
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781259633133
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 18.2, Problem 18.84P
The essential structure of a certain type of aircraft turn indicator is shown. Each spring has a constant of 500 N/m, and the 200-g uniform disk of 40-mm radius spins at the rate of 10 000 rpm. The springs are stretched and exert equal vertical forces on yoke AB when the airplane is traveling in a straight path. Determine the angle through which the yoke will rotate when the pilot executes a horizontal turn of 750-m radius to the right at a speed of 800 km/h. Indicate whether point A will move up or down.
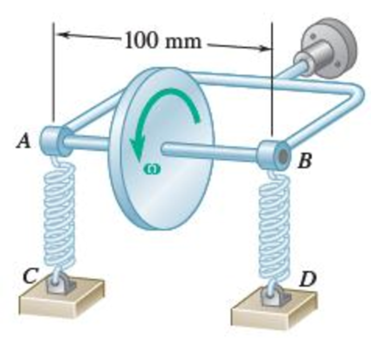
Fig. P18.84
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An AISI 1018 steel ball with 1.100-in diameter is used as a roller between a flat plate
made from 2024 T3 aluminum and a flat table surface made from ASTM No. 30 gray
cast iron. Determine the maximum amount of weight that can be stacked on the
aluminum plate without exceeding a maximum shear stress of 19.00 kpsi in any of the
three pieces. Assume the figure given below, which is based on a typical Poisson's
ratio of 0.3, is applicable to estimate the depth at which the maximum shear stress
occurs for these materials.
1.0
0.8
Ratio of stress to Pmax
0.4
90
0.6
στ
Tmax
0.2
0.5a
a
1.5a
2a
2.5a
За
Distance from contact surface
The maximum amount of weight that can be stacked on the aluminum plate is
lbf.
A carbon steel ball with 27.00-mm diameter is pressed together with an aluminum ball
with a 36.00-mm diameter by a force of 11.00 N. Determine the maximum shear
stress and the depth at which it will occur for the aluminum ball. Assume the figure
given below, which is based on a typical Poisson's ratio of 0.3, is applicable to estimate
the depth at which the maximum shear stress occurs for these materials.
1.0
0.8
Ratio of stress to Pma
9 0.6
στ
24
0.4
Tmax
0.2
0
0.5a
a
1.5a
Z
2a
2.5a
За
Distance from contact surface
The maximum shear stress is determined to be
MPa.
The depth in the aluminum ball at which the maximum shear stress will occur is
determined to be [
mm.
Show all work please
Chapter 18 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Ch. 18.1 - A thin, homogeneous disk of mass m and radius r...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.2PCh. 18.1 - 18.3 Two uniform rods AB and CE, each of weight 3...Ch. 18.1 - A homogeneous disk of weight W = 6 lb rotates at...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.5PCh. 18.1 - A solid rectangular parallelepiped of mass m has a...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.8PCh. 18.1 - Determine the angular momentum HD of the disk of...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.10PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.11P
Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.12PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.13PCh. 18.1 - Two L-shaped arms each have a mass of 5 kg and are...Ch. 18.1 - For the assembly of Prob. 18.15, determine (a) the...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.17PCh. 18.1 - Determine the angular momentum of the shaft of...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.20PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.21PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.22PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.23PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.24PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.25PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.26PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.27PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.28PCh. 18.1 - A circular plate of mass m is falling with a...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.30PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.31PCh. 18.1 - Determine the impulse exerted on the plate of...Ch. 18.1 - The coordinate axes shown represent the principal...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.34PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.37PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.38PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.39PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.40PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.41PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.42PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.43PCh. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the solid...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.45PCh. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the disk of Prob....Ch. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the assembly of...Ch. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the shaft of Prob....Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.49PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.50PCh. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy lost when edge C of...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.52PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.53PCh. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the space probe of...Ch. 18.2 - Determine the rate of change HG of the angular...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.56PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.57PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.58PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.59PCh. 18.2 - Determine the rate of change HG of the angular...Ch. 18.2 - 18.61 Determine the rate of change of the angular...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.62PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.63PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.64PCh. 18.2 - A slender, uniform rod AB of mass m and a vertical...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.66PCh. 18.2 - The assembly shown consists of pieces of sheet...Ch. 18.2 - The 8-kg shaft shown has a uniform cross-section....Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.69PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.70PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.71PCh. 18.2 - Knowing that the plate of Prob. 18.66 is initially...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.73PCh. 18.2 - The shaft of Prob. 18.68 is initially at rest ( =...Ch. 18.2 - The assembly shown weighs 12 lb and consists of 4...