
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
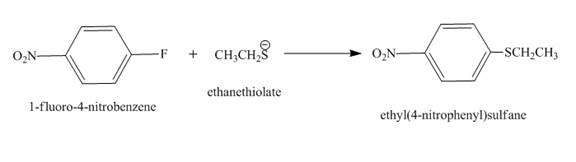
The reaction occurs by the nucleophilic substitution reaction mechanism in which ethanethiolate is substituted and fluoride ion is eliminated.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
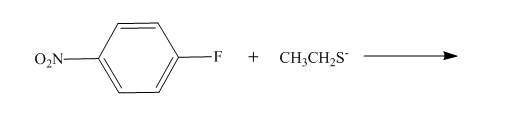
Figure 1
Nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place between
The complete reaction is shown below.
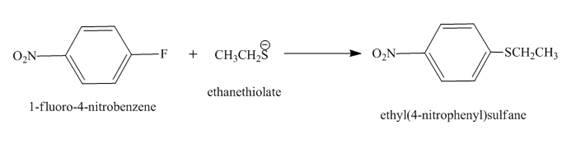
Figure 2
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
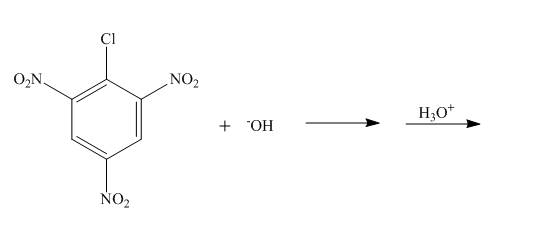
Figure 3
The nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place when
The complete reaction is shown below.
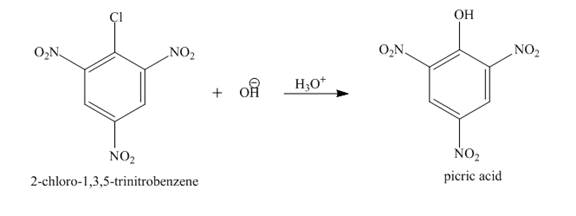
Figure 4
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
When a base reacts with a compound, it abstracts a proton from the compound.
Catalytic hydrogenation is a reduction process of addition of hydrogen atoms in an
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
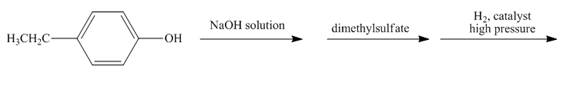
Figure 5
The hydrogen ion is abstracted from
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
No reaction takes place when chlorobenzene reacts with propylamine at
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
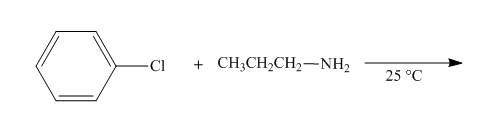
Figure 7
No reaction takes place when chlorobenzene reacts with propylamine at
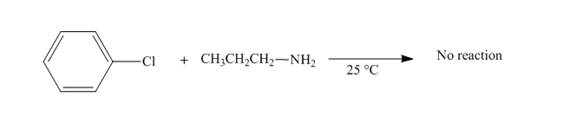
Figure 8
No reaction takes place when chlorobenzene reacts with propylamine at
(e)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Suzuki coupling reaction is a cross-coupling reaction in which boronic acid reacts with alkyl, aryl, and vinyl halides in presence of
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
No reaction takes place when boronic acid reacts with
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
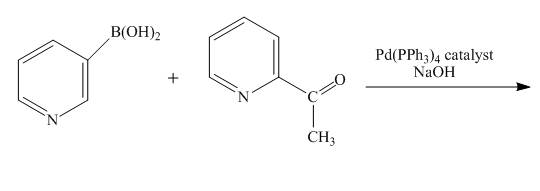
Figure 9
No reaction takes place when boronic acid reacts with
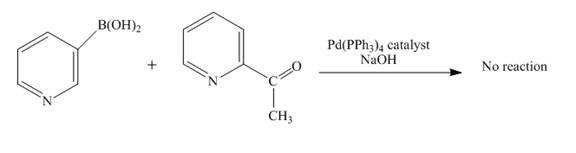
Figure 10
No reaction takes place when boronic acid reacts with
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Suzuki coupling reaction is a cross-coupling reaction in which boronic acid reacts with alkyl, aryl, and vinyl halides in presence of
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
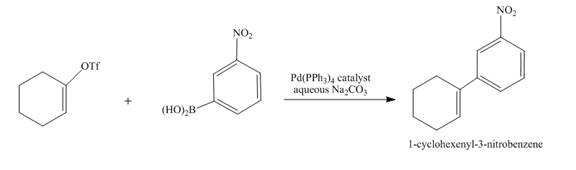
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
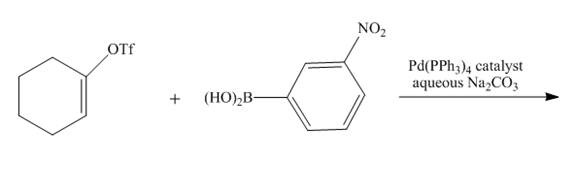
Figure 11
Suzuki coupling reaction occurs when boronic acid reacts with triflate in presence of

