
Concept explainers
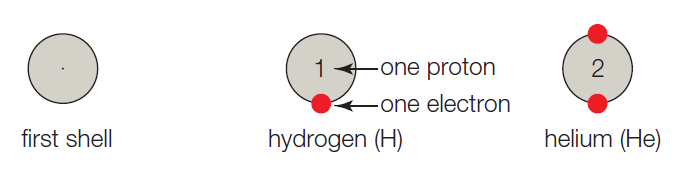
- A. The first shell corresponds to the first energy level, and it can hold up to 2 electrons. Hydrogen has one proton, so it has 1 electron and one vacancy. A helium atom has 2 protons, 2 electrons, and no vacancies.
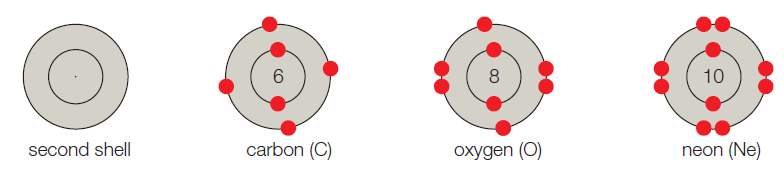
- B. The second shell corresponds to the second energy level, and it can hold up to 8 electrons. Carbon has 6 electrons, so its first shell is full. Its second shell has 4 electrons and four vacancies. Oxygen has 8 electrons and two vacancies. Neon has 10 electrons and no vacancies.
- C. The third shell corresponds to the third energy level, and it can hold up to 8 electrons. A sodium atom has 11 electrons, so its first two shells are full; the third shell has one electron. Thus, sodium has seven vacancies. Chlorine has 17 electrons and one vacancy. Argon has 18 electrons and no vacancies.
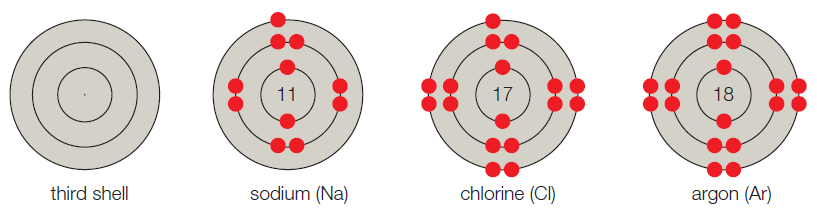
Figure It Out: Which of these models have unpaired electrons in their outer shell?
The atoms are referred to as building blocks of all substances. In other words, it is the basic fundamental unit of the matter. In every atom, the uncharged neutron and positively charged protons are present in the nucleus whereas the negatively charged electron moves around the nucleus. Generally, the shell model system is used to study the valence status of an atom. The atomic number is the number of protons present in the atom which determines the type of the atom
Explanation of Solution
The given shell model consists of about eight atoms namely helium, neon, hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, sodium, chloride, and argon. Of this given atom in the model the hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, chlorine and sodium have unpaired electrons in the outer shell. These unpaired electrons are available to pair with other unpaired electrons in another atom. Thus these atoms combine to form molecules.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (MindTap Course List)
- Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Zero-Order Absorption Questions SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution, report your regression lines and axes names (with units if appropriate) :Calculate a-q a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardWhat are some external influences that keep people from making healthy eating decisions?arrow_forwardWhat type of structure(s) would you expect to see in peripheral membrane proteins? (mark all that apply) A. Amphipathic alpha helix (one side is hydrophilic and one side is hydrophobic) B. A hydrophobic beta barrel C. A hydrophobic alpha helix D. A chemical group attached to the protein that can anchor it to the membranearrow_forward
- Temporal flexibility (the ability to change over time) of actin structures within a cell is maintained by… A. The growth/shrinkage cycle B. Periodic catastrophe C. GTP hydrolysis D. Treadmilling E. None of the abovearrow_forwardDuring in vitro polymerization of actin and microtubule filaments from their subunits, what causes the initial delay in filament growth? A.Nucleation B.Reaching homeostasis C.Nucleotide exchange D.ATP or GTP hydrolysis E.Treadmillingarrow_forwardYou expect to find which of the following in the Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC)...(mark all that apply) A. Gamma tubulin B. XMAP215 C. Centrioles D. Kinesin-13arrow_forward
- The actin-nucleating protein formin has flexible “arms” containing binding sites that help recruit subunits in order to enhance microfilament polymerization. What protein binds these sites? A.Thymosin B.Profilin C.Cofilin D.Actin E.Tropomodulinarrow_forwardWhile investigating an unidentified motor protein, you discover that it has two heads that bind to actin. Based on this information, you could confidently determine that it is NOT... (mark all that apply) A. A myosin I motor B. A dynein motor C. A myosin VI motor D. A kinesin motorarrow_forwardYou isolate the plasma membrane of cells and find that . . . A. it contains regions with different lipid compositions B. it has different lipid types on the outer and cytosolic leaflets of the membrane C. neither are possible D. A and B both occurarrow_forward
- You are studying the mobility of a transmembrane protein that contains extracellular domains, one transmembrane domain, and a large cytosolic domain. Under normal conditions, this protein is confined to a particular region of the membrane due to the cortical actin cytoskeletal network. Which of the following changes is most likely to increase mobility of this protein beyond the normal restricted region of the membrane? A. Increased temperature B. Protease cleavage of the extracellular domain of the protein C. Binding to a free-floating extracellular ligand, such as a hormone D. Protease cleavage of the cytosolic domain of the protein E. Aggregation of the protein with other transmembrane proteinsarrow_forwardTopic: Benthic invertebrates as an indicator species for climate change, mapping changes in ecosystems (Historical Analysis & GIS) What objects or events has the team chosen to analyze? How does your team wish to delineate the domain or scale in which these objects or events operate? How does that limited domain facilitate a more feasible research project? What is your understanding of their relationships to other objects and events? Are you excluding other things from consideration which may influence the phenomena you seek to understand? Examples of such exclusions might include certain air-born pollutants; a general class of water bodies near Ottawa, or measurements recorded at other months of the year; interview participants from other organizations that are involved in the development of your central topic or issue. In what ways do your research questions follow as the most appropriate and/or most practical questions (given the circumstances) to pursue to better understand…arrow_forwardThe Esp gene encodes a protein that alters the structure of the insulin receptor on osteoblasts and interferes with the binding of insulin to the receptor. A researcher created a group of osteoblasts with an Esp mutation that prevented the production of a functional Esp product (mutant). The researcher then exposed the mutant strain and a normal strain that expresses Esp to glucose and compared the levels of insulin in the blood near the osteoblasts (Figure 2). Which of the following claims is most consistent with the data shown in Figure 2 ? A Esp expression is necessary to prevent the overproduction of insulin. B Esp protein does not regulate blood-sarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





