
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of propanal with the given reagents has to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride are strong reducing agents. They are inorganic compounds which are used as the reducing agents in
In the reaction of
By catalytic hydrogenation, aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols. Grignard reagents react with ketones and aldehydes to form alcohols. These reactions are nucleophilic addition reactions. The Grignard reagent adds to the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen.
An organolithium reagent acts like a good nucleophiles and strong bases. They used for the conversion of aldehydes and ketones into primary and secondary alcohols. Acetal is an organic compound with general formula
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
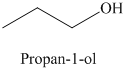
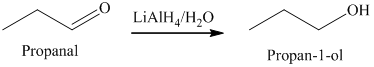
a) The product of the reaction of propanal with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water is shown below.
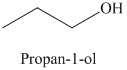
b) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium borohydride, methanol is shown below.
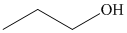
c) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydrogen (nickel catalyst) is shown below.
d) The product of the reaction of propanal with methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
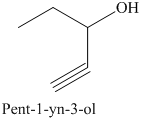
e) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
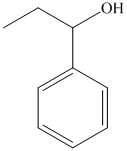
f) The product of the reaction of propanal with phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
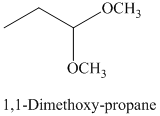
g) The product of the reaction of propanal with methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride is shown below.
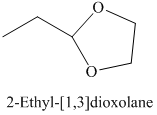
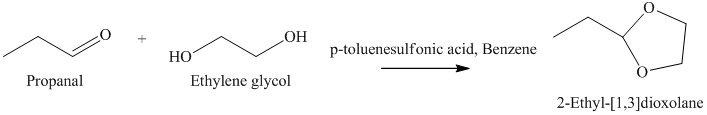
h) The product of the reaction of propanal with ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene is shown below.
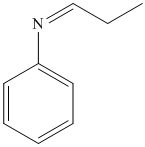
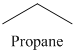
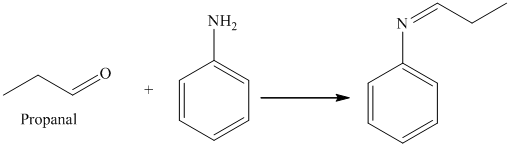
i) The product of the reaction of propanal with aniline
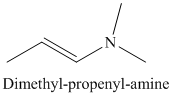
j) The product of the reaction of propanal with dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene is shown below.
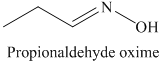
k) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydroxylamine is shown below.
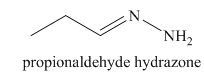
l) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydrazine is shown below.
m) The product of the reaction of propanal with product of part (l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide is shown below.
n) The product of the reaction of propanal with p-Nitrophenylhydrazine is shown below.
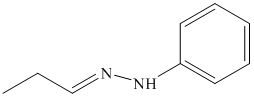
o) The product of the reaction of propanal with semicarbazide is shown below.
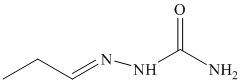
p) The product of the reaction of propanal with ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane is shown below.
q) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid is shown below.
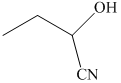
r) The product of the reaction of propanal with chromic acid is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
a) The product obtained by the reaction between, propanal and the reagent, lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water.
The reaction of propanal with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water gives primary alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
b) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, sodium borohydride, methanol.
The reaction of propanal with sodium borohydride, followed by methanol gives primary alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
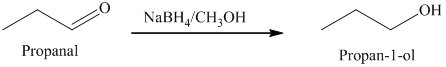
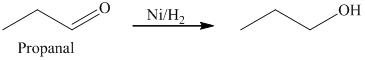
c) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydrogen (nickel catalyst).
The reaction of propanal with hydrogen in the presence of nickel catalyst gives
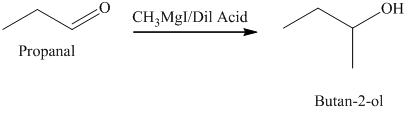
d) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of propanal with methylmagnesium iodide that is Grignard reagent, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
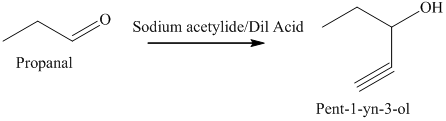
e) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of aldehyde with sodium acetylide is fundamentally similar to the Grignard reaction. The reaction of propanal with sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
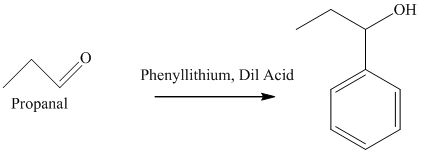
f) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of propanal with phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
g) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride.
The reaction of aldehydes with two equivalents of an alcohol results in the formation of acetals. The product of this reaction is shown below.
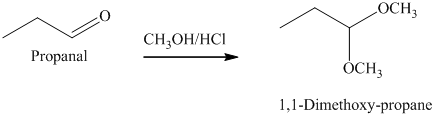
h) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, Ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene.
In the reaction of aldehyde with ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzene, the protection of the carbonyl group of aldehyde takes place. For carbonyl protection, ethylene glycol is the commonly used group. The final product resembles like ether and known as ketal during the protection of carbonyl group using ethylene glycol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
i) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, aniline
The reaction of aldehyde with primary
j) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene.
The reaction of aldehyde with secondary amine forms enamine as the final product. The reaction of propanal with dimethylamine in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzene gives

k) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydroxylamine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydroxylamine gives oxime as the final product. The reaction of propanal with hydroxylamine results in the formation of propionaldehyde oxime. The product of this reaction is shown below.
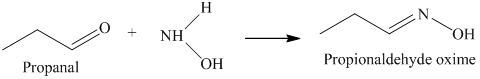
l) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydrazine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with hydrazine gives propionaldehyde hydrazone as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
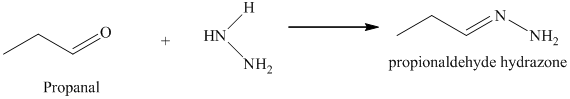
m) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the product of part (l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with hydrazine gives propionaldehyde hydrazone as the final product. The heating of propionaldehyde hydrazone in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide forms

n) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and p-nitrophenylhydrazine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with p-Nitrophenylhydrazine gives propionaldehyde phenylhydrazone as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
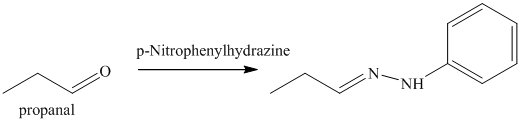
o) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and semicarbazide.
The reaction of aldehyde with semicarbazide results in the formation of semicarbazone. The reaction of propanal with
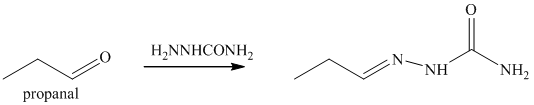
p) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane.
The reaction of propanal with ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane gives
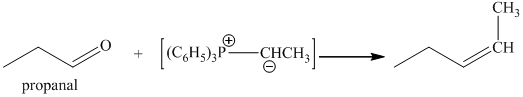
q) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid.
The reaction of aldehyde with sodium cyanide results in the formation of cyanohydrin. The product of this reaction is shown below.
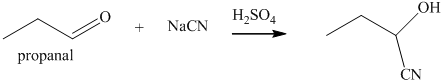
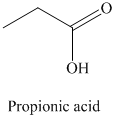
r) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and chromic acid.
The reaction of propanal with chromic acid gives propionic acid as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LOOSELEAF)-PACKAGE
- Draw the major elimination and substitution products formed in this reavtion. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicatr the stereochemistry of substituents on assymetric centers, wheere applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw the two possible products produced in this E2 elimination. Ignore any inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the major products of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
- Draw the major elimination and substitution products formed in this reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, wehre applicable. Ignore and inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Drawing Arrows THE Problem 33 of 35 N. C:0 Na + Submit Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore and inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
- Draw the major producrs of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the sereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers where appllicable.arrow_forward5) Oxaloacetic Acid is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of citric acid. Synthesize oxaloacetic acid using a mixed Claisen Condensation reaction with two different esters and a sodium ethoxide base. Give your answer as a scheme Hint 1: Your final acid product is producing using a decarboxylation reaction. Hint 2: Look up the structure of oxalic acid. HO all OH oxaloacetic acidarrow_forward20. The Brusselator. This hypothetical system was first proposed by a group work- ing in Brussels [see Prigogine and Lefever (1968)] in connection with spatially nonuniform chemical patterns. Because certain steps involve trimolecular reac tions, it is not a model of any real chemical system but rather a prototype that has been studied extensively. The reaction steps are A-X. B+X-Y+D. 2X+ Y-3X, X-E. 305 It is assumed that concentrations of A, B, D, and E are kept artificially con stant so that only X and Y vary with time. (a) Show that if all rate constants are chosen appropriately, the equations de scribing a Brusselator are: dt A-(B+ 1)x + x²y, dy =Bx-x²y. diarrow_forward
- Problem 3. Provide a mechanism for the following transformation: H₂SO A Me. Me Me Me Mearrow_forwardYou are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: xi 1. ☑ 2. H₂O хе i Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. There is no reagent that will make this synthesis work without complications. : ☐ S ☐arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: H OH 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G C टेarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