Figure 12
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 12.
(g)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The addition of a bromine atom in the given compound is known as bromination. Bromination occurs through an electrophilic substitution reaction. Bromine atom acts as an electrophile which causes the formation of sigma bond in the reaction
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
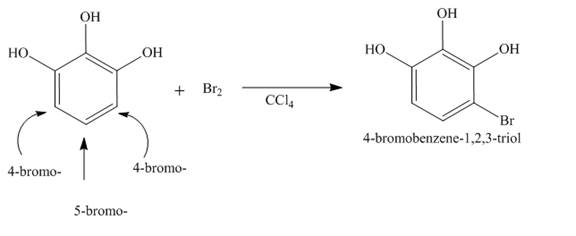
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
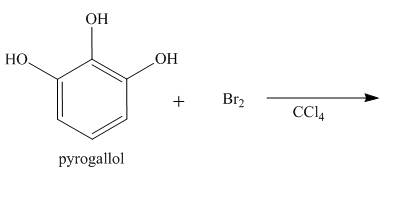
Figure 13
The reaction of Pyrogallol with bromine in the presence of

Figure 14
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 14.
(h)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Stille coupling reaction is a cross-coupling reaction in which stannanes reacts with alkyl, aryl, and pseudo halides in presence of
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
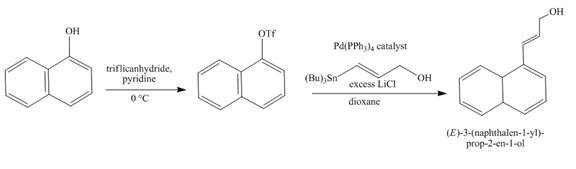
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
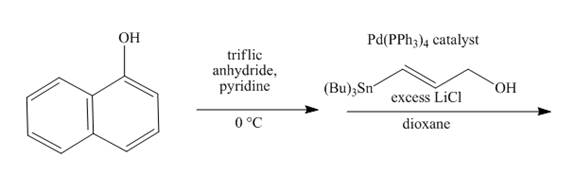
Figure 15
The reaction of

Figure 16
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 16.
(i)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The treatment of unsaturated halide with an alkene in the presence of a base and a
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
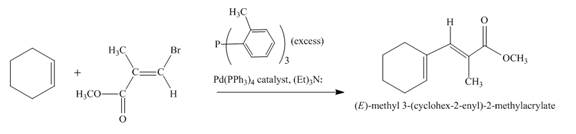
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
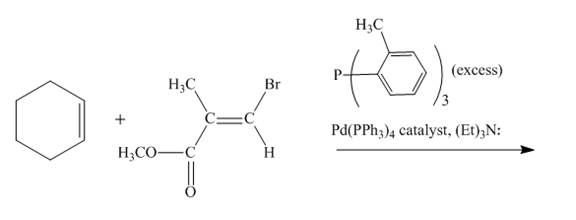
Figure 17
The reaction of cyclohexene couples with vinylbromo compound in the presence of

Figure 18
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 18.
(j)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is a process in which an oxygen atom is added, or a hydrogen atom is removed from a compound.
The compounds which oxidise the other compound are known as oxidising agents. Oxidizing agents after oxidise gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
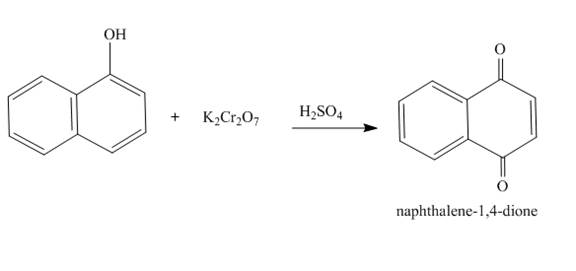
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
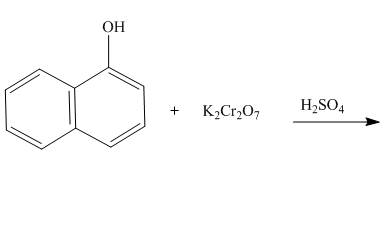
Figure 19
The reaction of

