
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with the given reagents is to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride are strong reducing agents. They are inorganic compounds which are used as the reducing agents in
In the reaction of
By catalytic hydrogenation, aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols. Grignard reagents react with ketones and aldehydes to form alcohols. These reactions are nucleophilic addition reactions. The Grignard reagent adds to the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen.
An organolithium reagent acts like a good nucleophiles and strong bases. They used for the conversion of aldehydes and ketones into primary and secondary alcohols. Acetal is an organic compound with general formula
Answer to Problem 28P
Solution:
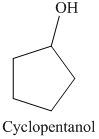
a) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water is shown below.
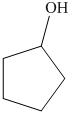
b) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with sodium borohydride, methanol is shown below.
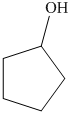
c) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with hydrogen (nickel catalyst) is shown below.
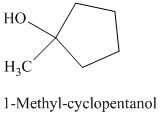
d) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
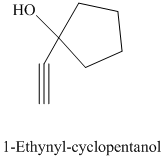
e) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
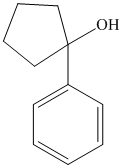
f) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
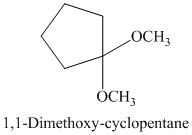
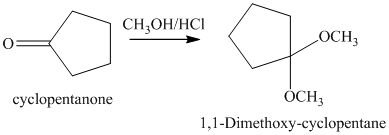
g) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride is shown below.
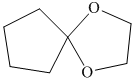
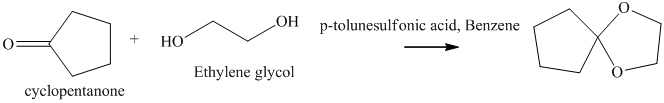
h) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene is shown below.
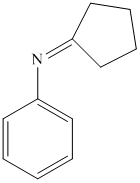
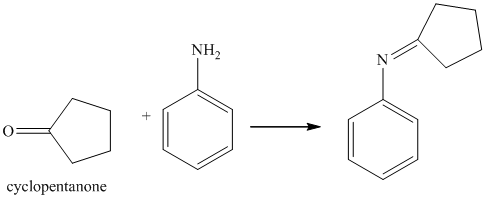
i) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with aniline
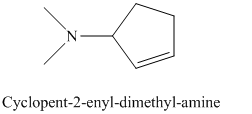
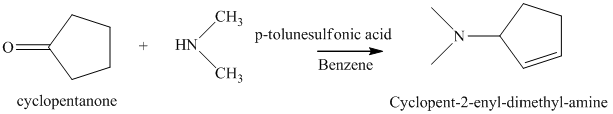
j) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene is shown below.
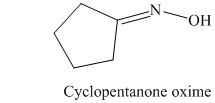
k) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with hydroxylamine is shown below.
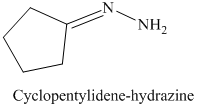
l) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with hydrazine is shown below.
m) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with product of part (l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide is shown below.
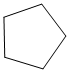
n) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with p-Nitrophenylhydrazine is shown below.
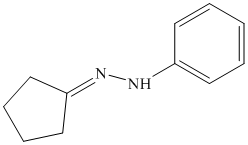
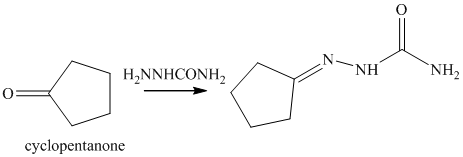
o) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with semicarbazide is shown below.
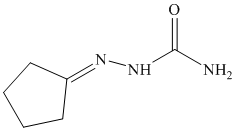
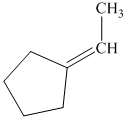
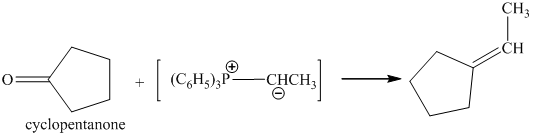
p) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane is shown below.
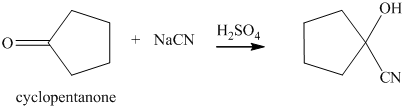
q) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid is shown below.
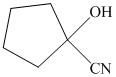
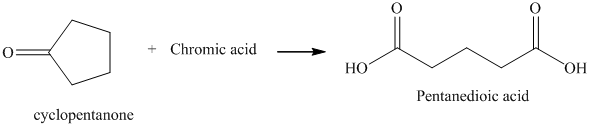
r) The product of the reaction of cyclopentanone with chromic acid is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
a) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and lithium aluminum hydride followed by water.
The reaction of cyclopentanone with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water gives alcohol as the final product. Lithium aluminum hydride reduces cyclopentanone to cyclopentanol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
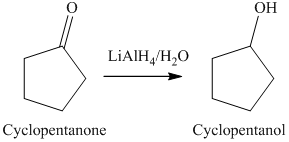
b) The product obtained by the reaction between, cyclopentanone and the reagent, sodium borohydride, methanol.
The reaction ofcyclopentanone with sodium borohydride, followed by methanol gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
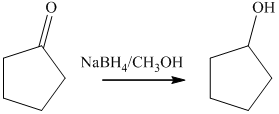
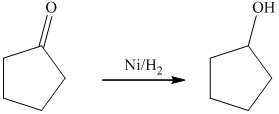
c) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and the reagent, hydrogen (nickel catalyst).
The reaction of cyclopentanone with hydrogen in the presence of nickel catalyst gives cyclopentanol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
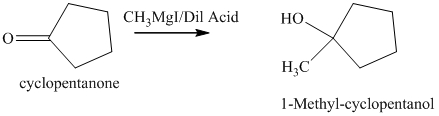
d) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, cyclopentanone and the reagent, methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of cyclopentanone with methylmagnesium iodide that is Grignard reagent, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
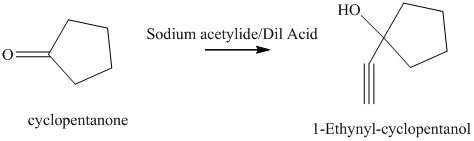
e) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, cyclopentanone and the reagent, sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction ofcyclopentanone with sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
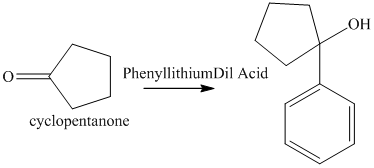
f) The product obtained by the reaction between, cyclopentanone and the reagent, phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of cyclopentanone with phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
g) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, cyclopentanone and the reagent, methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride.
The reaction of aldehydes and ketones with two equivalents of an alcohol results in the formation of acetals. The product of this reaction is shown below.
h) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, cyclopentanone and the reagent, Ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene.
In the reaction of ketone with ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzene, the protection of the carbonyl group of ketone takes place. For carbonyl protection, ethylene glycol is the commonly used group. The final product resembles like ether and known as ketal during the protection of carbonyl group using ethylene glycol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
i) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, cyclopentanone and the reagent, aniline
The reaction of ketone with primary
j) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, cyclopentanone and the reagent, dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene.
The reaction of ketone with secondary amine forms enamine as the final product. The reaction of cyclopentanone with dimethylamine in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzene gives
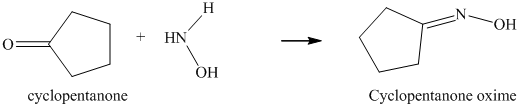
k) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, cyclopentanone and the reagent, hydroxylamine.
The reaction of cyclopentanone with hydroxylamine results in the formation of cyclopentanone oxime. The product of this reaction is shown below.
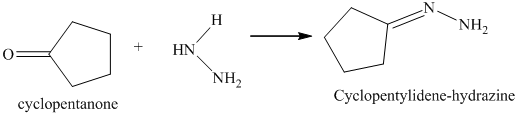
l) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and the reagent, hydrazine.
The reaction of cyclopentanone with hydrazine gives cyclopentylidene hydrazine as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
m) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and the product of part (l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide.
The reaction of ketone with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of cyclopentanone with hydrazine gives cyclopentylidene hydrazine as the final product. The heating of cyclopentylidene hydrazine in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide forms cycloalkane as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
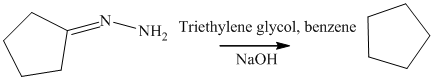
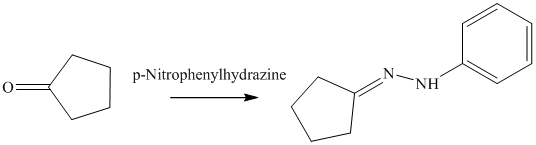
n) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and p-nitrophenylhydrazine.
The reaction of ketone with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of cyclopentanone with p-Nitrophenylhydrazine gives hydrazone as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
o) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and semicarbazide.
The reaction of ketone with semicarbazide results in the formation of semicarbazone. The reaction of propanal with
p) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane.
The reaction of cyclopentanone with ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane gives ethylidenecyclopentane as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
q) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid.
The reaction of ketone with sodium cyanide results in the formation of cyanohydrin. The product of this reaction is shown below.
r) The product obtained by the reaction between cyclopentanone and chromic acid.
The reaction of ketone with chromic acid results in the formation of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LOOSELEAF)-PACKAGE
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forwardProvide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene and I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene, indicate the compound that I should add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Ο HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Select to Draw I Submitarrow_forward
- Feedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forwardIf I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


