
Concept explainers
Top Quality Fruit Company, based on Oahu, grows, processes, cans, and sells three main pineapple products: sliced, crushed, and juice. The outside skin is cut off in the Cutting Department and processed as animal feed. The feed is treated as a by-product. The company’s production process is as follows:
- Pineapples first are processed in the Cutting Department. The pineapples are washed and the outside skin is cut away. Then the pineapples are cored and trimmed for slicing. The three main products (sliced, crushed, juice) and the by-product (animal feed) are recognizable after processing in the Cutting Department. Each product then is transferred to a separate department for final processing.
- The trimmed pineapples are sent to the Slicing Department, where the pineapples are sliced and canned. Any juice generated during the slicing operation is packed in the cans with the slices.
- The pieces of pineapple trimmed from the fruit are diced and canned in the Crushing Department. Again, the juice generated during this operation is packed in the can with the crushed pineapple.
- The core and surplus pineapple generated from the Cutting Department are pulverized into a liquid in the Juicing Department. There is an evaporation loss equal to 8 percent of the weight of the good output produced in this department that occurs as the juices are heated.
- The outside skin is chopped into animal feed in the Feed Department.
Top Quality Fruit Company uses the net-realizable-value method to assign the costs of the joint process to its main products. The net realizable value of the by-product is subtracted from the joint cost before the allocation.
A total of 270,000 pounds were entered into the Cutting Department during June. The following schedule shows the costs incurred in each department, the proportion by weight transferred to the four final processing departments, and the selling price of each end product.
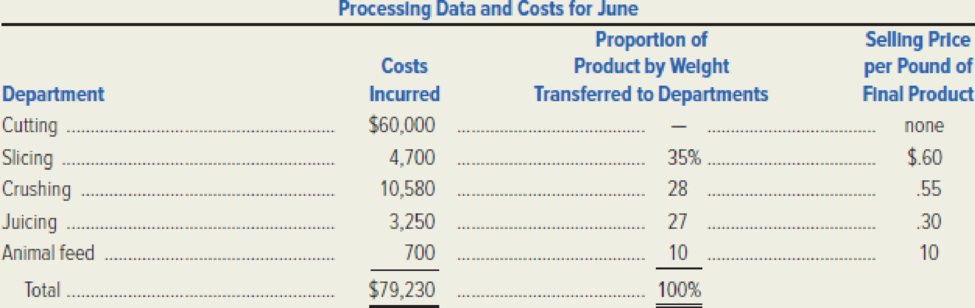
Required: Compute each of the following amounts.
- 1. The number of pounds of pineapple that result as output for pineapple slices, crushed pineapple, pineapple juice, and animal feed.
- 2. The net realizable value at the split-off point of the three main products.
- 3. The amount of the cost of the Cutting Department allocated to each of the three main products.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Access Card for Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment (NEW!!)
- GroFast Company manufactures a high-quality fertilizer, which is used primarily by commercial veg-etable growers. Two departments are involved in the production process. In the Mixing Department, various chemicals are entered into production. After processing, the Mixing Department transfers a chemical called Chemgro to the Finishing Department. There the product is completed, packaged, and shipped under the brand name Vegegro. Various chemicals --> Mixing Dept (Chemgro)-->Finishing Dept (Vegegro) ---> In the Mixing Department, the raw material is added at the beginning of the process. Labor and overhead are applied continuously throughout the process. All direct departmental overhead is traced to the departments, and plant overhead is allocated to the departments on the basis of direct-labor. The plant overhead rate for 20x2 is $.40 per direct-labor dollar. The following information relates to production during November 20x2 in the Mixing Department. a. Work in process,…arrow_forwardCooperative San José of southern Sonora state in Mexico makes a unique syrup using cane sugar and local herbs. The syrup is sold in small bottles and is prized as a flavoring for drinks and for use in desserts. The bottles are sold for $12 each. The first stage in the production process is carried out in the Mixing Department, which removes foreign matter from the raw materials and mixes them in the proper proportions in large vats. The company uses the weighted-average method in its process costing system. A hastily prepared report for the Mixing Department for April appears below: Units to be accounted for: Work in process, April 1 (materials 90% complete; conversion 80% complete) Started into production 9,700 31,900 Total units to be accounted for 41,600 Units accounted for as follows: Transferred to next department Work in process, April 30 (materials 75% complete; conversion 50% complete) Total units accounted for 27,600 14,000 41,600 Cost Reconciliation o be accounte Work in…arrow_forward1. What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for April? 2. What were the Mixing Department's cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for April? The beginning inventory consisted of the following costs: materials, $19, 251; and conversion cost, $9,177. The costs added during the month consisted of: materials, $88, 688; and conversion cost, $43,523. 3. How many of the units transferred out of the Mixing Department in April were started and completed during that month? 4. The manager of the Mixing Department stated, "Materials prices jumped from about $2.60 per unit in March to $3.10 per unit in April, but due to good cost control I was able to hold our materials cost to less than $3.10 per unit for the month." Should this manager be rewarded for good cost control?arrow_forward
- Boney Corporation processes sugar beets that it purchases from farmers. Sugar beets are processed in batches. A batch of sugar beets costs $53 to buy from farmers and $18 to crush in the company's plant. Two intermediate products, beet fiber and beet juice, emerge from the crushing process. The beet fiber can be sold as is for $25 or processed further for $18 to make the end product industrial fiber that is sold for $39. The beet juice can be sold as is for $32 or processed further for $28 to make the end product refined sugar that is sold for $79. What is the financial advantage (disadvantage) for the company from processing the intermediate product beet juice into refined sugar rather than selling it as is?arrow_forwardKLM, Inc., processes sugar beets in batches. A batch of sugar beets costs $51 to buy from farmers and $16 to crush in the company's plant. Two intermediate products, beet fiber and beet juice, emerge from the crushing process. The beet fiber can be sold as is for $23 or processed further for $18 to make the end product industrial fiber that is sold for $47. The beet juice can be sold as is for $46 or processed further for $20 to make the end product refined sugar that is sold for $59. How much profit (loss) does the company make by processing the intermediate product beet julce into refined sugar rather than selling it as is?arrow_forwardAmazon Beverages produces and bottles a line of soft drinks using exotic fruits from Latin America and Asia. The manufacturing process entails mixing and adding juices and coloring ingredients at the bottling plant, which is a part of Mixing Division. The finished product is packaged in a company-produced glass bottle and packed in cases of 24 bottles each. Because the appearance of the bottle heavily influences sales volume, Amazon developed a unique bottle production process at the company’s container plant, which is a part of Container Division. Mixing Division uses all of the container plant’s production. Each division (Mixing and Container) is considered a separate profit center and evaluated as such. As the new corporate controller, you are responsible for determining the proper transfer price to use for the bottles produced for Mixing Division. At your request, Container Division’s general manager asked other bottle manufacturers to quote a price for the number and sizes…arrow_forward
- Amazon Beverages produces and bottles a line of soft drinks using exotic fruits from Latin America and Asia. The manufacturing process entails mixing and adding juices and coloring ingredients at the bottling plant, which is a part of Mixing Division. The finished product is packaged in a company-produced glass bottle and packed in cases of 24 bottles each. Because the appearance of the bottle heavily influences sales volume, Amazon developed a unique bottle production process at the company’s container plant, which is a part of Container Division. Mixing Division uses all of the container plant’s production. Each division (Mixing and Container) is considered a separate profit center and evaluated as such. As the new corporate controller, you are responsible for determining the proper transfer price to use for the bottles produced for Mixing Division. At your request, Container Division’s general manager asked other bottle manufacturers to quote a price for the number and sizes…arrow_forwardBoney Corporation processes sugar beets that it purchases from farmers. Sugar beets are processed in batches. A batch of sugar beets costs $54 to buy from farmers and $11 to crush in the company's plant. Two intermediate products, beet fiber and beet juice, emerge from the crushing process. The beet fiber can be sold as is for $16 or processed further for $15 to make the end product industrial fiber that is sold for $66. The beet juice can be sold as is for $49 or processed further for $19 to make the end product refined sugar that is sold for $66. What is the financial advantage (disadvantage) for the company from processing the intermediate product beet juice into refined sugar rather than selling it as is? Multiple Choice O ($33) ($2) ($21) ($75)arrow_forwardWashington, Inc., makes three models of motorized carts for vacation resorts, X-10, X-20, and X-40. Washington manufactures the carts in two assembly departments: Department A and Department B. All three models are processed initially in Department A, where all material is assembled. The X-10 model is then transferred to finished goods. After processing in Department A, the X-20 and X-40 models are transferred to Department B for final assembly, and then transferred to finished goods. There were no beginning work-in-process inventories on April 1. Data for April are shown in the following table. Ending work in process is 25 percent complete in Department A and 60 percent complete in Department B. Conversion costs are allocated based on the number of equivalent units processed in each department. Total X-10 X-20 X-40 Units started 500 300 200 Units completed in Department A 400 260 180 Units completed in Department B 225…arrow_forward
- Washington, Inc., makes three models of motorized carts for vacation resorts, X-10, X-20, and X-40. Washington manufactures the carts in two assembly departments: Department A and Department B. All three models are processed initially in Department A, where all material is assembled. The X-10 model is then transferred to finished goods. After processing in Department A, the X-20 and X-40 models are transferred to Department B for final assembly, and then transferred to finished goods.There were no beginning work-in-process inventories on April 1. Data for April are shown in the following table. Ending work in process is 20 percent complete in Department A and 60 percent complete in Department B. Conversion costs are allocated based on the number of equivalent units processed in each department. Total X-10 X-20 X-40 Units started 510 390 270 Units completed in Department A 440 250 180 Units completed in Department B 225…arrow_forwardCooperative San José of southern Sonora state in Mexico makes a unique syrup using cane sugar and local herbs. The syrup is sold in small bottles and prized as a flavoring for drinks and desserts. The bottles are sold for $12 each. The first stage in the production process occurs in the Mixing Department, which removes foreign matter from the raw materials and mixes them in the proper proportions in large vats. The company uses the weighted average method of process costing. A hastily prepared report for the Mixing Department for April appears below: Units to be accounted for: Work in process, April 1 (materials 90% complete; conversion 80% complete )30,000Started into production200,000 Total units to be accounted for230,000 Units accounted for as follows: Transferred to next department190,000 Work in process, April 30 (materials 75% complete; conversion 60% complete)40,000 Total units accounted for230,000 Cost Reconciliation Cost to be accounted for: Work in process, April 1$…arrow_forwardStinehelfer Beet Processors, Inc., processes sugar beets in batches. A batch of sugar beets costs $39 to buy from farmers and $13 to crush in the company's plant. Two intermediate products, beet fiber and beet juice, emerge from the crushing process. The beet fiber can be sold as is for $21 or processed further for $13 to make the end product industrial fiber that is sold for $33. The beet juice can be sold as is for $41 or processed further for $37 to make the end product refined sugar that is sold for $73. What is the financial advantage (disadvantage) for the company from processing the intermediate product beet juice into refined sugar rather than selling it as is?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
