
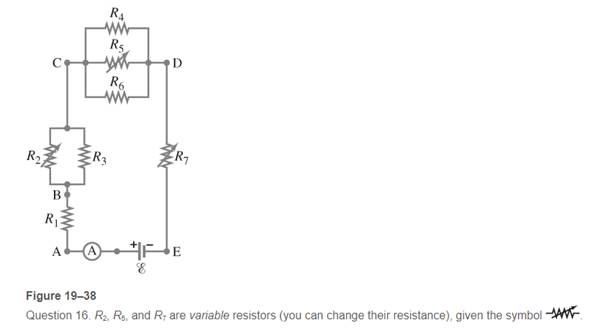
Given the circuit shown in Fig. 19-38,  use the words “increases,” “decreases,”or ”stays the same” to complete the following statements:
use the words “increases,” “decreases,”or ”stays the same” to complete the following statements:
a. If R7increases, the potential difference between A and E____ . Assume no resistancein  and E.
and E.
b. If R7-increases, the potential difference between A and E_____. Assume  and Ehaveresistance.
and Ehaveresistance.
c. If R7 increases, the voltage drop across R4_____
d. If R2 decreases, the current through R1_______
e. If R2 decreases, the current through R6______
f. If R2 decreases, the current through R3_____
g. If R5 increases, the voltage drop across R2________
h. If R5 increases, the voltage drop across R4 _________
I. If R2, R5, and R7 increase, E (r=0)______
(a) To determine:
Whether the potential difference between point A and E increases, decreases or stays the same by increasing the value of resistance and assume there is no resistance between point A and E.
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The potential difference between point A and E increases by increasing the value of resistance if the value of resistance between point A and E is zero.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The circuit diagram of the given situation is shown below:
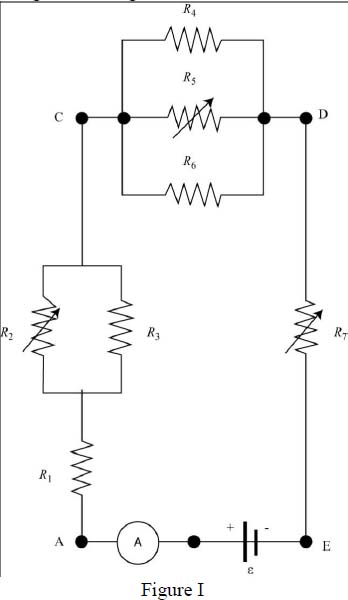
In the given circuit, the resistance is variable, means the magnitude of this resistance can be change. Since the resistance is connected in series with the circuit so, if the value of this resistance increases, the net equivalent resistance in the circuit increases.
From
Formula to calculate the Potential difference between points A and E from Ohm’s law is,
(I)
• is the potential difference between points and .
• is the current flowing in the circuit.
• is the net equivalent resistance in the circuit.
The net equivalent resistance from the circuit is,
Substitute for in equation (I).
From the above equation, if the value of resistance increases the potential difference between the point A and E increases.
(b) To determine:
Whether the potential difference between point A and E increases, decreases or stays the same by increasing the value of resistance and assume the resistance between point A and E have some value.
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The potential difference between point A and E increases by increasing the value of resistance if the point A and E have some resistance.
Explanation of Solution
Suppose the resistance between the point A and E is . This resistance connects in the circuit in series. Now, the net resistance in the circuit becomes .
Formula to calculate the Potential difference between points A and E from Ohm’s law is,
Substitute for .
From the above equation, if the value of resistance is increases the potential difference between the point A and E increases.
(c) To determine:
Whether the voltage drop across resistance increases, decreases or stays the same by increasing the value of resistance.
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The voltage drop across resistance decreases by increasing the value of resistance.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the voltage drop across resistance is,
• is the voltage drop across resistance .
If the magnitude of the resistance is increases, the net resistance in the circuit increase that decreases the magnitude of total current flowing in the circuit. So, decrease in the value of total current the voltage drop across resistance decreases.
(d) To determine:
Whether the current through resistance increases, decreases or stays the same by decreasing the value of resistance.
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The current through resistance increases by decreasing the value of resistance.
Explanation of Solution
In the given circuit, the resistance and are connected in parallel between points B and C. So, if the resistance decreases the equivalent resistance between B and C decreases that further decreases the net equivalent resistance in the circuit.
From the ohm’s law, if the net resistance in the circuit decreases for a given potential difference, the value of current flowing increases. So, the value of current through resistance increases.
(e) To determine:
Whether the current through resistance increases, decreases or stays the same by decreasing the value of resistance.
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The current through resistance increases by decreasing the value of resistance.
Explanation of Solution
In the given circuit, the resistance and are connected in parallel between points B and C. So, if the resistance decreases the equivalent resistance between B and C decreases that further decreases the net equivalent resistance in the circuit.
From the ohm’s law, if the net resistance in the circuit decreases for a given potential difference, the value of current flowing increases. So, the value of current through resistance
increases.
(f) To determine:
Whether the current through resistance increases, decreases or stays the same by decreasing the value of resistance.
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The current through resistance decreases by decreasing the value of resistance.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the potential difference across resistance is,
• is the potential difference across resistance .
• is the current flow through resistance .
Formula to calculate the potential difference across resistance is,
• is the potential difference across resistance .
• is the current flow through resistance .
The resistance and are connected in parallel between points B and C. The current flow will be different in both the resistance but the potential difference across remains same across both resistances.
Substitute for and for .
From the above expression if the value of resistance decreases, the value of current flowing through resistance decreases.
(g)To determine:
Whether the voltage drop across resistance increases, decreases or stays the same by increasing the value of resistance.
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The voltage drop across resistance decreases by increasing the value of resistance.
Explanation of Solution
In the given circuit, the resistance, and are connected in parallel between points C and D. So, if the resistance increases the equivalent resistance between C and D increases that further increases the net equivalent resistance in the circuit.
Formula to calculate the voltage drop across resistance is,
• is the voltage drop across resistance .
Hence, increases in the net equivalent resistance the total value of current decreases so, the voltage drop across resistance decreases.
(h)To determine:
Whether the voltage drop across resistance increases, decreases or stays the same by increasing the value of resistance.
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The voltage drop across resistance increases by increasing the value of resistance.
Explanation of Solution
In the given circuit, the resistance
, and are connected in parallel between points C and D. So, if the resistance increases the equivalent resistance between C and D increases that further increases the net equivalent resistance in the circuit.
Formula to calculate the voltage drop across resistance is,
• is the voltage drop across resistance .
Formula to calculate the potential difference across resistance is,
• is the potential difference across resistance .
• is the current flow through resistance .
The resistance, and are connected in parallel between points C and D. The current flow will be different in all the resistance but the potential difference across remains same across both resistances.
Substitute for and for .
From the above expression if the value of resistance increase, the value of current flows through resistance increase. So, the potential difference across the resistance increases.
(i) To determine:
Whether the emf of the battery increases, decreases or stays the same by increasing the value of resistances, and .
Answer to Problem 17Q
Solution:
The emf of the battery stays the same by increasing the value of resistances, and .
Explanation of Solution
In the given circuit, the resistance if the value of , and are increases. The net equivalent resistance equivalent resistance in the circuit increases. But the emf of the battery is depend upon the potential difference across battery and the internal resistance of the battery.
Formula to calculate the emf of the battery is,
• is the emf of the battery.
• is the internal resistance.
Substitute for .
The potential difference across the battery remains constant whatever the resistance of the circuit. So, the emf of the battery remains constant.
Chapter 19 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





