
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Oxidation and reduction should be described and also the electron transfer in a redox reaction and electron donation in a Lewis acid-base reaction has to be compared.
Concept Introduction:
Redox reaction and Half-reaction
- The redox reaction is the combination of
oxidation and reduction reactions and these two reactions are called half-reactions.
Oxidation reaction:
- The loss of electrons or the gain of oxygen atoms is called as oxidation.
Reduction reaction:
- The gaining of electrons or addition of hydrogen atoms is called as reduction.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation is the reaction in which loss of electron occurs and reduction reaction is the reaction in which gain of electron occurs. Redox reaction is a common term used for a reduction and an oxidation reaction.
In a redox reaction, oxidation always accompanies reduction. Thus one atom must lose electrons and other must gain electrons.
Oxidation reaction:
In the above reaction, Ag atom loses one electron and changes their oxidation state 0 to 1.
Reduction reaction:
In the above reaction
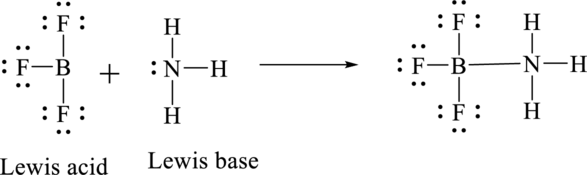
According to Lewis concept of acid and bases,
Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor.
Lewis base is an electron pair donor.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- An organic chemistry Teaching Assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area. 1. NaOMe CH3O N. OCH3 ? 2. H3O+arrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. + More... ☐ ☐ : ☐ + G 1. NaOMe Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forward6. Ammonia reacts with nitrogen monoxide and oxygen to form nitrogen and water vapor. If the rate of consumption of NO is 4.5 mollitermin) (a) Find the rate of reaction (b) Find the rate of formations of N; and HO (c) Find the rate of consumption of NH, and O 4NH: 4NO 0:4: +60arrow_forward
- 34. Give the expected major product of each of the following reactions. Conc. HI a. CH3CH2CH2OH b. (CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH Conc. HBr H Conc. HI C. OH Conc.HCI d. (CH3CH2)3COHarrow_forward42. Which of the following halogenated compounds can be used successfully to prepare a Grignard reagent for alcohol synthesis by subsequent reaction with an aldehyde or ketone? Which ones cannot and why? H3C CH3 a. Br H OH b. Cl C. I H H d. Cl e. H OCH3 Br Harrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. ? Will the first MgBr product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? olo ? OH جمله O Yes Ⓒ No MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Yes No X ☐ : ☐ टे PHarrow_forward
- Assign all the carbonsarrow_forward9 7 8 C 9 8 200 190 B 5 A -197.72 9 8 7 15 4 3 0: ང་ 200 190 180 147.52 134.98 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 90 OH 10 4 3 1 2 -143.04 140. 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 CI 3 5 1 2 141.89 140.07 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 ៖- 90 129. 126.25 80 70 60 -60 50 40 10 125.19 -129.21 80 70 3.0 20 20 -8 60 50 10 ppm -20 40 128.31 80 80 70 60 50 40 40 -70.27 3.0 20 10 ppm 00˚0-- 77.17 30 20 20 -45.36 10 ppm -0.00 26.48 22.32 ―30.10 ―-0.00arrow_forwardAssign all the carbonsarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





