
Statistical quality control. Harvest Cereals produces a wide variety of breakfast products. The company’s three best-selling breakfast cereals are Double Bran Bits, Honey Wheat Squares, and Sugar King Pops. Each box of a particular type of cereal is required to meet predetermined weight specifications, so that no single box contains more or less cereal than another. The company measures the mean weight per production run to determine if there are variances over or under the company’s specified upper- and lower-level control limits. A production run that falls outside of the specified control limit does not meet quality standards and is investigated further by management to determine the cause of the variance. The three Harvest breakfast cereals had the following weight standards and production run data for the month of March:
Quality Standard: Mean Weight per Production Run
| Double Bran Bits | Honey Wheat Squares | Sugar King Pops |
| 17.97 ounces | 14 ounces | 16.02 ounces |
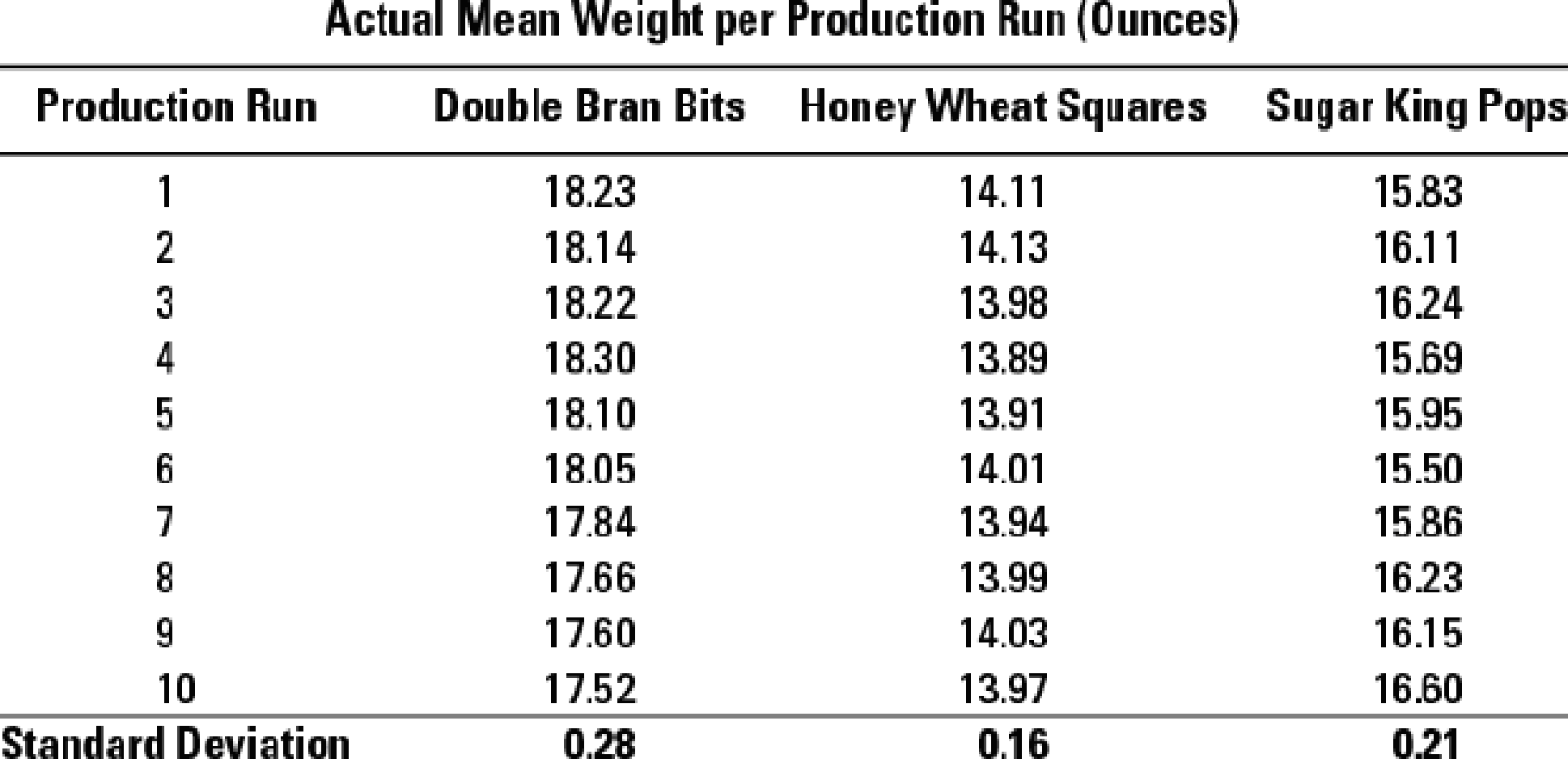
- 1. Using the ±2σ rule, what variance investigation decisions would be made?
- 2. Present control charts for each of the three breakfast cereals for March. What inferences can you draw from the charts?
- 3. What are the costs of quality in this example? How could Harvest employ Six Sigma programs to improve quality?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub



