
Concept explainers
a) Bromoacetone
Interpretation:
The structure for bromoacetone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
To show:
The structure for bromoacetone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of bromoacetone is
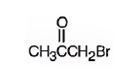
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is a ketone with three carbon straight chain with a bromine atom attached to C1.
The structure of bromoacetone is

b) (S)-2-Hydroxypropanal
Interpretation:
The structure for (S)-2-hydroxypropanal is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
To show:
The structure for (S)-2-hydroxypropanal.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of (S)-2-hydroxypropanal is
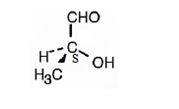
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is an aldehyde with three carbon straight chain with a hydroxyl group attached to C2. The molecule is chiral. The three groups, -OH(first highest priority), -CHO (second highest priority) and -CH3(third highest priority) are arranged anticlockwise when viewed from the side away from H (fourth highest priority). Hence it has S stereochemistry.
The structure of (S)-2-hydroxypropanal is

c) 2-Methyl-3-heptanone
Interpretation:
The structure for 2-methyl-3-heptanone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To show:
The structure for 2-methyl-3-heptanone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of 2-methyl-3-heptanone is
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is a ketone with seven carbon straight chain having the keto group at position three and a methyl group attached to C2.
The structure of 2-methyl-3-heptanone is
d) (2S,3R)-2,3,4-Trihydroxybutanal
Interpretation:
The structure for (2S,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –al. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the -CHO group and the –CHO group is numbered as carbon 1. For cyclic alcohols in which the –CHO group is directly attached to the ring, the suffix –carbaldehyde is used.
To show:
The structure for (2S,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of (2S,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal is
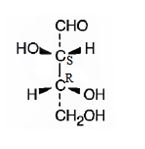
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is an aldehyde with four carbon straight chain and has three hydroxyl groups attached to C2, C3 and C4.
The molecule is chiral. The C2 is attached to the three groups, -OH(first highest priority), -CHO (second highest priority) and –C3 (third highest priority) arranged anticlockwise when viewed from the side away from H (fourth highest priority). Hence it has S stereochemistry.
The C3 is attached to the three groups, -OH(first highest priority), –C2 (second highest priority) and –CH2OH--(third highest priority) arranged clockwise when viewed from the side away from H (fourth highest priority). Hence it has R stereochemistry.
The structure of (2S,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal is

e) 2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-3-pentanone
Interpretation:
The structure for 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-3-pentanone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To show:
The structure for 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-3-pentanone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-3-pentanone is
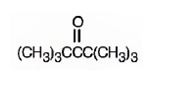
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is a ketone with five carbon straight chain with a keto group at position three attached to four methyl groups, two on C2 and other two on C4.
The structure of 2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-3-pentanone is
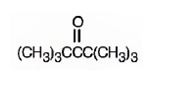
f) 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one
Interpretation:
The structure for 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To show:
The structure for 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one.
Answer to Problem 54AP
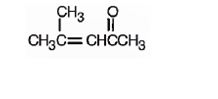
The structure of 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one is
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is a ketone containing a five carbon straight chain, having a keto group at position two and a double bond between C3 and C4 with a methyl group on C4.
The structure of 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one is

g) Butanedial
Interpretation:
The structure for butanedial is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –al. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the -CHO group and the –CHO group is numbered as carbon 1. For cyclic alcohols in which the –CHO group is directly attached to the ring, the suffix –carbaldehyde is used.
To show:
The structure for butanedial.
Answer to Problem 54AP
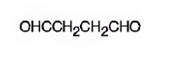
The structure of butanedial is
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound indicates that it has a four carbon straight chain with two aldehyde groups at both ends.
The structure of butanedial is

h) 3-Phenyl-2-propenal
Interpretation:
The structure for 3-phenyl-2-propenal is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –al. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the -CHO group and the –CHO group is numbered as carbon 1. For cyclic alcohols in which the –CHO group is directly attached to the ring, the suffix –carbaldehyde is used.
To show:
The structure for 3-phenyl-2-propenal.
Answer to Problem 54AP
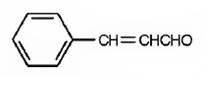
The structure of 3-phenyl-2-propenal is
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound indicates that the compound is a three carbon aldehyde with a double bond between C2 & C3 and has a phenyl group attached to C3.
The structure of 3-phenyl-2-propenal is

i) 6,6-Dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone
Interpretation:
The structure for 6,6-dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To show:
The structure for 6,6-dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of 6,6-dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone is
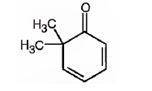
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound indicates that it is a cyclic ketone with a cyclohexadiene ring containing two double bonds, one between C2 & C3 and other between C4 & C5. It also has two methyl groups on C6.
The structure of 6,6-dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone is

j) p-Nitroacetophenone
Interpretation:
The structure for p-nitroacetophenone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo. Some common names like acetophenone are retained by IUPAC.
To show:
The structure for p-nitroacetophenone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of p-nitroacetophenone is
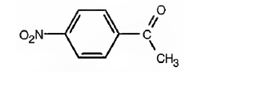
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound indicates that it contains an actyl and nitro groups attached to a benzene ring in para relationship.
The structure of p-nitroacetophenone is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- What would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forward
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


