
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
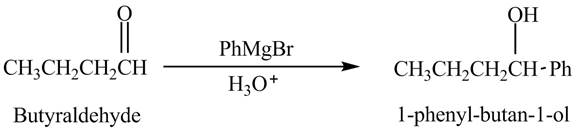
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
The reduction of butyraldehyde takes place to form the product. The reaction is shown below.

Figure 1
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
The gain of electrons involved in the particular reaction is termed as reduction. The reduction process also involves the removal of an electronegative atom from a molecule followed by the hydrogen atom addition into that molecule.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
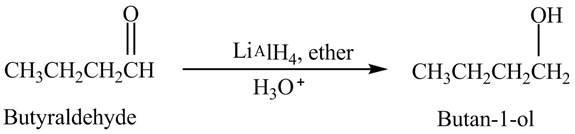
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
The reduction of butyraldehyde takes place to form the product. The reaction is shown below.
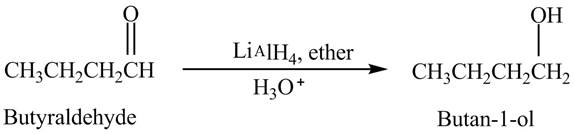
Figure 2
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and alkaline
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
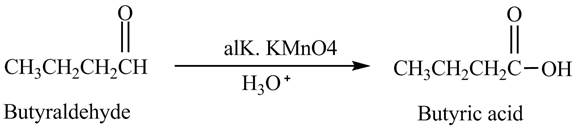
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
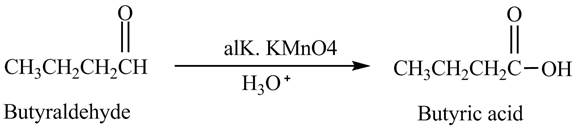
Figure 3
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and alkaline
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
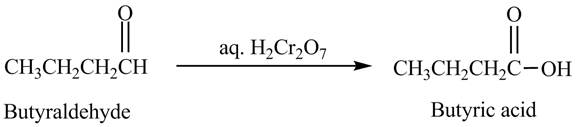
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with aqueous
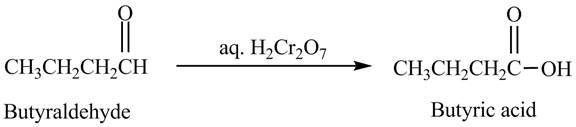
Figure 4
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Oxime belongs to the family of imines. The formula of oxime is
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
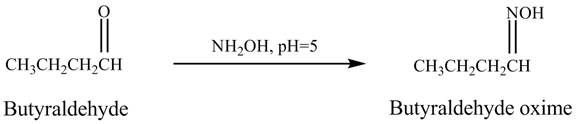
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with ![]() . When the
. When the ![]() is high then the product formed is an
is high then the product formed is an ![]() is low then the product is not formed. The reaction is shown below.
is low then the product is not formed. The reaction is shown below.
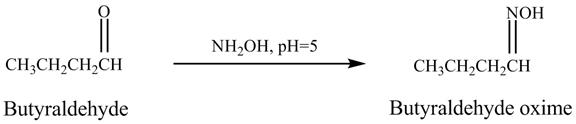
Figure 5
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(f)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
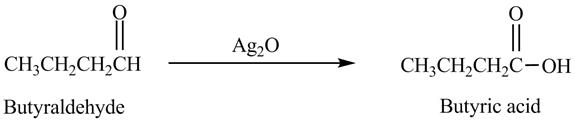
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
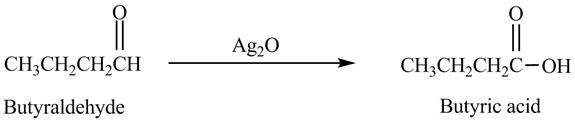
Figure 6
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(g)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
Concept introduction:
Clemmensen reduction is defined as the reduction in which aldehydes or
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
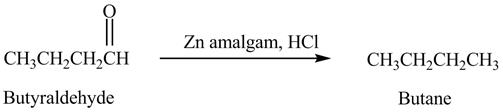
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with zinc amalgam in the presence of

Figure 7
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
(h)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
The Wittig reaction is the
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The geometrical isomers are formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
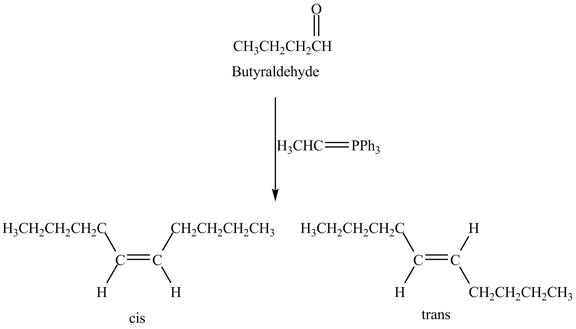
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
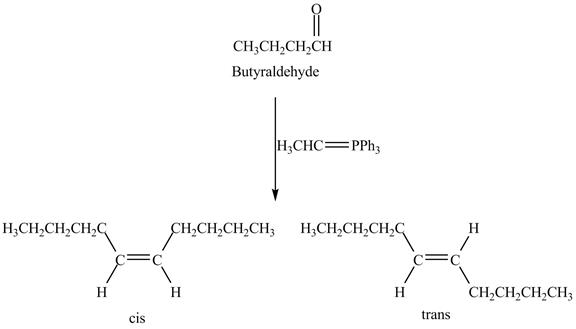
Figure 8
Butyraldehyde reacts with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





