
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.5, Problem 107P
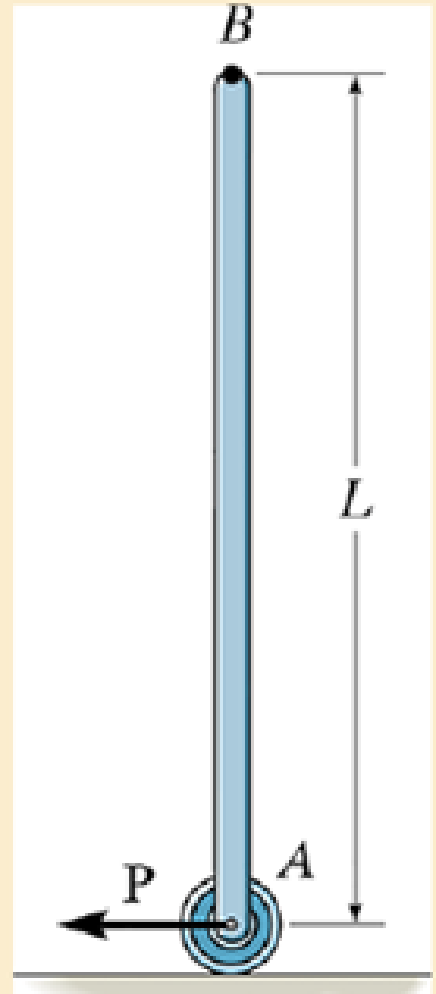
Solve Prob.17-106 if the roller is removed and the coefficient of kinetic friction at the ground is μk.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(Read Question)
In figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.
(Read image)
Chapter 17 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 17.1 - The rod's density end cross-sectional area. A are...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the mass of the cylinder end its moment...Ch. 17.1 - The nag has a mass m.Ch. 17.1 - Determine the radius of gyration kx. The density...Ch. 17.1 - The specific weight of the material is = 380...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Iz and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Ix and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Defending the moment of inertia Iy and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Express the result in terms of the mass m of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine me radius of gyration of the pendulum...
Ch. 17.1 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia of the solid steel...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the wheels moment of inertia about an...Ch. 17.1 - If the large ring, small ring and each of the...Ch. 17.1 - The thin plate has a hole in its center its...Ch. 17.1 - The material has a mass per unit area of 20 kg/m2.Ch. 17.1 - The block has a mass of 3 kg and the semicylinder...Ch. 17.1 - The block has a mass of 3 kg and the semicylinder...Ch. 17.1 - The material has a specific weight = 90 lb/ft3.Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 20PCh. 17.1 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 17.1 - The material is steel having a density of = 7.85...Ch. 17.1 - The material is steel having a density of = 7.85...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the acceleration of the can and the...Ch. 17.3 - If the 80-kg cabinet is allowed to roll down the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum acceleration of the frame...Ch. 17.3 - Also what is the corresponding normal reaction on...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the tension developed in the rods and...Ch. 17.3 - If it is subjected to a couple moment M = 450 N ...Ch. 17.3 - Determine how far the door moves in 25, starting...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the constant force F that must be...Ch. 17.3 - Initially at take-off the engines provide a thrust...Ch. 17.3 - If it starts from rest it causes the rear wheels...Ch. 17.3 - If the winch at B draws in the cable with an...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the greatest acceleration of the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the internal axial, shear, and...Ch. 17.3 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the reactions at both the wheels at A...Ch. 17.3 - Also, what is the acceleration of the cart? The...Ch. 17.3 - If it is subjected to a horizontal force of P =...Ch. 17.3 - Determine its initial acceleration if a man pushes...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the initial acceleration of a desk when...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - If it is released from rest, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - It is carried on a truck as shown. Determine the...Ch. 17.3 - It is carried on a truck as shown. If the truck...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the smallest acceleration that will...Ch. 17.3 - The coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.3 - If the collar is given a constant acceleration of...Ch. 17.3 - If it is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C,...Ch. 17.3 - If it is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C,...Ch. 17.3 - If the acceleration is a = 20 ft/s2, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - If h = 3 ft, determine the snowmobiles maximum...Ch. 17.3 - If the carts mass is 30 kg and it is subjected to...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform rod BC has a mass of 15 kg.Ch. 17.3 - If the acceleration of the truck is at = 0.5 m/s2,...Ch. 17.3 - If the angle = 30, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the initial friction and normal force of...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the normal force NE, shear force VE, and...Ch. 17.4 - If the wheel starts from rest determine its...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the disk when t...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the tangential and normal components of...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the tangential and normal components or...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.4 - If the rod has a counterclockwise angular velocity...Ch. 17.4 - If the wheel is subjected to a moment M = (5t) N ...Ch. 17.4 - Determine its initial angular acceleration and the...Ch. 17.4 - If it is released from rest when = 0. determine...Ch. 17.4 - If it is released from rest in the position shown,...Ch. 17.4 - The reel rests on rollers at A and B and has a...Ch. 17.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 5 lb ft/rad, so...Ch. 17.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 5 lb ft/rad, so...Ch. 17.4 - If a force of F=(142)N, where is in radians, is...Ch. 17.4 - If no slipping occurs between them determine the...Ch. 17.4 - Show that IG may be eliminated by moving the...Ch. 17.4 - Treat the beam as a uniform slender rod.Ch. 17.4 - It consists of a 100-kg steel plate AC and a...