
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of 2-hydroxyheptanoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
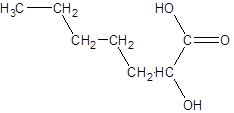
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest)
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 2-hydroxyheptanoic acid where the parent chain is heptane that is 7 carbon atom chain having a hydroxy substituent at carbon-2. So, the structure of 2-hydroxyheptanoic acid is:
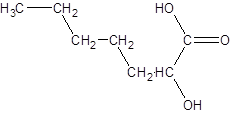
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of 4-chlorononanoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
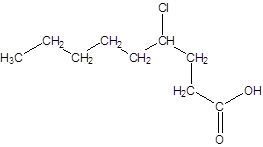
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 4-chlorononanoic acid where the parent chain is nonane that is 9 carbon atom chain having a chloro substituent at carbon-4. So, the structure of 4-chlorononanoic acid is:
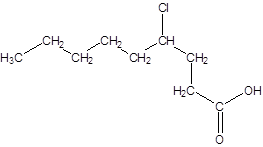
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,4-dibromobenzoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
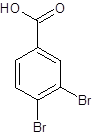
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 3,4-dibromobenzoic acid where the parent chain is benzene having 2 bromo substituents at carbon-3 and carbon-4. So, the structure of 3,4-dibromobenzoic acid is:
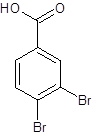
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of lithium propanoate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
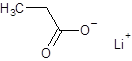
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When H of hydroxyl group present in carboxylic acid is replaced by an atom then it results in the formation of respective salt.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid salt according to the following steps:
- The parent (longest) carbon chain is identified.
- The name of metal is written first from which the salt is made up of.
- The ending of the for a carboxylic acid group is changed to -oate for naming salt of carboxylic acid.
- The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
- Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is lithium propanoate where the parent chain is propane having 3 carbon atoms and metal is lithium. So, the structure of lithium propanoate is:
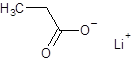
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of 2,2-dibromobutanoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
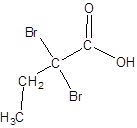
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 2,2-dibromobutanoic acid where the parent chain is butane that is 4 carbon atom chain having two bromo substituents at carbon-2. So, the structure of 2,2-dibromobutanoic acid is:
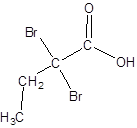
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of ethyl 2-methylpropanoate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
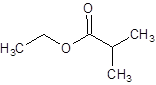
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -H of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (-R') then it results in the formation of an ester having general formula RCOOR'.
The reaction which results in the formation of at least one ester along with water on heating acids with alcohols is said to be esterification.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the esters, the following steps are followed:
- The alkyl substituent from the alcohol is named first.
- The name of the parent chain from carboxylic acid part is replaced as carboxylate.
In order to write the common name of the esters, the common of acids are written from which the ester has been formed.
The given name is ethyl 2-methylpropanoate where ethyl name is derived from ethanol and 2-methylpropanoate is derived from the name 2-methylpropanoic acid. So, the structure of ethyl 2-methylpropanoate is:
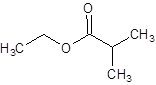
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
- Identify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
- in the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




