
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.5, Problem 101P
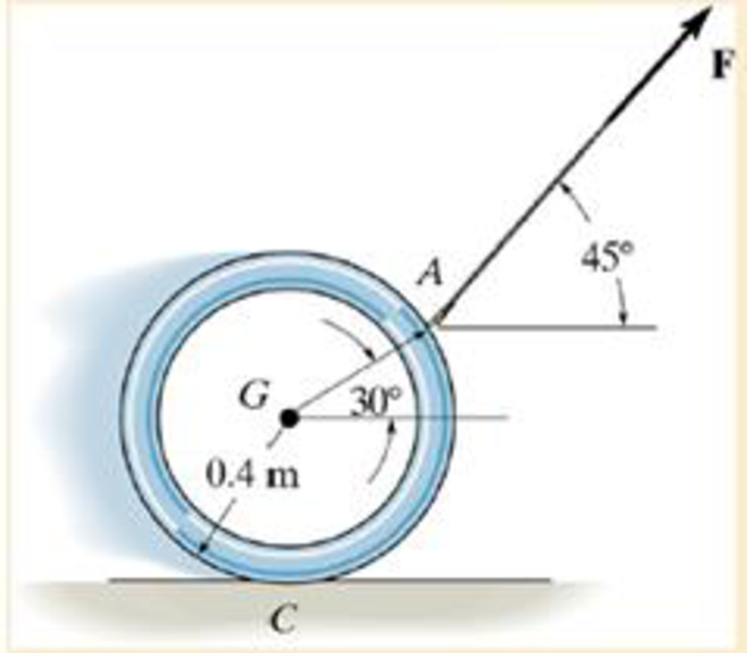
Neglect the thickness of the ring.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
13.64 The shaft shown in Sketch h transfers power between
the two pulleys. The tension on the slack side (right pul-
ley) is 30% of that on the tight side. The shaft rotates
at 900 rpm and is supported uniformly by a radial ball
bearing at points 0 and B. Select a pair of radial ball bear-
ings with 99% reliability and 40,000 hr of life. Assume
Eq. (13.83) can be used to account for lubricant clean-
liness. All length dimensions are in millimeters. Ans.
Cmin = 42,400 N.
A 4 inch wide, 12 inch tall cross section beam is subjected to an internal shear of 5.5 kips. What is the maximum transverse shear stress in the beam in psi if this bending is about the x axis?
A Brayton cycle produces 14 MW with an inlet state of 17°C, 100 kPa, and a compression ratio of 16:1. The heat added in the combustion is 960 kJ/kg. 0.7 MW of heat transferred from the turbine to the environment. What are the highest temperature and the mass flow rate of air? Assume cold air properties.
Chapter 17 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 17.1 - The rod's density end cross-sectional area. A are...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the mass of the cylinder end its moment...Ch. 17.1 - The nag has a mass m.Ch. 17.1 - Determine the radius of gyration kx. The density...Ch. 17.1 - The specific weight of the material is = 380...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Iz and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Ix and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Defending the moment of inertia Iy and express the...Ch. 17.1 - Express the result in terms of the mass m of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine me radius of gyration of the pendulum...
Ch. 17.1 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia of the solid steel...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the wheels moment of inertia about an...Ch. 17.1 - If the large ring, small ring and each of the...Ch. 17.1 - The thin plate has a hole in its center its...Ch. 17.1 - The material has a mass per unit area of 20 kg/m2.Ch. 17.1 - The block has a mass of 3 kg and the semicylinder...Ch. 17.1 - The block has a mass of 3 kg and the semicylinder...Ch. 17.1 - The material has a specific weight = 90 lb/ft3.Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 20PCh. 17.1 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 17.1 - The material is steel having a density of = 7.85...Ch. 17.1 - The material is steel having a density of = 7.85...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the acceleration of the can and the...Ch. 17.3 - If the 80-kg cabinet is allowed to roll down the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum acceleration of the frame...Ch. 17.3 - Also what is the corresponding normal reaction on...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the tension developed in the rods and...Ch. 17.3 - If it is subjected to a couple moment M = 450 N ...Ch. 17.3 - Determine how far the door moves in 25, starting...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the constant force F that must be...Ch. 17.3 - Initially at take-off the engines provide a thrust...Ch. 17.3 - If it starts from rest it causes the rear wheels...Ch. 17.3 - If the winch at B draws in the cable with an...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the greatest acceleration of the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the internal axial, shear, and...Ch. 17.3 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the reactions at both the wheels at A...Ch. 17.3 - Also, what is the acceleration of the cart? The...Ch. 17.3 - If it is subjected to a horizontal force of P =...Ch. 17.3 - Determine its initial acceleration if a man pushes...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the initial acceleration of a desk when...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - If it is released from rest, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - It is carried on a truck as shown. Determine the...Ch. 17.3 - It is carried on a truck as shown. If the truck...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the smallest acceleration that will...Ch. 17.3 - The coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.3 - If the collar is given a constant acceleration of...Ch. 17.3 - If it is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C,...Ch. 17.3 - If it is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C,...Ch. 17.3 - If the acceleration is a = 20 ft/s2, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - If h = 3 ft, determine the snowmobiles maximum...Ch. 17.3 - If the carts mass is 30 kg and it is subjected to...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform rod BC has a mass of 15 kg.Ch. 17.3 - If the acceleration of the truck is at = 0.5 m/s2,...Ch. 17.3 - If the angle = 30, determine the acceleration of...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the initial friction and normal force of...