
Concept explainers
Problems 32 and 33 are paired.
N Seismic waves travel outward from the epicenter of an earthquake. A single earthquake produces both longitudinal seismic waves known as P waves and transverse waves known as S waves. Both transverse and longitudinal waves can travel through solids such as rock. Longitudinal waves can travel through fluids, whereas transverse waves can only be sustained near the surface of a fluid, not inside the fluid. When seismic waves encounter a fluid medium such as the liquid outer core of the Earth, only the longitudinal P wave can propagate through. Geophysicists can model the interior of the Earth by knowing where and when S and P waves were detected by seismographs after an earthquake (Fig. P17.32). Assume the average speed of an S wave through the Earth’s mantle is 5.4 km/s and the average speed of a P wave is 9.3 km/s. After an earthquake, a seismograph finds that the P wave arrives 1.5 min before the S wave. How far is the epicenter from the detector?
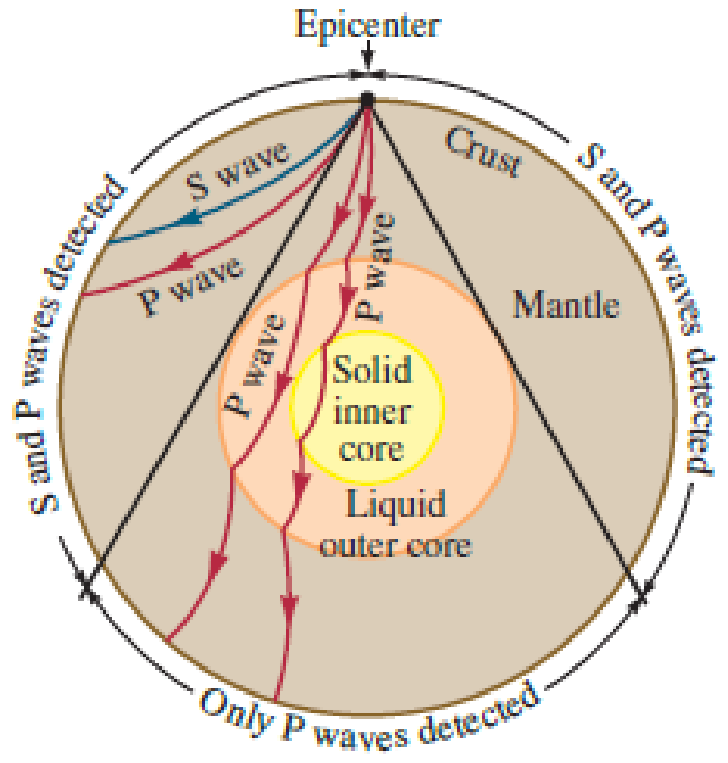
FIGURE P17.32
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- In general it is best to conceptualize vectors as arrows in space, and then to make calculations with them using their components. (You must first specify a coordinate system in order to find the components of each arrow.) This problem gives you some practice with the components. Let vectors A = (1,0, −3), B = (-2, 5, 1), and C = (3,1,1). Calculate the following, and express your answers as ordered triplets of values separated by commas.arrow_forwardOnly Part C.) is necessaryarrow_forwardOnly Part B.) is necessaryarrow_forward
- A (3.60 m) 30.0°- 70.0° x B (2.40 m)arrow_forwardIn general it is best to conceptualize vectors as arrows in space, and then to make calculations with them using their components. (You must first specify a coordinate system in order to find the components of each arrow.) This problem gives you some practice with the components. Let vectors A = (1,0, -3), B = (-2, 5, 1), and C = (3,1,1). Calculate the following, and express your answers as ordered triplets of values separated by commas.arrow_forwardfine the magnitude of the vector product express in sq meters what direction is the vector product in -z or +zarrow_forward
- 4) Three point charges of magnitude Q1 = +2.0 μC, Q2 = +3.0 μС, Q3 = = +4.0 μС are located at the corners of a triangle as shown in the figure below. Assume d = 20 cm. (a) Find the resultant force vector acting on Q3. (b) Find the magnitude and direction of the force. d Q3 60° d Q1 60° 60° Q2 darrow_forwardThree point charges of magnitudes Q₁ = +6.0 μС, Q₂ = −7.0 μС, Qз = −13.0 μC are placed on the x-axis at x = 0 cm, x = 40 cm, and x = 120 cm, respectively. What is the force on the Q3 due to the other two charges?arrow_forwardTwo point charges of +30.0 μС and -9.00 μC are separated by a distance of 20.0 cm. What is the intensity of electric field E midway between these two charges?arrow_forward
- Two point charges of +7.00 μС and +10.0 μС are placed inside a cube of edge length 0.100 m. What is the net electric flux due to these charges?arrow_forwardA conducting hollow sphere has a charge density of σ = 12.2 μC/m². If the sphere has a radius of 25 cm, what net charge is on the sphere?arrow_forward9) Consider an electric field right Ĕ = 21+3ĵ. What is the magnitude of the flux of this field through a 4.0 m² square surface whose corners are located at (x,y,z) = (0, 2, 1), (2, 2, 1), (2, 2, −1), (0, 2, −1)? Ꮓ ту x (0,2,1) Surface 2 Surface (2,2,1) y Ē (0,2,-1) (2,2,-1) 2 xarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





