
The charactimage of the image for object 1 and object 2.
Answer to Problem 28SSC
The image formed by both object 1 and object 2 is a reduced, upright and virtual image.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given ray diagram is shown below.
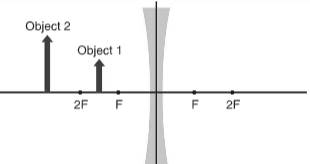
Concave lens is thin at the centre and thick at the edges. This surface of the lens curve inwards. The concave diverge the light rays falling on it.
Consider the givne ray diagram. The focus of the concave lens is denoted by F.The object 1 is placed between F and 2F.The object 2 is placed between the lens and F.The image formed by concave lens is always virtual, erect and diminished image regardless of how far the object is placed from the lens.Hence, the image formed by both object 1 and object 2 is a reduced, upright and virtual image.
Conclusion:
Thus, the image formed by both object 1 and object 2 is a reduced, upright and virtual image.
Chapter 18 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- What is the resistance (in (2) of a 27.5 m long piece of 17 gauge copper wire having a 1.150 mm diameter? 0.445 ΧΩarrow_forwardFind the ratio of the diameter of silver to iron wire, if they have the same resistance per unit length (as they might in household wiring). d. Ag dFe = 2.47 ×arrow_forwardFind the ratio of the diameter of silver to iron wire, if they have the same resistance per unit length (as they might in household wiring). d Ag = 2.51 dFe ×arrow_forward
- Show that the units 1 v2/Q = 1 W, as implied by the equation P = V²/R. Starting with the equation P = V²/R, we can get an expression for a watt in terms of voltage and resistance. The units for voltage, V, are equivalent to [? v2 v2 A, are equivalent to J/C ✓ X . Therefore, 1 = 1 = 1 A V1 J/s Ω V-A X = 1 W. . The units for resistance, Q, are equivalent to ? The units for current,arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





