
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781259633133
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 18.150RP
A uniform rod of mass m and length 5a is bent into the shape shown and is suspended from a wire attached at point B. Knowing that the rod is hit at point A in the negative y direction and denoting the corresponding impulse by −(F Δt)j, determine immediately after the impact (a) the velocity of the mass center G, (b) the angular velocity of the rod.
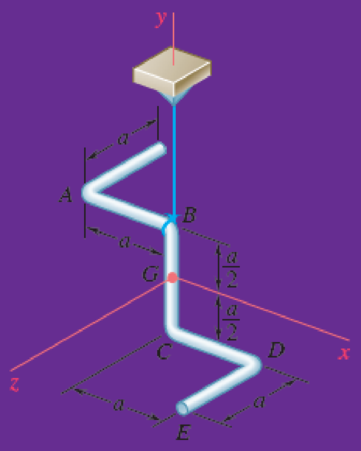
Fig. P18.150
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy = 16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try = 11.00 kpsi,
Tyz = 8.000 kpsi, and T = -14.00 kpsi.
Determine the principal stresses.
The principal normal stress σ₁ is determined to be [
The principal normal stress σ2 is determined to be [
The principal normal stress σ3 is determined to be
kpsi.
kpsi.
The principal shear stress 71/2 is determined to be [
The principal shear stress 7½ is determined to be [
The principal shear stress T₁/, is determined to be [
kpsi.
kpsi.
kpsi.
kpsi.
Repeat Problem 28, except using a shaft that is rotatingand transmitting a torque of 150 N * m from the left bearing to the middle of the shaft. Also, there is a profile keyseat at the middle under the load.
(I want to understand this problem)
Prob 2.
The material distorts into the dashed position
shown. Determine the average normal strains &x, Ey
and the shear strain Yxy at A, and the average
normal strain along line BE.
50 mm
B
200 mm
15 mm
30 mm
D
ΕΙ
50 mm
x
A
150 mm
F
Chapter 18 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Ch. 18.1 - A thin, homogeneous disk of mass m and radius r...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.2PCh. 18.1 - 18.3 Two uniform rods AB and CE, each of weight 3...Ch. 18.1 - A homogeneous disk of weight W = 6 lb rotates at...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.5PCh. 18.1 - A solid rectangular parallelepiped of mass m has a...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.8PCh. 18.1 - Determine the angular momentum HD of the disk of...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.10PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.11P
Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.12PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.13PCh. 18.1 - Two L-shaped arms each have a mass of 5 kg and are...Ch. 18.1 - For the assembly of Prob. 18.15, determine (a) the...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.17PCh. 18.1 - Determine the angular momentum of the shaft of...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.20PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.21PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.22PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.23PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.24PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.25PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.26PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.27PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.28PCh. 18.1 - A circular plate of mass m is falling with a...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.30PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.31PCh. 18.1 - Determine the impulse exerted on the plate of...Ch. 18.1 - The coordinate axes shown represent the principal...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.34PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.37PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.38PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.39PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.40PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.41PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.42PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.43PCh. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the solid...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.45PCh. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the disk of Prob....Ch. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the assembly of...Ch. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the shaft of Prob....Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.49PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.50PCh. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy lost when edge C of...Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.52PCh. 18.1 - Prob. 18.53PCh. 18.1 - Determine the kinetic energy of the space probe of...Ch. 18.2 - Determine the rate of change HG of the angular...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.56PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.57PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.58PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.59PCh. 18.2 - Determine the rate of change HG of the angular...Ch. 18.2 - 18.61 Determine the rate of change of the angular...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.62PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.63PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.64PCh. 18.2 - A slender, uniform rod AB of mass m and a vertical...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.66PCh. 18.2 - The assembly shown consists of pieces of sheet...Ch. 18.2 - The 8-kg shaft shown has a uniform cross-section....Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.69PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.70PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.71PCh. 18.2 - Knowing that the plate of Prob. 18.66 is initially...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.73PCh. 18.2 - The shaft of Prob. 18.68 is initially at rest ( =...Ch. 18.2 - The assembly shown weighs 12 lb and consists of 4...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.76PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.79PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.80PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.81PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.82PCh. 18.2 - The uniform, thin 5-lb disk spins at a constant...Ch. 18.2 - The essential structure of a certain type of...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.85PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.86PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.87PCh. 18.2 - The 2-lb gear A is constrained to roll on the...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.89PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.90PCh. 18.2 - 18.90 and 18.91The slender rod AB is attached by a...Ch. 18.2 - The essential structure of a certain type of...Ch. 18.2 - The 10-oz disk shown spins at the rate 1 = 750...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.94PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.95PCh. 18.2 - Two disks each have a mass of 5 kg and a radius of...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.97PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.98PCh. 18.2 - A thin disk of mass m = 4 kg rotates with an...Ch. 18.2 - Prob. 18.101PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.102PCh. 18.2 - A 2.5-kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates...Ch. 18.2 - A 2.5-kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates...Ch. 18.2 - For the disk of Prob. 18.99, determine (a) the...Ch. 18.3 - A uniform thin disk with a 6-in. diameter is...Ch. 18.3 - A uniform thin disk with a 6-in. diameter is...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.109PCh. 18.3 - The top shown is supported at the fixed point O...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.111PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.112PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.113PCh. 18.3 - A homogeneous cone with a height of h = 12 in. and...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.115PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.116PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.117PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.118PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.119PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.120PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.121PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.122PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.123PCh. 18.3 - A coin is tossed into the air. It is observed to...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.125PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.126PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.127PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.128PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.129PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.130PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.131PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.132PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.133PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.134PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.135PCh. 18.3 - A homogeneous disk with a radius of 9 in. is...Ch. 18.3 - The top shown is supported at the fixed point O....Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.138PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.139PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.140PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.141PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.142PCh. 18.3 - Consider a rigid body of arbitrary shape that is...Ch. 18.3 - Prob. 18.144PCh. 18.3 - Prob. 18.145PCh. 18 - Three 25-lb rotor disks are attached to a shaft...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.148RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.149RPCh. 18 - A uniform rod of mass m and length 5a is bent into...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.151RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.152RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.153RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.154RPCh. 18 - Prob. 18.155RPCh. 18 - The space capsule has no angular velocity when the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.157RPCh. 18 - The essential features of the gyrocompass are...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Prob 3. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the shear strain, Yxy, at A. Prob 4. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain & along the x axis. Prob 5. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain &x along the x' axis. x' 45° 800 mm 45° 45% 800 mm 5 mmarrow_forwardAn airplane lands on the straight runaway, originally travelling at 110 ft/s when s = 0. If it is subjected to the decelerations shown, determine the time t' needed to stop the plane and construct the s -t graph for the motion. draw a graph and show all work step by steparrow_forwarddny dn-1y dn-1u dn-24 +a1 + + Any = bi +b₂- + +bnu. dtn dtn-1 dtn-1 dtn-2 a) Let be a root of the characteristic equation 1 sn+a1sn- + +an = : 0. Show that if u(t) = 0, the differential equation has the solution y(t) = e\t. b) Let к be a zero of the polynomial b(s) = b₁s-1+b2sn−2+ Show that if the input is u(t) equation that is identically zero. = .. +bn. ekt, then there is a solution to the differentialarrow_forward
- B 60 ft WAB AB 30% : The crane's telescopic boom rotates with the angular velocity w = 0.06 rad/s and angular acceleration a = 0.07 rad/s². At the same instant, the boom is extending with a constant speed of 0.8 ft/s, measured relative to the boom. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point B at this instant.arrow_forwardThe motion of peg P is constrained by the lemniscate curved slot in OB and by the slotted arm OA. (Figure 1) If OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant angular velocity of 0 = 3 rad/s, determine the magnitude of the velocity of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0 (4 cos 2 0)m² B Aarrow_forward5: The structure shown was designed to support a30-kN load. It consists of a boom AB with a 30 x 50-mmrectangular cross section and a rod BC with a 20-mm-diametercircular cross section. The boom and the rod are connected bya pin at B and are supported by pins and brackets at A and C,respectively.1. Calculate the normal stress in boom AB and rod BC,indicate if in tension or compression.2. Calculate the shear stress of pins at A, B and C.3. Calculate the bearing stresses at A in member AB,and in the bracket.arrow_forward
- 4: The boom AC is a 4-in. square steel tube with a wallthickness of 0.25 in. The boom is supported by the 0.5-in.-diameter pinat A, and the 0.375-in.-diameter cable BC. The working stresses are 25ksi for the cable, 18 ksi for the boom, and 13.6 ksi for shear in the pin.Neglect the weight of the boom.1. Calculate the maximum value of P (kips) based on boom compression and the maximum value of P (kips) based on tension in the cable.2. Calculate the maximum value of P (kips) based on shear in pin.arrow_forward3: A steel strut S serving as a brace for a boat hoist transmits a compressive force P = 54 kN to the deck of a pier as shown in Fig. STR-08. The strut has a hollow square cross section with a wall thickness t =12mm and the angle θ between the strut and the horizontal is 40°. A pin through the strut transmits the compressive force from the strut to two gusset plates G that are welded to the base plate B. Four anchor bolts fasten the base plate to the deck. The diameter of the pin is 20mm, the thickness of the gusset plates is 16mm, the thickness of the base plate is 8mm, and the diameter of the anchor bolts is 12mm. Disregard any friction between the base plate and the deck.1. Determine the shear stress in the pin, in MPa and the shear stress in the anchor bolts, in MPa.2. Determine the bearing stress in the strut holes, in MPa.arrow_forward1. In the figure, the beam, W410x67, with 9 mm web thicknesssubjects the girder, W530x109 with 12 mm web thickness to a shear load,P (kN). 2L – 90 mm × 90 mm × 6 mm with bolts frame the beam to thegirder.Given: S1 = S2 = S5 = 40 mm; S3 = 75 mm; S4 = 110 mmAllowable Stresses are as follows:Bolt shear stress, Fv = 125 MPaBolt bearing stress, Fp = 510 MPa1. Determine the allowable load, P (kN), based on the shearcapacity of the 4 – 25 mm diameter bolts (4 – d1) and calculate the allowable load, P (kN), based on bolt bearing stress on the web of the beam.2. If P = 450 kN, determine the minimum diameter (mm) of 4 – d1based on allowable bolt shear stress and bearing stress of thebeam web.arrow_forward
- 6: The 6-kN load P is supported by two wooden members of 75 x 125-mm uniform cross section that are joined by the simple glued scarf splice shown.1. Calculate the normal stress in the glue, in MPa.2. Calculate the shear stress in the glue, in MPa.arrow_forwardUsing Matlab calculate the following performance characteristics for a Tesla Model S undergoing the 4506 drive cycle test Prated Trated Ebat 80kW 254 Nm 85kWh/1645kg MUEH A rwheel 0.315M 133.3 C 0.491 Ng ng 7g 8.190.315 8.19 0.315 7ed= 85% Ebpt 35-956 DRIVE AXLE Ebfb chę =85% V Minverter H/A Battery Charger En AC Pry 9) required energy output from the motor to drive this cycle Cassume no regenerative braking) b) range of the Tesla Model S for this drive cycle (assume no regenerative breaking c) estimated mpge cycle of the Tesla Model S for this drive Cassume no regenerative breaking) d) Recalculate parts abc now assuming you can regenerate returns correctly due to inefficiency. from braking. Be careful to handle the diminishing energy braking makes in terms of required e) Quantify the percentage difference that regenerative required energy, range and mpge, DI L Ta a ra OLarrow_forwardHW.5.1 Determine the vertical displacement of joint C on the truss as shown by using Castigliano's theorem. Let E = 200(109) GPa and A = 300 mm² 4 m E 20 kN 3 m 3 m B D 30 kN Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Differences between Temporary Joining and Permanent Joining.; Author: Academic Gain Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTr8QZhgXyg;License: Standard Youtube License