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.76PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.79PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.80PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.81PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.82PCh. 18.2 - The uniform, thin 5-lb disk spins at a constant...Ch. 18.2 - The essential structure of a certain type of...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.85PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.86PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.87PCh. 18.2 - The 2-lb gear A is constrained to roll on the...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.89PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.90PCh. 18.2 - 18.90 and 18.91The slender rod AB is attached by a...Ch. 18.2 - The essential structure of a certain type of...Ch. 18.2 - The 10-oz disk shown spins at the rate 1 = 750...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.94PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.95PCh. 18.2 - Two disks each have a mass of 5 kg and a radius of...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.97PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.98PCh. 18.2 - A thin disk of mass m = 4 kg rotates with an...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.101PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.102PCh. 18.2 - A 2.5-kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates...Ch. 18.2 - A 2.5-kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates...Ch. 18.2 - For the disk of Prob. 18.99, determine (a) the...Ch. 18.3 - A uniform thin disk with a 6-in. diameter is...Ch. 18.3 - A uniform thin disk with a 6-in. diameter is...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.109PCh. 18.3 - The top shown is supported at the fixed point O...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.111PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.112PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.113PCh. 18.3 - A homogeneous cone with a height of h = 12 in. and...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.115PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.116PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.117PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.118PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.119PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.120PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.121PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.122PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.123PCh. 18.3 - A coin is tossed into the air. It is observed to...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.125PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.126PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.127PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.128PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.129PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.130PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.131PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.132PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.133PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.134PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.135PCh. 18.3 - A homogeneous disk with a radius of 9 in. is...Ch. 18.3 - The top shown is supported at the fixed point O....Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.138PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.139PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.140PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.141PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.142PCh. 18.3 - Consider a rigid body of arbitrary shape that is...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.144PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.145PCh. 18 - Three 25-lb rotor disks are attached to a shaft...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.148RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.149RPCh. 18 - A uniform rod of mass m and length 5a is bent into...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.151RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.152RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.153RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.154RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.155RPCh. 18 - The space capsule has no angular velocity when the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.157RPCh. 18 - The essential features of the gyrocompass are...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw top, side, front view With pen(cil) and paper Multi view drawing and handwriting all of itarrow_forwardA wheel of diameter 150.0 mm and width 37.00 mm carrying a load 2.200 kN rolls on a flat rail. Take the wheel material as steel and the rail material as cast iron. Assume the figure given, which is based on a Poisson's ratio of 0.3, is applicable to estimate the depth at which the maximum shear stress occurs for these materials. At this critical depth, calculate the Hertzian stresses σr, σy, σz, and Tmax for the wheel. 1.0 0.8 0, т Ratio of stress to Pmax 0.4 0.6 90 69 0.2 0.5b b 1.5b Tmax 2b Distance from contact surface The Hertizian stresses are as follows: 02 = or = -23.8 psi for the wheel =| necessary.) σy for the wheel =| MPa σz for the wheel = MPa V4 for the wheel = | MPa 2.5b ཡི 3b MPa (Include a minus sign ifarrow_forwardOnly question 3arrow_forward
- In cold isostatic pressing, the mold is most typically made of which one of the following: thermosetting polymer tool steel sheet metal textile rubberarrow_forwardThe coefficient of friction between the part and the tool in cold working tends to be: lower higher no different relative to its value in hot workingarrow_forwardThe force F={25i−45j+15k}F={25i−45j+15k} lblb acts at the end A of the pipe assembly shown in (Figure 1). Determine the magnitude of the component F1 which acts along the member AB. Determine the magnitude of the component F2 which acts perpendicular to the AB.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mod-01 Lec-16 Basics of Instrumentation; Author: nptelhrd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qbKnW42ZM5c;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY