
(a)
Interpretation:
The reactivity of cyclohexanol and phenol with aqueous
Concept introduction:
The phenol is an aromatic compound having a formula,
Answer to Problem 18.53AP
Phenol is more reactive than cyclohexanol with an aqueous
Explanation of Solution
The sodium hydroxide is a strong base. It abstracts a proton from the stronger acidic compound and forms its sodium salt. In the given case, sodium hydroxide abstracts a proton from phenol and cyclohexanol and form phenoxide ion and cyclohexanol conjugate base respectively. The phenoxide ion gets stabilized by resonance structures, but this is not possible in case of cyclohexanol conjugate base. It is known that more the stability of the conjugate base more the acidity of the compound. In the given case, phenoxide ion is more stable due to this phenoxide is more acidic. Therefore, phenoxide ion is more reactive toward an aqueous
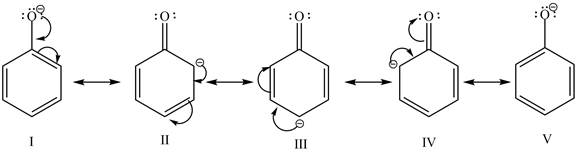
Figure 1
The reactivity of phenol is more as compared to cyclohexanol with an aqueous solution of
(b)
Interpretation:
The reactivity of cyclohexanol and phenol with
Concept introduction:
The phenol is an aromatic compound having a formula,
Answer to Problem 18.53AP
Phenol is more reactive than cyclohexanol with an aqueous
Explanation of Solution
The sodium hydride is a strong base. It abstracts a proton from the stronger acidic compound and forms its sodium salt and hydrogen gas is evolved. In the given case, sodium hydroxide abstracts a proton from phenol and cyclohexanol and form phenoxide ion and cyclohexanol conjugate base respectively. The phenoxide ion gets stabilized by resonance structures, but this is not possible in case of cyclohexanol conjugate base. It is known that more the stability of the conjugate base more the acidity of the compound. In the given case, phenoxide ion is more stable due to this phenoxide is more acidic. Therefore, phenoxide ion is more reactive toward an aqueous
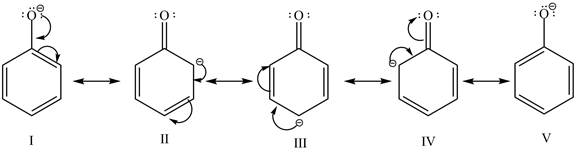
Figure 2
The reactivity of phenol is more as compared to cyclohexanol with an aqueous solution of
(c)
Interpretation:
The reactivity of cyclohexanol and phenol with triflic anhydride in pyridine at
Concept introduction:
The triflic anhydride is a chemical compound which is also known as Trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride. It has a molecular formula
Answer to Problem 18.53AP
The presence of the more nucleophilic character of cyclohexanol makes it more reactive towards triflic anhydride in pyridine at
Explanation of Solution
In the given case, when triflic acid reacts with cyclohexanol and phenol in the presence of pyridine at
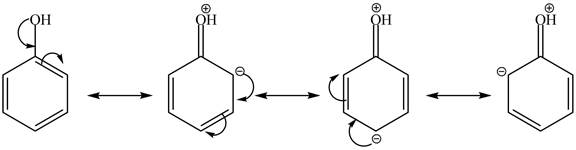
Figure 3
The reactivity of cyclohexanol is more as compared to phenol with triflic acid in pyridine at
(d)
Interpretation:
The reactivity of cyclohexanol and phenol with concentrated aqueous
Concept introduction:
The phenol is an aromatic compound having a formula,
Answer to Problem 18.53AP
The deactivation of the aromatic ring of phenol makes it less reactive toward concentrated aqueous
Explanation of Solution
Cyclohexanol is more nucleophilic as compared to phenol. It is due to the participation of the lone pair of electrons on oxygen in resonance structures of phenol. Therefore, in the given conditions cyclohexanol reacts more rapidly as compared to phenol. When cyclohexanol undergoes protonation in the presence of
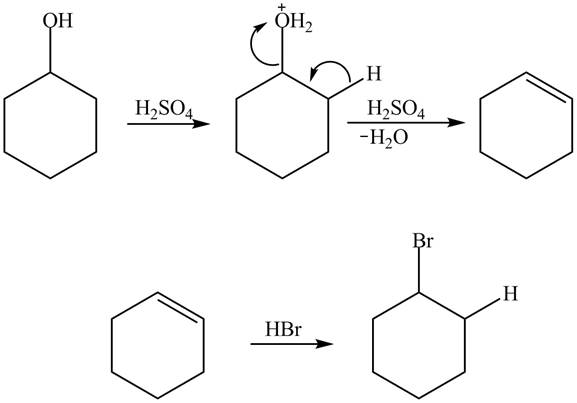
Figure 4
In the case of phenol, it undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction with
The reactivity of phenol is less with concentrated aqueous
(e)
Interpretation:
The reactivity of cyclohexanol and phenol with
Concept introduction:
The phenol is an aromatic compound having a formula,
Answer to Problem 18.53AP
The phenol is more reactive toward
Explanation of Solution
The phenol is an aromatic compound which shows similar reactions as
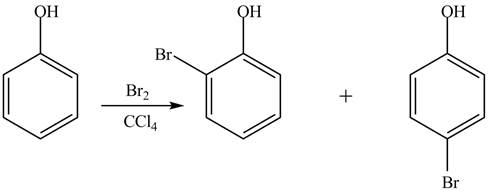
Figure 5
Whereas no such reaction is possible with cyclohexanol because this compound gives addition reaction.
The phenol is an aromatic compound which undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction. Due to this, it is more reactive toward
(f)
Interpretation:
The reactivity of cyclohexanol and phenol with
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is defined as the addition of oxygen atom or removal of the hydrogen atom. The oxidizing agent is the substance that causes oxidation and itself get reduced. The reagent
Answer to Problem 18.53AP
The phenol is an aromatic compound which loses its aromatic character on reaction with
Explanation of Solution
In the given conditions, both the given compounds undergo an oxidation reaction. The reaction of cyclohexanol with
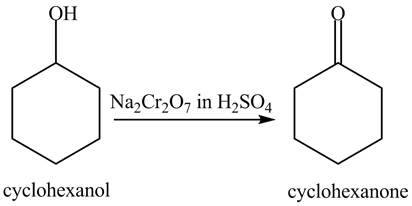
Figure 6
The reaction of phenol with
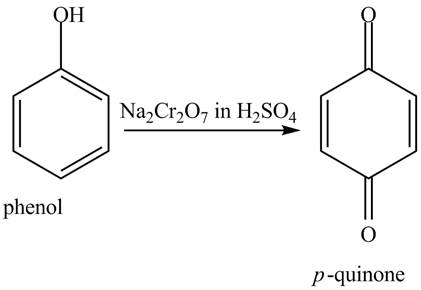
Figure 7
When phenol undergoes oxidation reaction, it loses its aromatic character which means it loses its stability. Therefore, cyclohexanol is more reactive toward
The phenol on reaction with
(g)
Interpretation:
The reactivity of cyclohexanol and phenol with
Concept introduction:
The phenol is an aromatic compound having a formula,
Answer to Problem 18.53AP
The deactivation of the aromatic ring of phenol due to protonation of the hydroxyl group makes it less reactive toward
Explanation of Solution
Cyclohexanol is more nucleophilic as compared to phenol. It is due to the participation of the lone pair of electrons on oxygen in resonance structures of phenol. Therefore, in the given conditions cyclohexanol reacts more rapidly as compared to phenol. When cyclohexanol undergoes protonation in the presence of
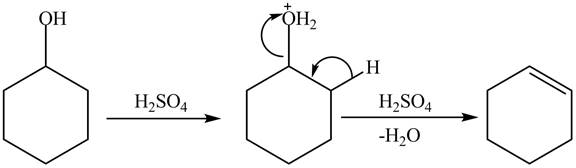
Figure 8
The less nucleophilic character makes phenol less reactive toward
The reactivity of phenol is less with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- In the table below, the correct structure for (2R)-3-methylpentan-2-ol (IUPAC name) can be represented by the letter OH OH HE > ' ÕH C B OH D A/ E OHarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardWhy is analysing salt content (using Mohr titration) in both regular & salt reduced tomato sauce important?arrow_forward
- In the image below, correctly name the glassware # _P ( Blank 1) and T ( Blank 2). 景 A W Blank # 1 Blank #2 1000 +19 E E D 0 0-0 G H A A K Π 12 R M N S 0-0-arrow_forwardFeedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: CN Δ + A ? NC Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. esc Check 80 MH F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 50 @ # C % 95 € Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C A DII F6 F7 F8 7 * 8 Λ & 6 F9 F10 9 0 4arrow_forwardIncorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: ཤིགས་བྱ རྩ་ཅད་ཀྱིས་༢༩ + Some important notes: A ^ ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. E Check 0 لا Save For La ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of All F9 Aarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Δ A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privaarrow_forwardesc 2 Incorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? A O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Check F1 ! @ X C Save For Later Submit Assignment 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility 80 et A ད 1 4 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 # $ 45 % A 6 87 & * 8 9 ) 0 + ||arrow_forwardCan the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ?A Δ O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilit ku F11arrow_forward
- १ eq ine teaching and × + rn/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator-assignment-take [Review Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. The IUPAC name is In progress mit Answer Retry Entire Group 5 more group attempts remaining Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support Save and Exitarrow_forwardDraw the molecules.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-hexan-2-ol with arrows please.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

