
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under strongly acidic condition is to be drawn and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
When an
Answer to Problem 18.58P
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
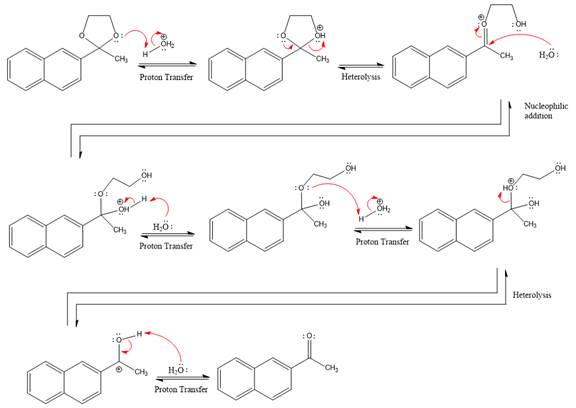
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
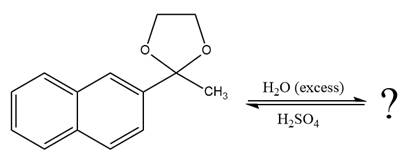
This is an acetal hydrolysis reaction under strongly acidic conditions to produce ketone as a major product. The leaving group is an uncharged alcohol and water acts as the nucleophile.
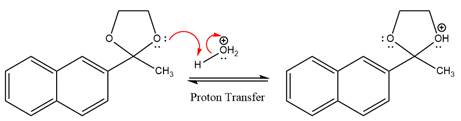
In the first step, the lone pairs on the O atom abstract the proton from water, which makes positively charged O ion.
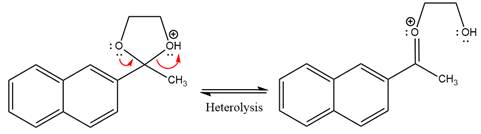
In the next step, the bond between positively charged O and C breaks and forms a new double bond in another
Next, nucleophile water attacks on the electropositive carbon atom in the nucleophilic addition reaction.
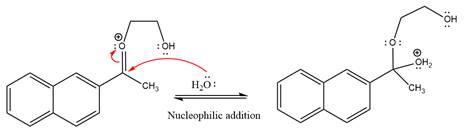
In the deprotonation step, water abstracts the H atom and produces a hemiacetal group.
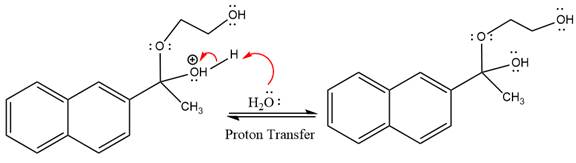
The lone pairs on
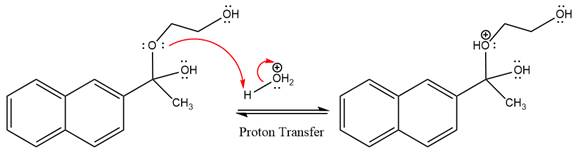
The diol leaving group departs and forms resonance stabilized carbocation.
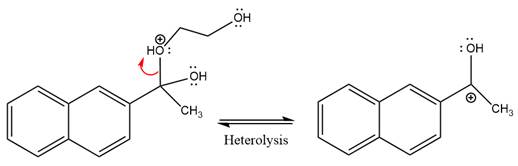
Water nucleophile abstracts the proton from the
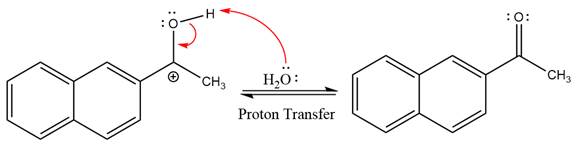
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
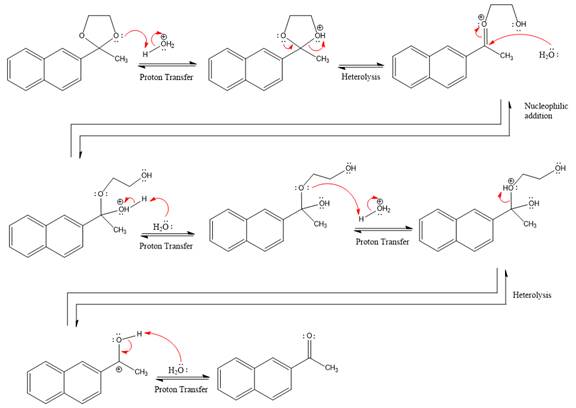
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction under acidic medium and excess water is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under stongly acidic condition is to be drawn and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
When an aldehyde or ketone is treated with an alcohol under acidic conditions, the hemiacetal product is formed. By using an excess amount of alcohol under acidic conditions, after that nucleophilic addition produces hemiacetal, which further forms an acetal. The acetal has two alkoxy groups are bonded to the same carbon. The formation of the acetal product is favored by using excess alcohol. In the hydrolysis of acetal reaction, because of the addition of water results in the breaking of
The hydrolysis reaction of acetal produces ketone as a major product.
Answer to Problem 18.58P
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
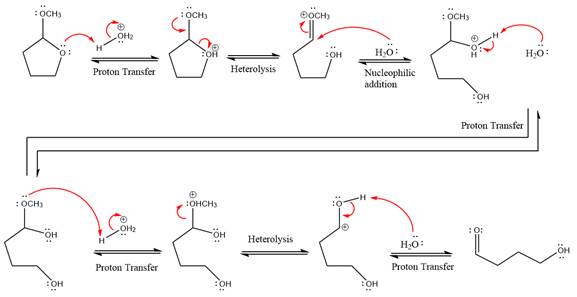
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
This is an acetal hydrolysis reaction under strongly acidic condition, not strong bases should appear to produce ketone as a major product. The leaving group is an uncharged alcohol, and water acts as the nucleophile.
In the first step, the lone pairs on the O atom abstract the proton from water, which makes positively charged O ion.
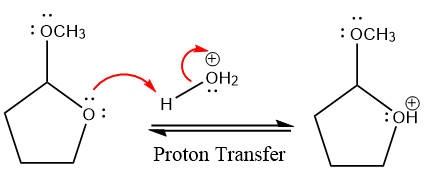
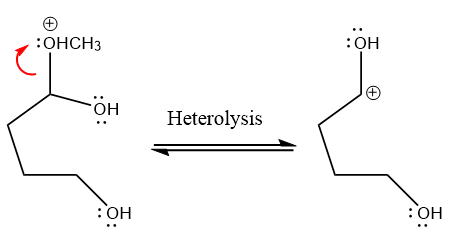
In the next step, the bond between positively charged O and C breaks and forms a new double bond in another
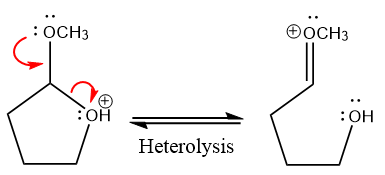
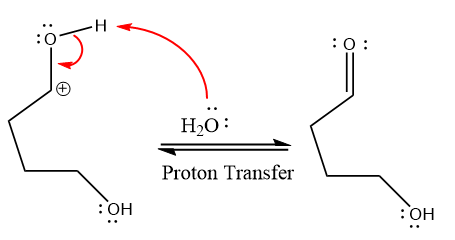
Next, nucleophile water attacks the electropositive carbon atom in the nucleophilic addition reaction.
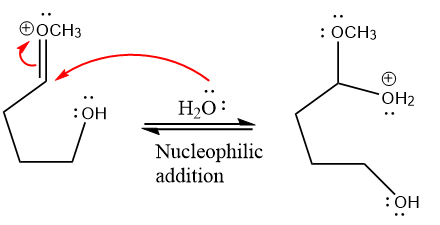
In the deprotonation step, water abstracts the H atom and produces a hemiacetal group.
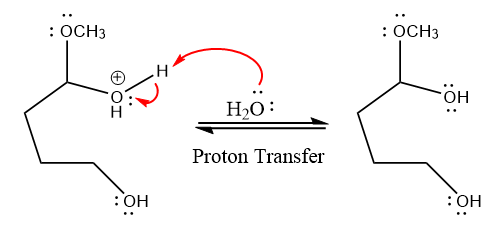
The lone pairs on
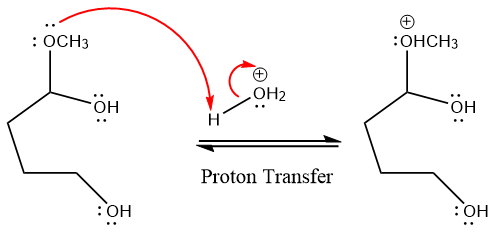
The methanol leaving group departs and form resonance stabilized carbocation.
water nucleophile abstracts the proton from the amino group and makes ketone as a product.
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under acidic medium is shown below and a ketone is a major product.

The complete, detailed mechanism of given reaction under acidic medium and excess water is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under strongly acidic condition is to be drawn and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
In the hydrolysis of nitriles reaction, addition of water results in the breaking of
Answer to Problem 18.58P
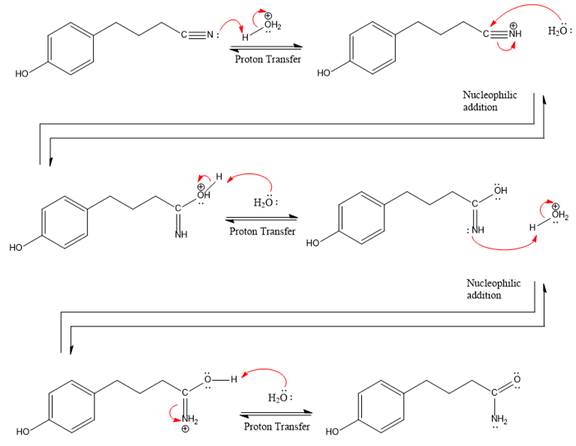
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and amide is a major product.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
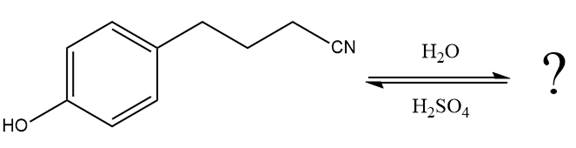
This is a nitrile hydrolysis reaction under the strongly acidic condition to produce an amide as a major product. The nitrile group is protonated first and water act as the nucleophile.
In the first step, the lone pairs on the N atom abstract the proton from water, which makes positively charged N ion.
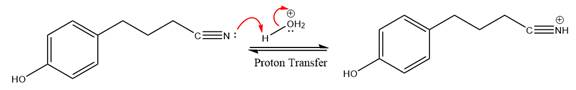
Next, nucleophile water attacks on the electropositive carbon atom in the nucleophilic addition reaction.
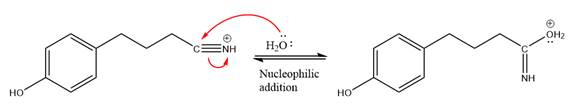
In the deprotonation step, water abstracts the H atom in the protonation step.
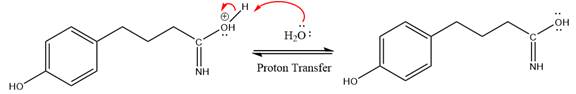
The lone pairs on N atom accept the proton in the protonation step by generating an amino group.
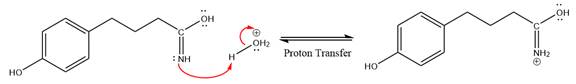
The nucleophile water abstracts the proton in the resonance stabilized carbocation and produces amide as a major product.
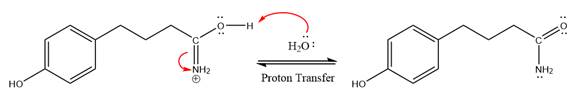
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under the strongly acidic medium is shown below and an amide is a major product.
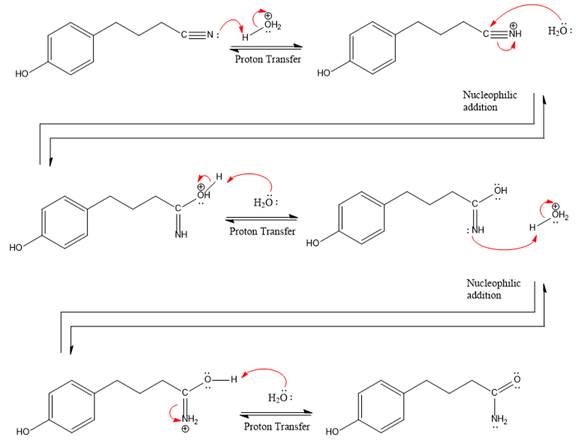
The complete, detailed mechanism of given reaction under acidic medium and excess water is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under stongly acidic condition is to be drawn and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
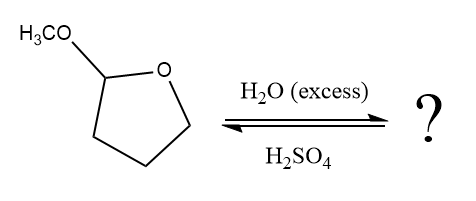
When an aldehyde or ketone is treated with an alcohol under acidic conditions, the hemiacetal product is formed. By using an excess amount of alcohol under acidic conditions the hemiacetals, nucleophilic addition produces hemiacetal, which further form an acetal. The acetal has two alkoxy groups are bonded to the same carbon. The formation of the acetal product is favored by using excess alcohol. In the hydrolysis of acetal reaction, addition of water results in the breaking of
Answer to Problem 18.58P
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
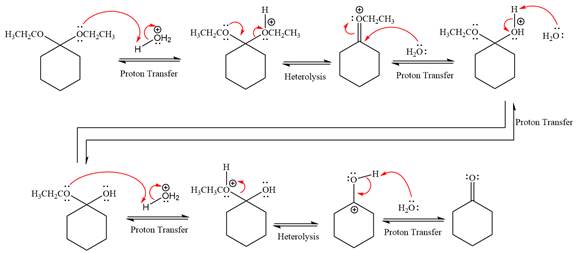
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
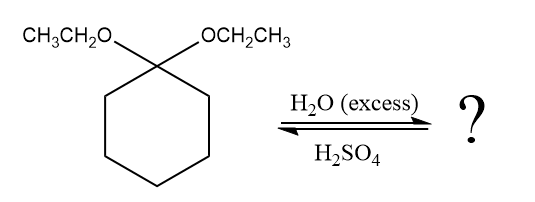
This is an acetal hydrolysis reaction under strongly acidic condition, not strong bases should appear to produce ketone as a major product. The leaving group is an uncharged alcohol and water acts as the nucleophile.
In the first step, the lone pairs on the O atom abstract the proton from water, which makes positively charged O ion as a good leaving group.
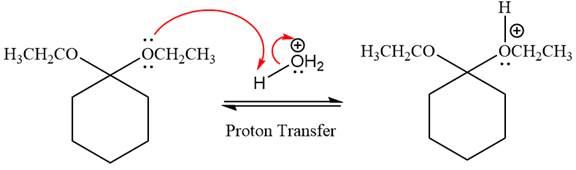
In the next step, the ethanol good leaving group departs and forms a new double bond in another
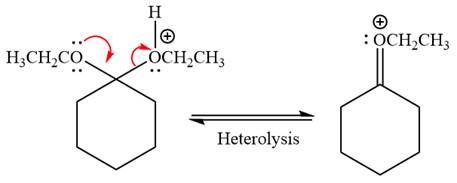
Next, nucleophile water attacks on the electropositive carbon atom in the nucleophilic addition reaction.
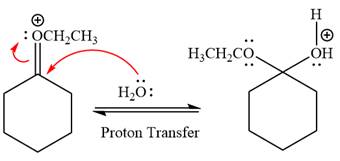
In the deprotonation step, water abstracts the H atom and produces a hemiacetal group.
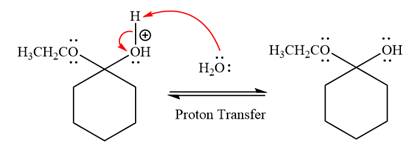
The lone pairs on
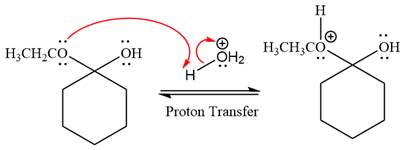
In the next step, the ethanol good leaving group departs and forms resonance stabilized carbocation.
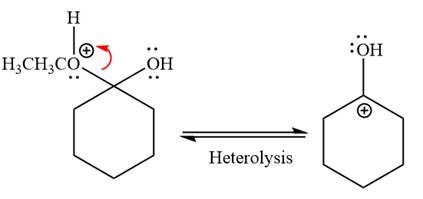
Water nucleophile abstracts the proton from the carbon ring and forms ketone as a product.
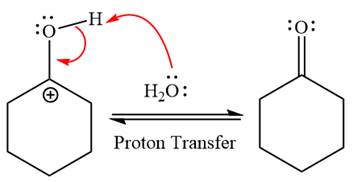
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
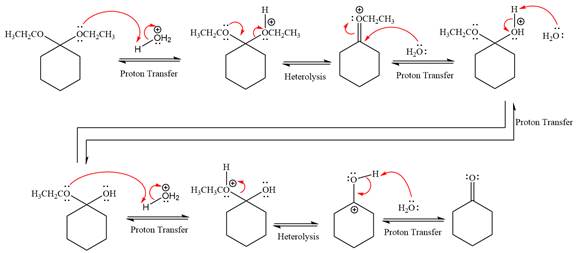
The complete, detailed mechanism of given reaction under acidic medium and excess water is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ORG CHEM W/ EBOOK & SW5 + STUDY GUIDE
- Pls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward
- 11) The Ksp expression for copper (II) sulfate is: a. [Cu2+][SO4²¯] b. [Cu²+]² [SO4²]² c. [Cu²+]²[SO4²] d. [CuSO4] 12) Which of the following is true about a chemical system in equilibrium? a. All chemical reactions have stopped b. The concentration of reactants is equal to the concertation of products c. The forward and reverse reaction rates become equal d. The system will remain at equilibrium regardless of any external factorsarrow_forward21) Explain the difference between the rate of a reaction and the extent of a reaction. Why are both of these concepts important, if you are a chemical engineer that is trying to develop a process to produce a large volume of a specific type of chemical compound?arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