Figure 20
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 20.
(k)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is a process in which an oxygen atom is added, or a hydrogen atom is removed from a compound.
The compounds which oxidize the other compound are known as oxidizing agents. Oxidizing agents after oxidize gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
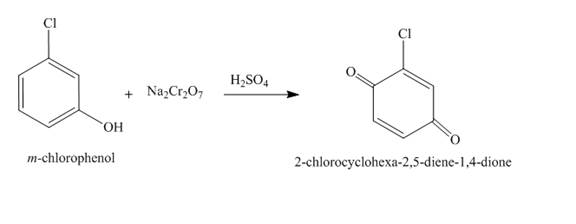
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
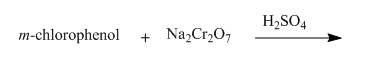
Figure 21
The reaction of

Figure 22
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 22.
(l)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
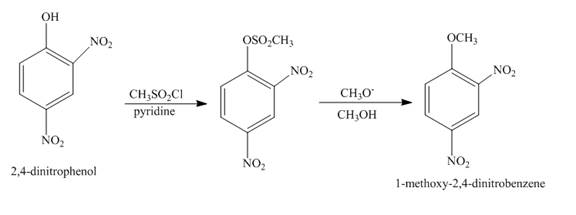
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
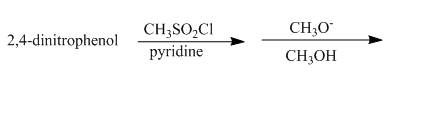
Figure 23
The reaction of

Figure 24
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 24.
(m)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
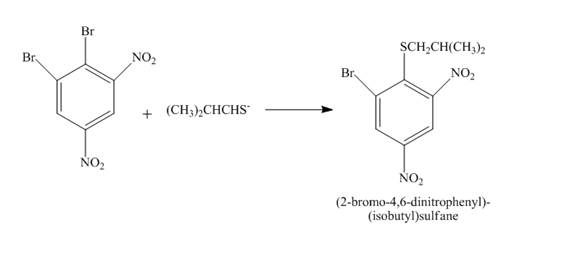
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
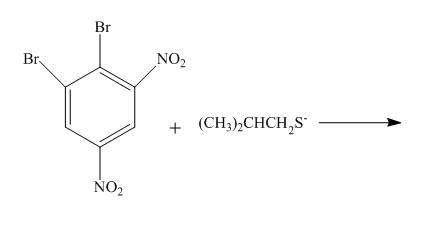
Figure 25
The reaction of
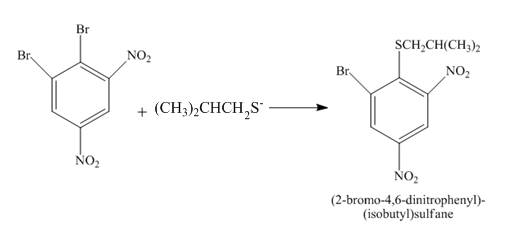
Figure 26
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 26.
(n)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The treatment of ether with substituted halide in the presence of heat to form corresponding alcohol. This process is known as demethylation of the methoxy group.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
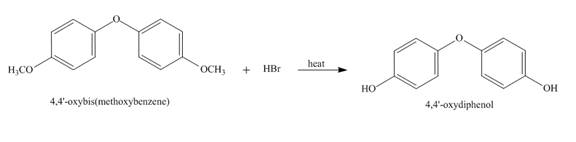
Explanation of Solution
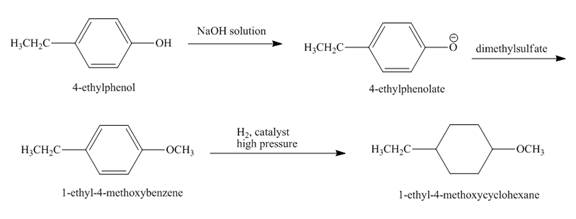
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
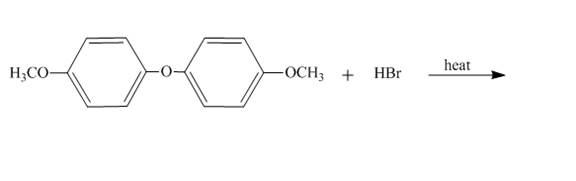
Figure 27
The reaction of

