
Concept explainers
18-4 Answer true or false.
(a) The
(b) The VSEPR model predicts bond angles of 180° about the carbonyl carbon of a carboxyl group.
(c) The VSEPR model predicts bond angles of 109.5° about the oxygen of the OH group of a carboxyl group.
(d) The carbonyl carbon of a carboxyl group can be a stereocenter, depending on its location within a molecule.
(e) Carboxylic acids can be prepared by chromic acid oxidation of primary alcohols and of
(f) The product of chromic acid oxidation of hexanoic acid is 1-hexanol.
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement.
The functional groups of carboxylic acids are a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Carboxylic acid group contain one carbonyl group and one hydroxyl group that is −COOH.
Explanation of Solution
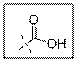
As per the given structure the carboxyl group contains a carbonyl group which is bonded to a hydroxyl group. So the statement is true.
Carboxylic acid functional group is known as COOH. When this group is elaborately written it shows two functional groups. Those groups are carbonyl group and another is hydroxyl group.
So the carboxyl group contains a carbonyl group which is bonded to a hydroxyl group.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement.
The VSEPR model predicts bond angles of
Concept Introduction:
Carboxylic acid group contain one carbonyl group and one hydroxyl group. VSEPR theory stands for valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory predict the geometry of molecules on the basis of the number of electron pairs present surrounding the central atoms.
Explanation of Solution
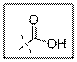
As per the given structure the carboxyl group contains a carbonyl group which is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The angle is
Carboxylic acid functional group is known as COOH. When this group is elaborately written it shows two functional groups. Those groups are carbonyl group and another is hydroxyl group. The hybridization of the carbonyl carbon is sp2 and thus expected bond angle is
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement.
The VSEPR model predicts bond angles of
Concept Introduction:
Carboxylic acid group contain one carbonyl group and one hydroxyl group and the oxygen atom of hydroxyl group is sp3 hybridized. VSEPR theory stands for valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory predict the geometry of molecules on the basis of the number of electron pairs present surrounding the central atoms.
Explanation of Solution
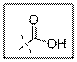
As per the given structure the carboxyl group contains a carbonyl group which is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The oxygen atom of hydroxyl group is sp3 hybridized. So expected bond angle is angle is
But due to two lone pair electrons on oxygen atom bond angle will be lesser than
Carboxylic acid functional group is known as COOH. When this group is elaborately written it shows two functional groups. Those groups are carbonyl group and another is hydroxyl group. The hybridization of the oxygen atom of hydroxyl group is sp3 and thus expected bond angle is
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement.
The carbonyl carbon of a carboxyl group can be a stereocenter, depending on its location within a molecule is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl carbon has double bonded oxygen atom and also linked with hydroxyl group. Stereocentre is defined as the centre in which all the groups attached to the atom generally carbon atom, should be different.
Explanation of Solution
As carbonyl group has double bonded oxygen atom and thus it can’t be a stereocenter. So the statement is false.
Carboxyl group is a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group. Carbonyl carbon being double bonded to oxygen it is not a stereocenter.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement.
Carboxylic acid can be prepared by chromic acid oxidation of primary alcohols and of aldehydes is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Chromic acid is very strong oxidizing agent. Oxidizing agent is defined as the oxidant which gains electrons and reduced in the chemical reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Chromic acid being very strong oxidizing agent it is possible to oxidize primary alcohols and aldehydes to carboxylic acid. So the statement is true.
When primary alcohols are oxidized with chromic acid then the alcohol is first converted to aldehyde which in turn converted to carboxylic acid.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement.
The product of chromic acid oxidation of hexanoic acid is 1-hexanol is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
When 1-hexanol is oxidized it is converted to hexanoic acid. Oxidation is the process in which either loss of electrons or increase in the oxidation number takes plcae.
Explanation of Solution
1-Hexanol can be converted to hexanoic acid after treatment with chromic acid but the product of chromic acid oxidation of hexanoic acid is not 1-hexanol.
So the statement is false.
1-Hexanol can be converted to hexanoic acid with chromic acid. But 1-hexanol can’t be obtained after oxidizing hexanoic acid with chromic acid. For getting 1-hexanol from hexanoic acid reducing agent is required instead of chromic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




