
a)
Interpretation:
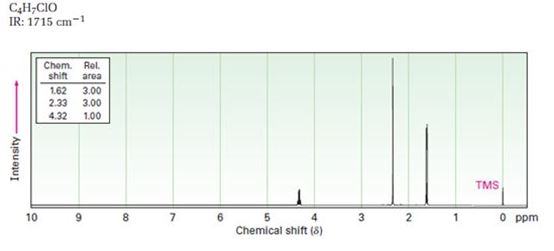
A structure for ketone or aldehyde with the following descriptions is to be proposed.
C4H7ClO, IR: 1715 cm-1; 1HNMR: 1.62 δ (Rel.area=3.00), 2.33 δ (Rel.area=3.00), 4.32δ (Rel.area=1.00).
Concept introduction:
In 1HNMR the aldehyde protons absorb near 10 δ with a coupling constant , J = 3Hz. Hydrogens on the carbon next to aldehyde group absorb near 2.0-2.3 δ. Methyl ketones show a sharp three proton singlet near 2.1 δ.
To purpose:
A structure for ketone or aldehyde with the following descriptions.
C4H7ClO, IR: 1715 cm-1; 1HNMR: 1.62 δ (Rel.area=3.00), 2.33 δ (Rel.area=3.00), 4.32δ (Rel.area=1.00).
b)
Interpretation:
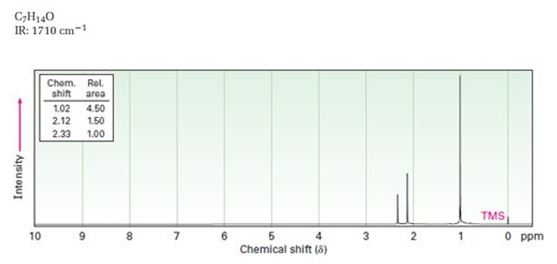
A structure for ketone or aldehyde with the following descriptions is to be proposed.
C7H14O, IR: 1710 cm-1; 1HNMR: 1.02 δ (Rel.area=4.50), 2.12 δ (Rel.area=1.50), 2.33δ (Rel.area=1.00).
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones show a strong absorption band in IR from 1660-1770 cm-1. Aldehydes show two characteristic C-H absorptions between 2700-2760 cm-1 and 2800-2860 cm-1. Saturated aldehydes absorb near 1730 cm-1 while aromatic aldehydes and α, β- unsaturated aldehydes absorb near 1705 cm-1. Saturated ketones and cyclohexanones absorb near 1715 cm-1 while aromatic ketones and α, β- unsaturated ketones absorb near 1685-1690 cm-1. Cyclopentanones absorb around 1750 cm-1.
In 1HNMR the aldehyde protons absorb near 10 δ with a coupling constant , J = 3Hz. Hydrogens on the carbon next to aldehyde group absorb near 2.0-2.3 δ. Methyl ketones show a sharp three proton singlet near 2.1 δ.
To purpose:
A structure for ketone or aldehyde with the following descriptions.
C7H14O, IR: 1710 cm-1; 1HNMR: 1.02 δ (Rel.area=4.50), 2.12 δ (Rel.area=1.50), 2.33δ (Rel.area=1.00).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- R₂ R₁ R₁ a R Rg Nu R₂ Rg R₁ R R₁₂ R3 R R Nu enolate forming R₁ R B-Alkylated carbonyl species or amines Cyclic B-Ketoester R₁₁ HOB R R₁B R R₁₂ B-Hydroxy carbonyl R diester R2 R3 R₁ RB OR R₂ 0 aB-Unsaturated carbonyl NaOR Aldol HOR reaction 1) LDA 2) R-X 3) H₂O/H₂O ketone, aldehyde 1) 2°-amine 2) acid chloride 3) H₂O'/H₂O 0 O R₁ R₁ R R₁ R₁₂ Alkylated a-carbon R₁ H.C R₁ H.C Alkylated methyl ketone acetoacetic ester B-Ketoester ester R₁ HO R₂ R B-Dicarbonyl HO Alkylated carboxylic acid malonic ester Write the reagents required to bring about each reaction next to the arrows shown. Next, record any regiochemistry or stereochemistry considerations relevant to the reaction. You should also record any key aspects of the mechanism, such as forma- tion of an important intermediate, as a helpful reminder. You may want to keep track of all reactions that make carbon-carbon bonds, because these help you build large molecules from smaller fragments. This especially applies to the reactions in…arrow_forwardProvide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.arrow_forwardIdentify which compound is more acidic. Justify your choice.arrow_forward
- Provide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.arrow_forwardWhen anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forward
- For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forwardConsider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning



