
Concept explainers
The ratio of
Answer to Problem 68AP
The ratio of
Explanation of Solution
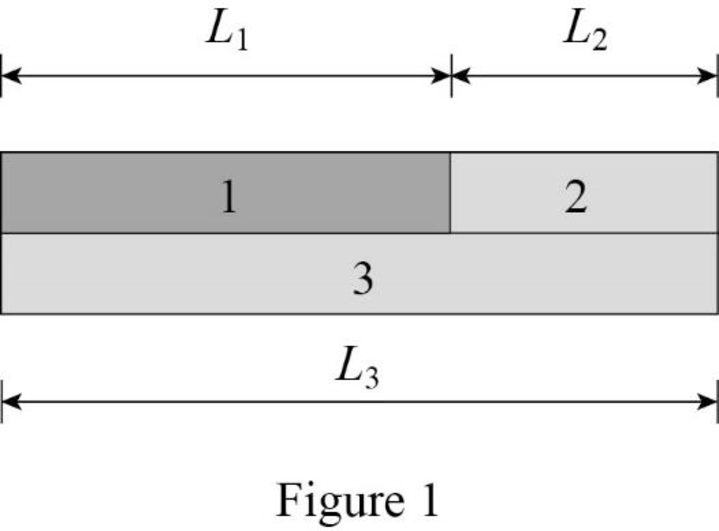
The time taken by the wave to travel a length
Here,
Substitute,
Use the above equation (II) to find the time taken to travel through each rod.
The time taken to travel through rod 1.
The time taken to travel through rod 2.
Substitute.
The time taken to travel through rod 3.
The required time is.
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
Since,
Take the ratio of length’s.
Therefore, the ratio of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- 1. What is the spring constant of a spring that starts 10.0 cm long and extends to 11.4 cm with a 300 g mass hanging from it?arrow_forwardplease help me solve all parts of this question from physics. thanks so much in advance! :)))arrow_forwardA fluid with density 263 kg/m3 flows through a pipe of varying diameter and height. At location 1 the flow speed is 13.5 m/s and the diameter of the pipe is 7.4 cm down to location 2 the pipe diameter is 16.9 cm. Location 1 is 6.3 meters higher than location 2. What is the difference in pressure P2 - P1? Using units in Pascals and use g = 9.81 m/s2.arrow_forward
- The kitchen had a temperature 46 degrees Fahrenheit and was converted it to Kelvin. What is the correct number for this temperature (46 F) on the Kelvin scale?arrow_forwardWater is traveling at a speed of 0.65 m/s through a pipe with a cross-section radius of 0.23 meters. The water enters a section of pipe that has a smaller radius, only 0.11 meters. What is the speed of the water traveling in this narrower section of pipe?arrow_forwardA particular water pipe has a radius of 0.28 meters. If the pipe is completely filled with water, moving with average velocity 0.45 m/s, what is the flow rate of water through the pipe with units of cubic meters of water per second?arrow_forward
- Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe with two segments. In one segment, the water flows at a speed v1 = 4.52 m/s. In the second segment the speed of the water is v2 = 2.38 m/s. Based on Bernoulli's Principle, what is the difference in pressure (P2 - P1) between the two segments? Assume that the density of the water is 997 kg/m3 and give your answer as the number of Pascals (i.e. N/m2).arrow_forwardWater from the faucet is supplied to the hose at a rate of 0.00057 m3/s. At what speed (number of meters per second) does the water exit the nozzle if the cross sectional area of the narrow nozzle is 2.1 x 10-6 m2?arrow_forwardJason Fruits/Indiana University Research Communications Silver/ silver oxide Zinc zinc/oxidearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