Figure 28
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 28.
(o)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
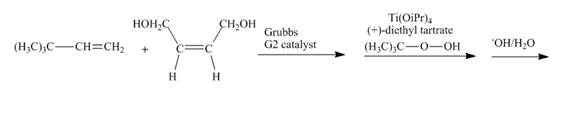
Figure 29
In the first step, the reaction of

Figure 30
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 30.
(p)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Grubbs catalyst is used to exchange of substituents between two different alkenes. Catalytic hydrogenation is a reduction process of addition of hydrogen atoms in an alkene or an alkyne by using a metal catalyst like
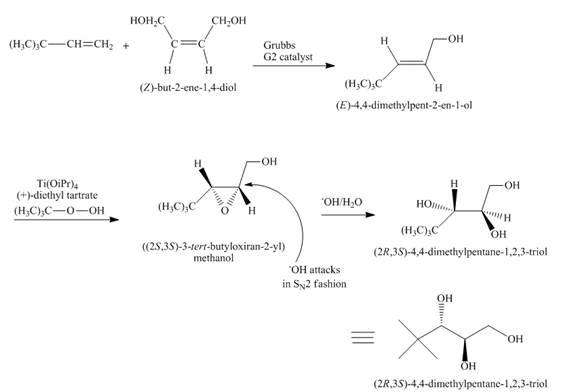
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
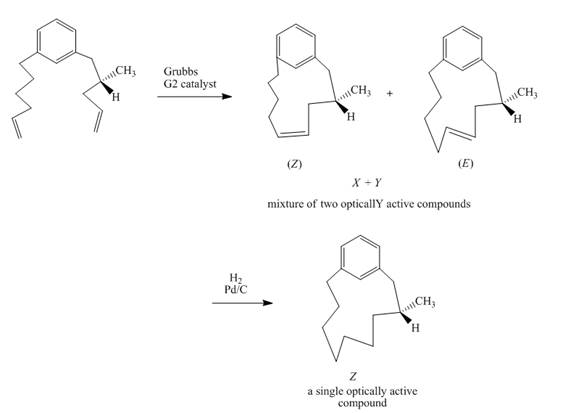
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
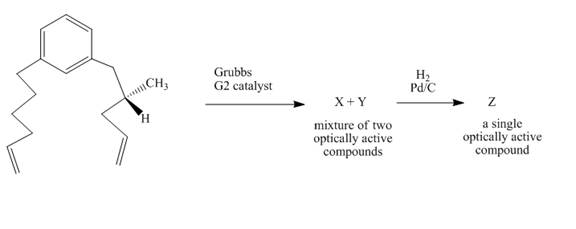
Figure 31
In the first step, the reaction of a diene with Grubbs

Figure 32
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 32.
(q)
Interpretation:
The reaction is to be completed by giving the major product. Also, the explanation for the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Suzuki coupling reaction is a cross-coupling reaction in which boronic acid reacts with alkyl, aryl, and vinyl halides in the presence of
Answer to Problem 18.70AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
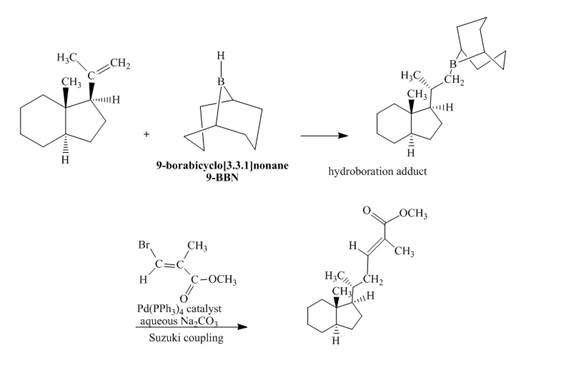
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
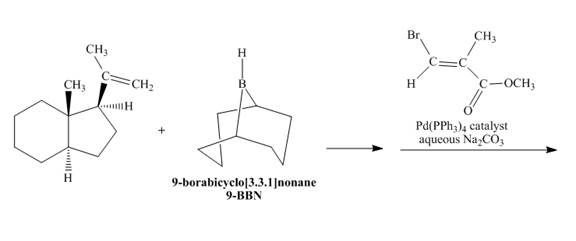
Figure 33
In the first step, the reaction of a given alkene with
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 34
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 34.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- 14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forwardΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward:0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forward
- Draw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
- answer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forwardTrue or false, chemistryarrow_forward
- answer thse questions with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardC app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Drawingarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CHзBr Drawingarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