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the normal force NE, shear force VE, and...Ch. 17.4 - If the wheel starts from rest determine its...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the disk when t...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the tangential and normal components of...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the tangential and normal components or...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.4 - If the rod has a counterclockwise angular velocity...Ch. 17.4 - If the wheel is subjected to a moment M = (5t) N ...Ch. 17.4 - Determine its initial angular acceleration and the...Ch. 17.4 - If it is released from rest when = 0. determine...Ch. 17.4 - If it is released from rest in the position shown,...Ch. 17.4 - The reel rests on rollers at A and B and has a...Ch. 17.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 5 lb ft/rad, so...Ch. 17.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 5 lb ft/rad, so...Ch. 17.4 - If a force of F=(142)N, where is in radians, is...Ch. 17.4 - If no slipping occurs between them determine the...Ch. 17.4 - Show that IG may be eliminated by moving the...Ch. 17.4 - Treat the beam as a uniform slender rod.Ch. 17.4 - It consists of a 100-kg steel plate AC and a...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - Determine its angular velocity when t = 2 s...Ch. 17.4 - If it is placed on the ground for which the...Ch. 17.4 - Compute the time needed to unravel 5 m of cable...Ch. 17.4 - If the rotor always maintains a constant clockwise...Ch. 17.4 - It is originally spinning at = 40 rad/s. If it is...Ch. 17.4 - It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets...Ch. 17.4 - Disk E has a weight of 60 lb and is initially at...Ch. 17.4 - If the cylinders are released from rest, determine...Ch. 17.4 - If the pulley can be treated as a disk of mass 3...Ch. 17.4 - If the pulley can be treated as a disk of mass M,...Ch. 17.4 - Assume that the board is uniform and rigid, and...Ch. 17.4 - At the instant the rolor is horizontal it has an...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the initial tending moment at the fixed...Ch. 17.4 - Movement is controlled by the electromagnet E,...Ch. 17.4 - If it is rotating in the vertical plane at a...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the angular acceleration of the rod and...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 17.5 - If the powder burns at a constant rate of 20 g/s...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the acceleration of the bars mass center...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the acceleration of its mass center and...Ch. 17.5 - When the wheel is subjected to the couple moment,...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the angular acceleration of the sphere...Ch. 17.5 - If the couple moment is applied to the spool and...Ch. 17.5 - If the rod is released from rest at = 0,...Ch. 17.5 - rolls without slipping, show that when moments are...Ch. 17.5 - If it is initially at rest and is subjected to a...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-96 if the cord and force P = 50 N...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction...Ch. 17.5 - If a horizontal force of F = 80 N is applied to...Ch. 17.5 - If slipping does not occur, determine the rings...Ch. 17.5 - Neglect the thickness of the ring.Ch. 17.5 - Using a collar of negligible mass, its end A is...Ch. 17.5 - If the pin is connected to a track which is giver...Ch. 17.5 - Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder and...Ch. 17.5 - Also, find the angular acceleration of the roller....Ch. 17.5 - Determine the bars initial angular acceleration...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-106 if the roller is removed and the...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at A is s, =...Ch. 17.5 - If the truck has an acceleration of 3 m/s2...Ch. 17.5 - A cord is wrapped around the periphery of the disk...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at A is s =...Ch. 17.5 - At this instant the center of gravity of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the initial angular acceleration of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the time before it starts to roll...Ch. 17.5 - If they are released from rest determine the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the normal force which the path exerts...Ch. 17.5 - If it is originally at rest while being supported...Ch. 17.5 - If the pin support at A suddenly fails, determine...Ch. 17.5 - Determine its angular acceleration.Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the normal reactions at each of the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the internal axial force Ex, shear force...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the maximum acceleration it can have if...Ch. 17.5 - The roil rest against a wall for which the...Ch. 17.5 - Determine the magnitude of force F and the initial...Ch. 17.5 - Compute the reaction at the pin O just after the...Ch. 17.5 - if the coefficient of kinetic friction at the...Ch. 17.5 - The coefficient of kinetic friction is A = 0.3.
