
(a)
Interpretation:
The ammonium salt produced by the reaction between HCl and coniine alkaloid should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkaloids are natural organic compounds present in plants. They are
Amines have basic properties, meaning they can act as proton acceptors.
Because of the basicity, amines react with acids such as HCl to form water-soluble ammonium salts. Below shown is the general reaction between a primary amine and HCl.
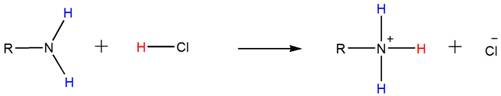
Accordingly, both the secondary and tertiary amines also form their respective ammonium salts with HCl.
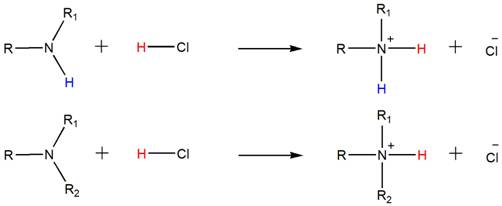
(b)
Interpretation:
The ammonium salt produced by the reaction between HCl and morphine alkaloid should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkaloids are natural organic compounds present in plants. They are amines.
Amines have basic properties, meaning they can act as proton acceptors.
Because of the basicity, amines react with acids such as HCl to form water-soluble ammonium salts. Below shown is the general reaction between a primary amine and HCl.
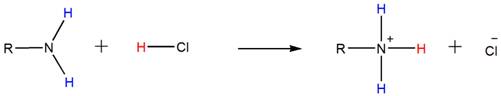
Accordingly, both the secondary and tertiary amines also form their respective ammonium salts with HCl.
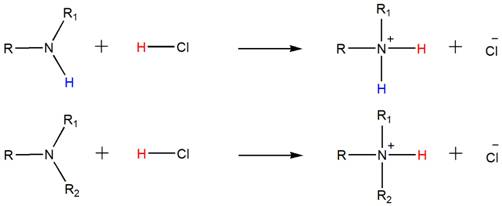
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- Please predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. cold KMnO4, NaOH 2. DMS 1. 03 CH3OH Br2 1. 03 2. (CH3)2S H₂ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 18 19 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) H₂O H₂SO4 HCI HI 17 16 6 15 MCPBA 1. BH3 THF 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. OsO4 2. H₂O₂ 110 CH3CO₂H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* Br2 H₂O BH3 THF B12 EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) Bra A B C D H OH H OH OH H OH α α α OH H OH OH фон d H "Harrow_forwardBriefly indicate the models that describe the structure of the interface: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, Stern and Grahame models.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. Briefly describe the Gibbs model and the Gibbs absorption equation.arrow_forward
- Briefly state the electrocapillary equation for ideally polarized electrodes.arrow_forwardWhat is surface excess according to the Gibbs model?arrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forward
- The molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



