
Identify the elements used in each example of molecular art.
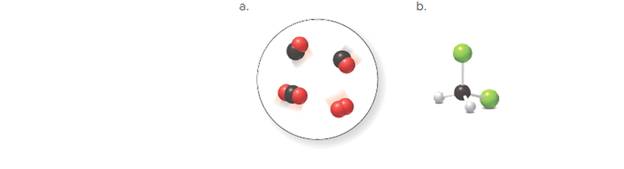
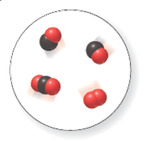
(a)
Interpretation:
The elements present in the following molecular art should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
Molecular art is defined as the art that showcases molecules as physical objects that have a definite shape and size. According to molecular art, some of the atoms are represented with a particular color as follows:
A carbon atom is represented by a black colored sphere.
The oxygen atom is represented by a red-colored sphere.
The nitrogen atom is represented by a blue-colored sphere.
The hydrogen atom is represented by a white-colored sphere.
Chlorine atom is represented by a green-colored sphere.
Bromine atom is represented by a brown-colored sphere.
Answer to Problem 2.33P
There are two molecules of
Explanation of Solution
In the given space-filling model, there are black and red spheres. Black spheres correspond to the element carbon whereas red spheres correspond to the element oxygen.
Therefore, two molecules contain one carbon atom and one oxygen atom each. Hence, its molecular formula is
Another, one molecule contains one carbon and two oxygen atoms. Hence, its molecular formula is
Another molecule contains only two oxygen atoms. Therefore, its molecular formula is
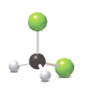
(b)
Interpretation:
The elements present in the following molecular art should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
Molecular art is defined as the art that shows molecules as physical objects that have a definite shape and size. According to the molecular art, some of the atoms are represented with a particular color as follows.
A carbon atom is represented by a black colored sphere.
The oxygen atom is represented by a red-colored sphere.
The nitrogen atom is represented by a blue-colored sphere.
The hydrogen atom is represented by a white-colored sphere.
Chlorine atom is represented by a green-colored sphere.
Bromine atom is represented by a brown-colored sphere.
Answer to Problem 2.33P
The given model contains two chlorine atoms, two hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom. So, elements present in this molecular art are carbon, hydrogen and chlorine.
Explanation of Solution
The given representation of the ball and stick model shows two green spheres, two white spheres and one black sphere.
As it is known that green color represents chlorine element, white color represents the hydrogen element and black color represents carbon element, the molecular formula in the given model is
Hence, it contains two chlorine atoms, two hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





