
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Ester Hydrolysis: Ester hydrolysis can be caused by acid and base.
Saponification: Ester hydrolysis taking place in presence of base such as
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
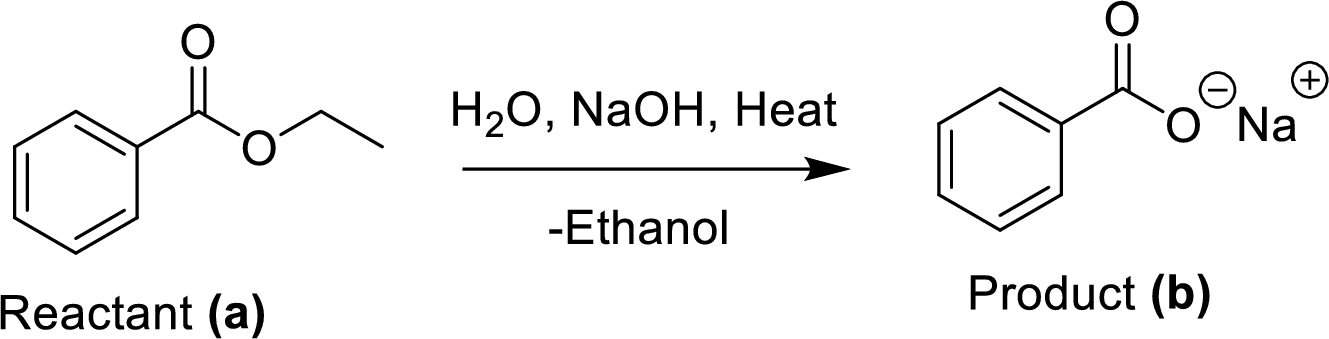
The ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with sodium hydroxide in presence of basic conditions which corresponding yields the product (B). In this reaction addition and elimination process was occurred.
(b)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Ester Hydrolysis: Ester hydrolysis can be caused by acid and base.
Saponification: Ester hydrolysis taking place in presence of base such as
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
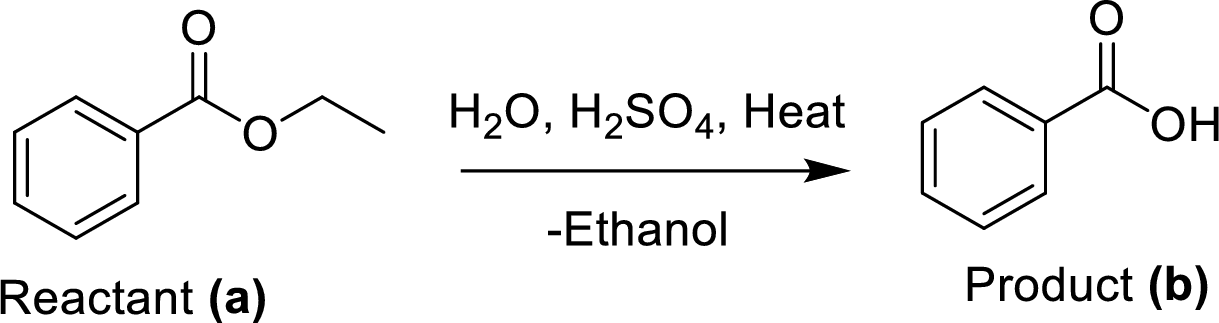
The ethyl benzoate (A) is undergoes for simple acid catalyzed hydrolysis, followed by heating to give a target compound (B), which is a benzoic acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amide: One
Amide Formation: Amide is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an
- Primary amide is produce when a carboxylic acid reacts with ammonia.
- Secondary and tertiary amide is produce when a carboxylic acid reacts with primary and secondary amine respectively.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
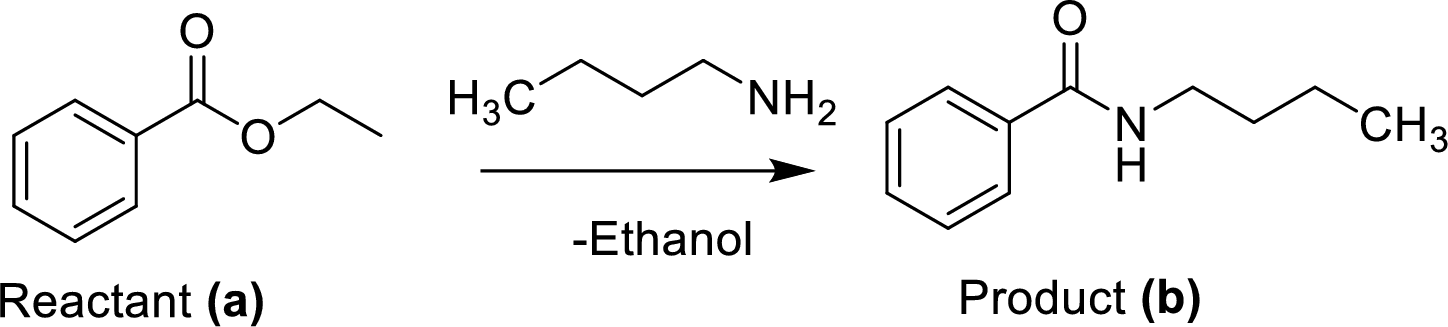
The ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with n-butylamine in presence of basic conditions which corresponding yields the product (B).
(d)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBALH): It is prepared by refluxing triisobutylaluminium in the solvent heptane.
DIBAL-H: is a strong reducing reagent most
DIBAL-H is a selective reagent (like,
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
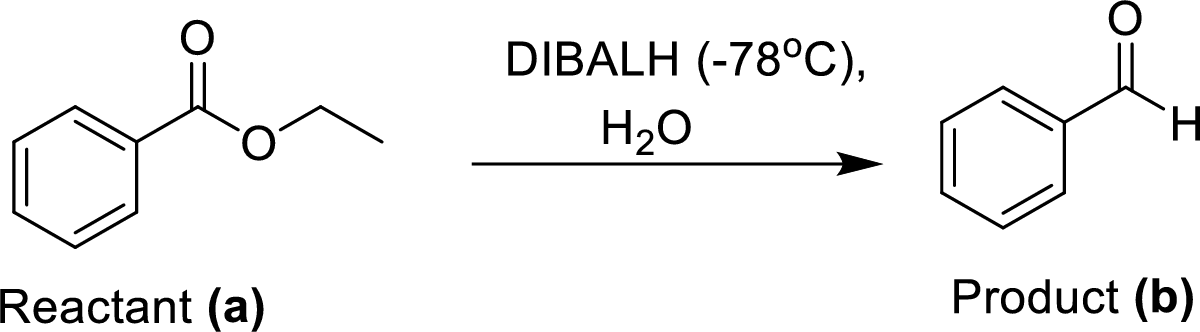
The equal amount of ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with Diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBALH) under dry ice conditions at
(e)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction: Aldehydes or ketones undergoing reduction by using reducing agent like
LAH Reduction: The saturated/unsaturated aldehyde and ketones in the presence of sodium metal in LAH and carbonyl compound produced saturated alcohols. The keto group involves in the reduction process of LAH, this end up reducing to give the alcohols.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
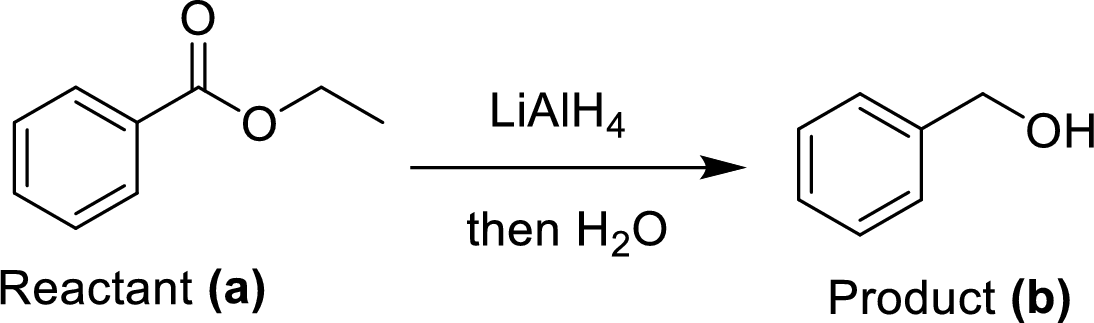
The ethyl benzoate (A) undergoes for LAH reduction process followed by simple hydrolysis workup method to give a target product (B). The obtained product namely benzyl alcohol.
(f)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alkyl or aryl magnesium halides (
Synthesis of Grignard reagent is shown below,
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
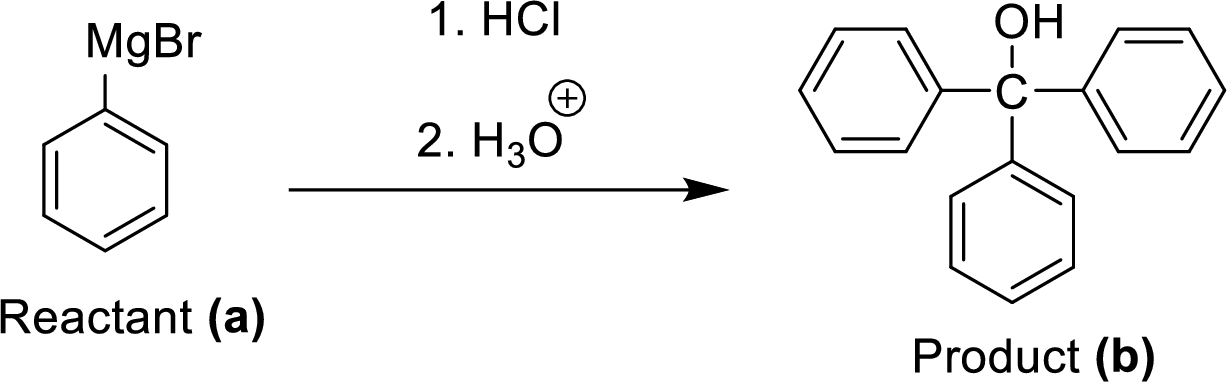
Two equivalents of Grignard reagent (A) is reacted with hydrogen chloride and fallowed by hydrolysis workup method, which corresponding yields the triphenyl methanol (B) it is a target molecule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Please helparrow_forward(a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forward
- Help me solve this problem.arrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forwardCHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

