
The criteria for the beam to float exactly on its diagonal.
Answer to Problem 2.121P
The beam will float on its surface for
Explanation of Solution
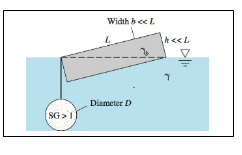
Given Information:
Let diameter of the sphere be D
Dimensions of the box − length-L, breadth − b, height -h
Specific weight of the box = γb
Specific weight of the water = γ
Specific gravity of the sphere = SG > 1
.
Calculation:
Conclusion:
Hence, proved for the given diameter of the sphere
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics
- I keep trying this problem but cant seem to get the sheer right can you help me figure this out please?arrow_forwardThe pillar crane is subjected to the crate having a mass of 1000 kgkg. The boom is held in position shown in (Figure 1).Determine the force in the tie rod ABAB.Determine the horizontal and vertical reactions at the pin support CC.arrow_forwardProblem 7.1 Part A In (Figure 1), F₁ = 550 lb, F2 = 250 lb, and F3 = 340 lb. Figure F F B Part B Determine the shear force at point C. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Vc=522 ? lb Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 15 attempts remaining Part C Determine the moment at point C. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 1 of 1 Mc = 1867 F E D lb.ft Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 24 attempts remaining ▸ Part D 6 ft- 4 ft- 4 ft- 6 ft 12 ftarrow_forward
- Sketch h, for Problem 13.64 13 13.65 In Sketch i the tension on the slack side of the left pulley is 20% of that on the tight side. The shaft rotates at 1000 rpm. Select a pair of deep-groove roller bearings to sup- port the shaft for 99% reliability and a life of 20,000 hr. Assume Eq. (13.83) can be used to account for lubricant cleanliness. All length dimensions are in millimeters. b Z 02 0 y 200 500. 187 100 30° B TONE 500 diam 800 N 650 diam 100 N Sketch i, for Problem 13.65 வarrow_forwardProblem 2: Consider the rectangular wood beam below. Use E=1.0. 1. Determine the slope at A. 2. Determine the largest deflection between A and B. Use the elastic curve equation. Show all work. (20%) 3 kN/m A 2.4 m - 50 mm AT 150 mm 0000 - B C 1.2 m→arrow_forwardPlease give a clear solution.arrow_forward
- USE MATLAB ONLY Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),... axis([-1 6 -4 4]), ... title('Velocity Triangle'), ... xlabel('x'),ylarrow_forwardThe wall of a furnace has a thickness of 5 cm and thermal conductivity of 0.7 W/m-°C. The inside surface is heated by convection with a hot gas at 402°C and a heat transfer coefficient of 37 W/m²-°C. The outside surface has an emissivity of 0.8 and is exposed to air at 27°C with a heat transfer coefficient of 20 W/m²-ºC. Assume that the furnace is inside a large room with walls, floor and ceiling at 27°C. Show the thermal circuit and determine the heat flux through the furnace wall. h₁ T₁ k -L T. sur ho Earrow_forwardTurbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),... axis([-1 6 -4 4]), ... title('Velocity Triangle'), ... xlabel('x'),ylabel('y'), gridarrow_forward
- To save fuel during the heating season it is suggested that glass windows be covered at night with a 1.2 cm layer of polystyrene. Estimate the percent savings in energy and discuss the feasibility of this idea. Show the thermal circuit with and without the insulation panel. Consider a typical case of 0.2 cm thick window glass with inside and outside heat transfer coefficients of 6 and 32 W/m²-ºC. Lg←←Lp h T₁ T。 g kp insulation panelarrow_forwardA plate of thickness L and thermal conductivity k is exposed to a fluid at temperature T1 with a heat transfer coefficient h, on one side and T2 and h₂ on the other side. Determine the one-dimensional temperature distribution in the plate. Assume steady state and constant conductivity. L h h T%2 k Tx1 0xarrow_forwardDetermine the heater capacity needed to maintain the inside temperature of a laboratory chamber at 38°C when placed in a room at 21°C. The chamber is cubical with each side measuring 35 cm. The walls are 1.2 cm thick and are made of polystyrene. The inside and outside heat transfer coefficients are 5 and 22 W/m²-°C.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