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - Determine its angular velocity when t = 2 s...Ch. 17.4 - If it is placed on the ground for which the...Ch. 17.4 - Compute the time needed to unravel 5 m of cable...Ch. 17.4 - If the rotor always maintains a constant clockwise...Ch. 17.4 - It is originally spinning at = 40 rad/s. If it is...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - Disk E has a weight of 60 lb and is initially at...Ch. 17.4 - If the cylinders are released from rest, determine...Ch. 17.4 - If the pulley can be treated as a disk of mass 3...Ch. 17.4 - If the pulley can be treated as a disk of mass M,...Ch. 17.4 - Assume that the board is uniform and rigid, and...Ch. 17.4 - At the instant the rolor is horizontal it has an...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the initial tending moment at the fixed...Ch. 17.4 - Movement is controlled by the electromagnet E,...Ch. 17.4 - If it is rotating in the vertical plane at a...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the angular acceleration of the rod and...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.5 - If the powder burns at a constant rate of 20 g/s...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the acceleration of the bars mass center...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the acceleration of its mass center and...Ch. 17.5 - When the wheel is subjected to the couple moment,...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the angular acceleration of the sphere...Ch. 17.5 - If the couple moment is applied to the spool and...Ch. 17.5 - If the rod is released from rest at = 0,...Ch. 17.5 - rolls without slipping, show that when moments are...Ch. 17.5 - If it is initially at rest and is subjected to a...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-96 if the cord and force P = 50 N...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If a horizontal force of F = 80 N is applied to...Ch. 17.5 - If slipping does not occur, determine the rings...Ch. 17.5 - Neglect the thickness of the ring.Ch. 17.5 - Using a collar of negligible mass, its end A is...Ch. 17.5 - If the pin is connected to a track which is giver...Ch. 17.5 - Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder and...Ch. 17.5 - Also, find the angular acceleration of the roller....Ch. 17.5 - Determine the bars initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-106 if the roller is removed and the...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at A is s, =...Ch. 17.5 - If the truck has an acceleration of 3 m/s2...Ch. 17.5 - A cord is wrapped around the periphery of the disk...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at A is s =...Ch. 17.5 - At this instant the center of gravity of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the initial angular acceleration of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the time before it starts to roll...Ch. 17.5 - If they are released from rest determine the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the normal force which the path exerts...Ch. 17.5 - If it is originally at rest while being supported...Ch. 17.5 - If the pin support at A suddenly fails, determine...Ch. 17.5 - Determine its angular acceleration.Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the normal reactions at each of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the internal axial force Ex, shear force...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the maximum acceleration it can have if...Ch. 17.5 - The roil rest against a wall for which the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the magnitude of force F and the initial...Ch. 17.5 - Compute the reaction at the pin O just after the...Ch. 17.5 - if the coefficient of kinetic friction at the...Ch. 17.5 - The coefficient of kinetic friction is A = 0.3.
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Read Image)arrow_forwardM16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forwardProblem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forward
- Problem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forwardOnly question 2arrow_forwardOnly question 1arrow_forward
- Only question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forwardDescribe at least 4 processes in engineering where control charts are (or should be) appliedarrow_forward
- Describe at least two (2) processes where control charts are (or should be) applied.arrow_forwardProblem 3: A cube-shaped spacecraft is in a circular Earth orbit. Let N (n,) be inertial and the spacecraft is denoted S (ŝ₁). The spacecraft is described such that ¯½º = J ŝ₁ŝ₁ + J ŝ₂§₂ + J §¸Ŝ3 Location of the spacecraft in the orbit is determined by the orbit-fixed unit vectors ê, that are oriented by the angle (Qt), where is a constant angular rate. 52 €3 3> 2t 55 Λ Из At the instant when Qt = 90°, the spacecraft S is oriented relative to the orbit such that 8₁ = 0° Space-three 1-2-3 angles 0₂ = 60° and ES = $₂ rad/s 0₁ = 135° (a) At this instant, determine the direction cosine matrix that describes the orientation of the spacecraft with respect to the inertial frame N.arrow_forwardThis problem illustrates that the factor of safety for a machine element depends on the particular point selected for analysis. Here you are to compute factors of safety, based upon the distortion-energy theory, for stress elements at A and B of the member shown in the figure. This bar is made of AISI 1006 cold-drawn steel and is loaded by the forces F = 1.100 kN, P = 8.00 kN, and T = 50.00 N-m. Given: Sy = 280 MPa. B -100 mm- 15-mm D. a) Determine the value of the axial stress at point B. b) Determine the value of the shear stress at point B. c) Determine the value of the Von Mises stress at point B. P Farrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY