
Concept explainers
Calculate z and y parameters for the two-port network in Figure 19.78 in the textbook.
Answer to Problem 17P
The z and y parameters for the given two-port network are
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
Refer to Figure 19.78 in the textbook for the given two-port network.
Formula used:
Write the expressions for impedance parameters of a two-port network as follows:
Refer to the TABLE 19.1 in the textbook and write the expression for admittance parameters in terms of z parameters as follows:
Write the expression for
Calculation:
The impedance parameters
Draw the given circuit as shown in Figure 1 to obtain the parameters
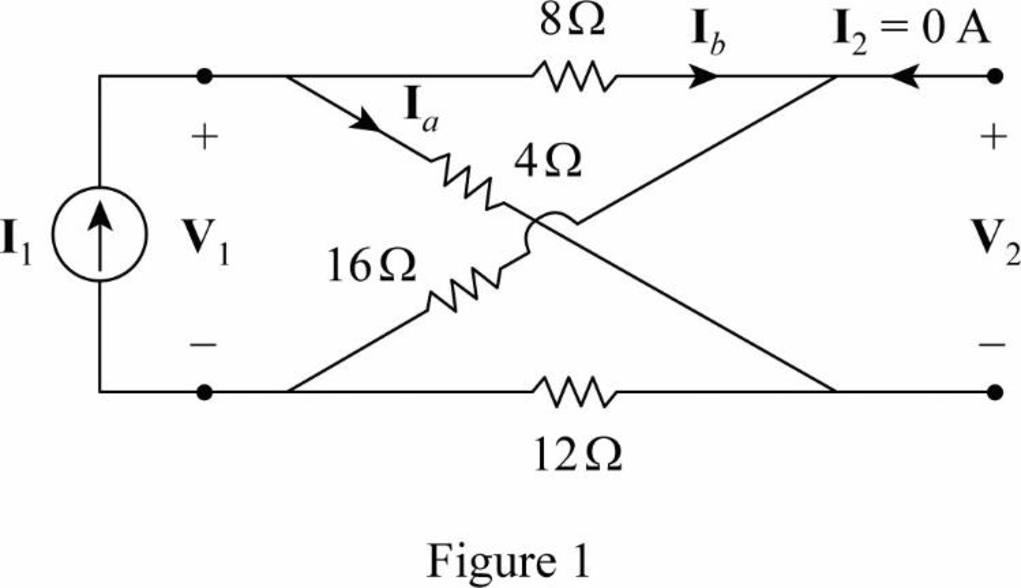
In Figure 1,
From Equation (5),
From Figure 1, write the expression for
From Figure 1, write the expression for
From Figure 1, write the expression for
Substitute
Rearrange the expression as follows:
Substitute
The impedance parameters
Draw the given circuit as shown in Figure 2 to obtain the parameters
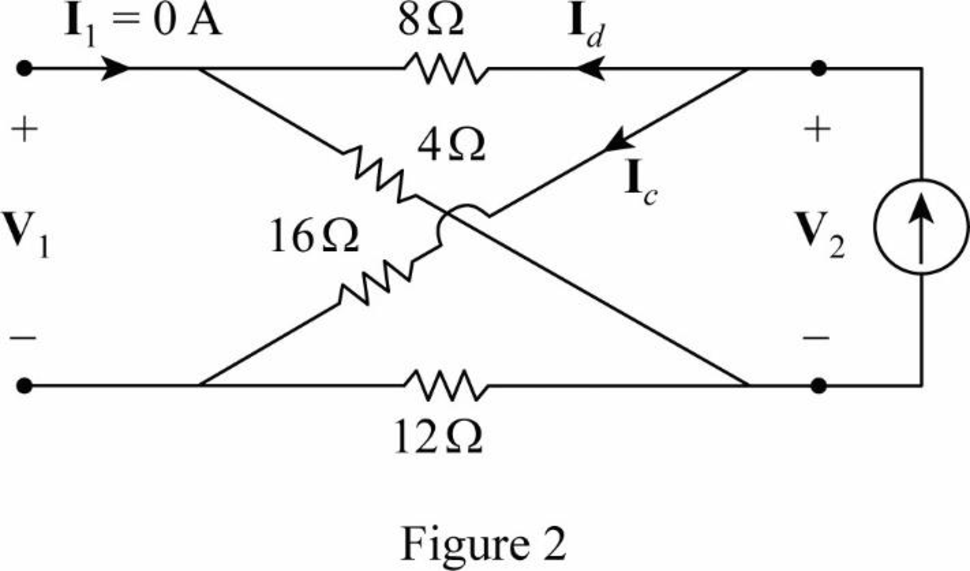
In Figure 2,
From Equation (8),
From Figure 2, write the expression for
From Figure 2, write the expression for
From Figure 2, write the expression for
Substitute
Rearrange the expression as follows:
Substitute
From the analysis, the impedance parameters for the given two-port network are written as follows:
Convert the obtained z parameters into admittance parameters to obtain the admittance parameters for the given two-port network.
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the z and y parameters for the given two-port network are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
- Can you rewrite the solution because it is unclear? AM (+) = 8(1+0.5 cos 1000kt +0.5 ros 2000 thts) = cos 10000 πt. 8 cos wat + 4 cos wit + 4 cos Wat coswet. J4000 t j11000rt $14+) = 45 jqooort +4e + e + e j 12000rt. 12000 kt + e +e +e Le jsoort -; goon t te +e Dcw> = 885(W- 100007) + 8 IS (W-10000) - USBarrow_forwardCan you rewrite the solution because it is unclear? Q2 AM ①(+) = 8 (1+0.5 cos 1000πt +0.5 ros 2000kt) $4+) = 45 = *cos 10000 πt. 8 cos wat + 4 cosat + 4 cos Wat coswet. j1000016 +4e -j10000πt j11000Rt j gooort -j 9000 πt + e +e j sooort te +e J11000 t + e te j 12000rt. -J12000 kt + с = 8th S(W- 100007) + 8 IS (W-10000) <&(w) = USB -5-5 -4-5-4 b) Pc 2² = 64 PSB = 42 + 4 2 Pt Pc+ PSB = y = Pe c) Puss = PLSB = = 32 4² = 8 w 32+ 8 = × 100% = 140 (1)³×2×2 31 = 20% x 2 = 3w 302 USB 4.5 5 5.6 6 ms Ac = 4 mi = 0.5 mz Ac = 4 ५ M2 = =0.5arrow_forwardA. Draw the waveform for the following binary sequence using Bipolar RZ, Bipolar NRZ, and Manchester code. Data sequence= (00110100) B. In a binary PCM system, the output signal-to-quantization ratio is to be hold to a minimum of 50 dB. If the message is a single tone with fm-5 kHz. Determine: 1) The number of required levels, and the corresponding output signal-to-quantizing noise ratio. 2) Minimum required system bandwidth.arrow_forward
- Find Io using Mesh analysisarrow_forwardFM station of 100 MHz carrier frequency modulated by a 20 kHz sinusoid with an amplitude of 10 volt, so that the peak frequency deviation is 25 kHz determine: 1) The BW of the FM signal. 2) The approximated BW if the modulating signal amplitude is increased to 50 volt. 3) The approximated BW if the modulating signal frequency is increased by 70%. 4) The amplitude of the modulating signal if the BW is 65 kHz.arrow_forwardAn FDM is used to multiplex two groups of signals using AM-SSB, the first group contains 25 speech signals, each has maximum frequency of 4 kHz, the second group contains 15 music signals, each has maximum frequency of 10 kHz. A guard bandwidth of 500 Hz is used bety each two signals and before the first one. 1. Find the BWmultiplexing 2. Find the BWtransmission if the multiplexing signal is modulated using AM-DSB-LC.arrow_forward
- An FM signal with 75 kHz deviation, has an input signal-to-noise ratio of 18 dB, with a modulating frequency of 15 kHz. 1) Find SNRO at demodulator o/p. 2) Find SNRO at demodulator o/p if AM is used with m=0.3. 3) Compare the performance in case 1) and 2).. Hint: for single tone AM-DSB-LC, SNR₁ = (2m²) (4)arrow_forwardFind Va and Vb using Nodal analysisarrow_forwardCalculate the nodal voltage in the circuitarrow_forward
- Calculate the mesh currents, find Ia, Ib, Ic. Apply mesh analysisarrow_forwardFind Va and Vb using Nodal analysisarrow_forward4. A battery operated sensor transmits to a receiver that is plugged in to a power outlet. The device is continuously operated. The battery is a 3.6 V coin-cell battery with a 245mAHr capacity. The application requires a bit rate of 36 Mbps and an error rate of less than 10^-3. The channel has a center frequency of 2.4 GHz, a bandwidth of 10 MHz and a noise power spectral density of 10^-14 W/Hz. The maximum distance is 36 meters and the losses in the channel attenuates the signal by 0.25 dB/meter. Your company has two families of chips that you can use. An M-ary ASK and an M-ary QAM chip. The have very different power requirements as shown in the table below. The total current for the system is the current required to achieve the desired Eb/No PLUS the current identified below: Hokies PSK Chip Set Operating Current NOT Including the required Eb/No for the application Hokies QAM Chip Set Operating Current NOT Including the required Eb/No for the application Chip ID M-ary Voltage (volts)…arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