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- . A gas turbine with air enters the compressor at 300 K, 1 bar, and exits from the turbine at 750 K, 1 bar. The thermal efficiency of the cycle is 40.1% and the back work ratio (BWR) is 0.4. Find the pressure ratio of the cycle. Assume variable specific heat.arrow_forwardA regenerative gas turbine power plant is shown in Fig. below. Air enters the compressor at 1 bar, 27°C with a mass flow rate of 0.562 kg/s and is compressed to 4 bar. The isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 80%, and the regenerator effectiveness is 90%. All the power developed by the high-pressure turbine is used to run the compressor. The low-pressure turbine provides the net power output. Each turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 87% and the temperature at the inlet to the highpressure turbine is 1200 K. Assume cold air properties, determine: a. The net power output, in kW. b. The thermal efficiency of the cycle.arrow_forwardFor tixed inlet state and exit pressure, use a cold-air standard analysis to show that the pressure ratio across the two compressor stages that gives nunimum work input is:=)) k/(k-1) when Ta Ti, where Ta is the temperature of the air entering the second stage compressor and Pi is the intercooler pressure. Put the suitable assumptionsarrow_forward
- Derive the equation below ah ap ax 12μ ax, +( ah ap ay 12μ ay Where P P (x, y) is the oil film pressure. 1..ah 2 axarrow_forwardCan you determine the eignevalues by hand?arrow_forwardMonthly exam 13 2021-2022 Power plant Time: 1.5 Hrs Q1. A The gas-turbine cycle shown in Fig. is used as an automotive engine. In the first turbine, the gas expands to pressure Ps, just low enough for this turbine to drive the compressor. The gas is then expanded through the second turbine connected to the drive wheels. The data for the engine are shown in the figure, and assume that all processes are ideal. Determine the intermediate pressure Ps, the net specific work output of the engine, and the mass flow rate through the engine. Find also the air temperature entering the burner T3 and the thermal efficiency of the engine. Exhaust Air intake Φ www Regenerator www Bumer Compressor Turbine Power turbine et 150 kW Wompressor P₁ = 100 kPa T₁ = 300 K PP₁ =60 P-100 kPa T₁ = 1600 K Q2. On the basis of a cold air-standard analysis, show that the thermal efficiency of an ideal regenerative gas turbine can be expressed as 77 = 1- where - () () гp is the compressor pressure ratio, and T₁ and…arrow_forward
- I need to find m in R = mD from the image given. Do you really need to know what R and D is to find R. I was thinking geometrically we can find a relationship between R and D. D = R*cos(30). Then R = mD becomes m = R/D = 1/cos(30) = 1.1547. Is that correct?arrow_forwardQ1] B/ (16 Marks) To produce a lightweight epoxy part to provide thermal insulation. The available material are hollow glass beads for which the outside diameter is 1.6 mm and the wall thickness is 0.04 mm. Determine the weight and number of beads that must be added to the epoxy to produce a 0.5 kg of composite with a density of 0.65 g/cm³. The density of the glass is 2.5 g/cm³ and that of the epoxy is 1.25 g/cm³.arrow_forwardBelow is a projection of the inertia ellipsoid in the b1-b2 plane (b1 and b2 are unit vectors). All points on the ellipsoid surface represent moments of inertia in various directions. The distance R is related to the distance D such that R = md. Determine m.arrow_forward
- Below is a projection of the inertia ellipsoid in the b1-b2 plane (b1 and b2 are unit vectors). All points on the ellipsoid surface represent moments of inertia in various directions. Determine I_aa ( moment of inertia) for direction n_a (this is a unit vector).arrow_forwardThe problems are generally based on the following model: A particular spacecraft can be represented as a single axisymmetric rigid body B. Let n₂ be inertially fixed unit vectors; then, 6, are parallel to central, principal axes. To make the mathematics simpler, introduce a frame C where n₂ = ĉ₁ = b; initially. 6₁ Assume a mass distribution such that J =₁₁• B* •b₁ = 450 kg - m² I = b² •Ï¾˜ • b₂ = b¸ •Ï¾* •b¸ = 200 kg - m² K J-I C³ =r₁₁ = r₁₁arrow_forwardThe problems are generally based on the following model: A particular spacecraft can be represented as a single axisymmetric rigid body B. Let n₂ be inertially fixed unit vectors; then, 6, are parallel to central, principal axes. To make the mathematics simpler, introduce a frame C where n₂ = ĉ₁ = b; initially. 6₁ Assume a mass distribution such that J =₁₁• B* •b₁ = 450 kg - m² I = b² •Ï¾˜ • b₂ = b¸ •Ï¾* •b¸ = 200 kg - m² K J-I C³ =r₁₁ = r₁₁arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781285444543Author:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian JanesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781285444543Author:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian JanesPublisher:Cengage Learning Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305494695Author:Larry JeffusPublisher:Cengage Learning
Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305494695Author:Larry JeffusPublisher:Cengage Learning

Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781285444543
Author:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305494695
Author:Larry Jeffus
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Force | Free Body Diagrams | Physics | Don't Memorise; Author: Don't Memorise;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Bwwq1munB0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY