40 kN [m] 3.0 3.0 3.0 Fackverket belastas med en punktlast i G enligt figuren. Bestäm normalkraften i stängerna BC, BF och EF.arrow_forwardL q=8 kN/m P= 12 kN En stång belastas av en punklast P vid sin ena ände samt av en jämnt utbredd last q längs hela sin längd. Stången har en tvärsnittsarea A = 150 mm² och är tillverkad av stål med elasticitetsmodul E-210 GPa. Stångens längd, i sitt obelastade tillstånd, är Z-3 m. a) Hur stor är den största normalspänning som uppstår i stången? b) Hur stor blir förlängningen av stången, orsakad av lasterna P och q?arrow_forwardA turbocharged engine with a compression ratio of 8 is being designed using an air standard cycle. The ambient air is assumed to be 300K and 100 kPa. The temperature at the end of the compression in the cylinder is desired to be 1000K, assuming no combustion prior to reaching TDC. At the end of the cylinder expansion the temperature is also desired to be 1000K. If both the turbine and the compressor have mechanical efficiencies of 80%, what will be the pressure ratio of the compressor and what will be the turbine exhaust temperature?arrow_forward
- Q6: A turbocharged engine with a compression ratio of 8 is being designed using an air standard cycle. The ambient air is assumed to be 300K and 100 kPa. The temperature at the end of the compression in the cylinder is desired to be 1000K, assuming no combustion prior to reaching TDC. At the end of the cylinder expansion the temperature is also desired to be 1000K. If both the turbine and the compressor have mechanical efficiencies of 80%, what will be the pressure ratio of the compressor and what will be the turbine exhaust temperature?arrow_forwardQ5: A 5.6 litre V8 engine with a compression ratio of 9.4:1 operates on an air-standard Otto cycle at 2800 RPM, with a volumetric efficiency of 90 % and a stoichiometric air-fuel ratio using gasoline. The exhaust flow undergoes a temperature drop of 44ºC as it passes through the turbine of the supercharger. Calculate (a) mass flow rate of exhaust gas and (b) power available to drive the turbocharger compressor.arrow_forwarddo handwrittenarrow_forward
- Create a report: An example of two people who do not understand each other due to lack of communication, and mention ways to resolve the issue between them .arrow_forwardI want the kinematic diagram to be draw like this plsarrow_forwardAccording to the principles and steps above, draw the kinematic diagram of following mechanisms. Mark the appropriate scale, calculates the degree of freedom. NO.1 NO.2 NO: 3 NO.: 4arrow_forward
- An office building is planned with a lateral-force-resisting system designed for earthquake resistance in aseismic zone. The seismic capacity of the proposed system, expressed as a force factor, is assumed tofollow a lognormal distribution with a median of 6.5 and a standard deviation of 1.5. The ground motionfrom the largest expected earthquake at the site is estimated to correspond to an equivalent force factor of 5.5.(a) What is the estimated probability that the building will experience damage when subjected to the largest expected earthquake? (b) If the building survives (i.e., experiences no damage) during a previous moderate earthquake with aforce factor of 4.0, what is the updated probability of failure of the building under the largest expectedearthquake?(c) Suppose future occurrences of the largest expected earthquake follow a Poisson process with a mean return period of 500 years. Assuming that damage events from different earthquakes are statisticallyindependent,…arrow_forwardDuring a plant visit, it was noticed that a 12-m-long section of a 10-cm-diameter steam pipe is completely exposed to the ambient air. The temperature measurements indicate that the average temperature of the outer surface of the steam pipe is 75°C when the ambient temperature is 5°C. There are also light winds in the area at 10 km/h. The emissivity of the outer surface of the pipe is 0.8, and the average temperature of the surfaces surrounding the pipe, including the sky, is estimated to be 0°C. Determine the amount of heat lost from the steam during a 10-h-long work day. Steam is supplied by a gas-fired steam generator that has an efficiency of 80 percent, and the plant pays $1.05/therm of natural gas. If the pipe is insulated and 90 percent of the heat loss is saved, determine the amount of money this facility will save a year as a result of insulating the steam pipes. Assume the plant operates every day of the year for 10 h. State your assumptions.arrow_forwardAn old fashioned ice cream kit consists of two concentric cylinders of radii Ra and Rb. The inner cylinder is filled with milk and ice cream ingredients while the space between the two cylinders is filled with an ice-brine mixture. Ice cream begins to form on the inner surface of the inner cylinder. To expedite the process, would you recommend rotating the inner cylinder? Justify your recommendation. icecream/ ice-brine Ra Rbarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





