
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780134421353
Author: Karen C. Timberlake
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.5, Problem 16.46PP
The following graph shows the activity versus pH curves for pepsin, sucrase, and trypsin. Estimate the optimum pH for each.
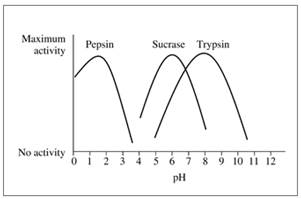
16.46 Refer to the graph in problem 16.45 to determine if the reaction rate in each condition will be at the optimum rate or not.
- Trypsin, pH 5.0
- Sucrase, pH 5.0
- Pepsin, pH 4.0
- Trypsin, pH 8.0
- Pepsin, pH 2.0
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Can you please help mne with this problem. Im a visual person, so can you redraw it, potentislly color code and then as well explain it. I know im given CO2 use that to explain to me, as well as maybe give me a second example just to clarify even more with drawings (visuals) and explanations.
Part 1. Aqueous 0.010M AgNO 3 is slowly added to a 50-ml solution containing both carbonate [co32-] = 0.105 M
and sulfate [soy] = 0.164 M anions. Given the ksp of Ag2CO3 and Ag₂ soy below. Answer the ff:
Ag₂ CO3 = 2 Ag+ caq) + co} (aq)
ksp = 8.10 × 10-12
Ag₂SO4 = 2Ag+(aq) + soy² (aq) ksp = 1.20 × 10-5
a) which salt will precipitate first?
(b)
What % of the first anion precipitated will remain in the solution.
by the time the second anion starts to precipitate?
(c) What is the effect of low pH (more acidic) condition on the separate of the carbonate and
sulfate anions via silver precipitation? What is the effect of high pH (more basic)? Provide appropriate
explanation per answer
Part 4. Butanoic acid (ka= 1.52× 10-5) has a partition coefficient of 3.0 (favors benzene) when distributed bet.
water and benzene. What is the formal concentration of butanoic acid in each phase when
0.10M aqueous butanoic acid is extracted w❘ 25 mL of benzene
100 mL of
a) at pit 5.00
b) at pH 9.00
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Ch. 16.1 - Classify each of the following proteins according...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.2PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.3PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.4PPCh. 16.1 - Draw the structure for each of the following amino...Ch. 16.1 - Draw the structure for each of the following amino...Ch. 16.1 - Draw the strcture for each of the following amino...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.8PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.9PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.10PP
Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.11PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.12PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.13PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.14PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.15PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.16PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 16.17PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 16.18PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 16.19PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 16.20PPCh. 16.3 - What type of interaction would you expect between...Ch. 16.3 - What type of interaction would you expect between...Ch. 16.3 - Prob. 16.23PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 16.24PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 16.25PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 16.26PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 16.27PPCh. 16.3 - Indicate the changes in secondary and tertiary...Ch. 16.4 - Why do chemical reactions in the body require...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 16.30PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 16.31PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 16.32PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 16.33PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 16.34PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 16.35PPCh. 16.4 - 16.36 Match the terms (1) active site, (2)...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 16.37PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 16.38PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 16.39PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 16.40PPCh. 16.4 - For problems 16.39 to 16.42, see Chemistry Link to...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 16.42PPCh. 16.5 - Trypsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes polypeptides,...Ch. 16.5 - pepsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes proteins,...Ch. 16.5 - The following graph shows the activity versus pH...Ch. 16.5 - The following graph shows the activity versus pH...Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 16.47PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 16.48PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 16.49PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 16.50PPCh. 16.5 - What is the chemical formula for hydroxyurea?Ch. 16.5 - What is the molar mass of hydroxyurea?Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 16.53PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 16.54PPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.55UTCCh. 16 - Prob. 16.56UTCCh. 16 - Prob. 16.57UTCCh. 16 - Prob. 16.58UTCCh. 16 - 16.59 Identify the amino acids and type of...Ch. 16 - What type of interaction would you expect between...Ch. 16 - Draw the condensed structural formula for...Ch. 16 - Draw the condensed structural formula for...Ch. 16 - Seed and vegetables are often deficient in one or...Ch. 16 - 16.64 Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.65APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.66APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.67APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.68APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.69APPCh. 16 - Why do enzymes function only under mild...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.71APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.72APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.73APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.74APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.75APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.76APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.77APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.78APPCh. 16 - If a blood test indicates a high level of LDH and...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.80APPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.81CPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.82CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0 Group of answer choices 0.0269 kJ/mole 2610 kJ/mole 27.6 kJ/mole 0.215 kJ/mole 20.8 kJ/molearrow_forwardCalculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0 choices: 0.0269 kJ/mole 2610 kJ/mole 27.6 kJ/mole 0.215 kJ/mole 20.8 kJ/molearrow_forwardCalculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0arrow_forward
- Please solvearrow_forwardRank the compounds in each group below according to their reactivity toward electrophilic aromatic substitution (most reactive = 1; least reactive = 3). Place the number corresponding to the compounds' relative reactivity in the blank below the compound. a. CH₂F CH3 F b. At what position, and on what ring, is bromination of phenyl benzoate expected to occur? Explain your answer. :0: C-O phenyl benzoate 6.Consider the reaction below to answer the following questions. A B C NO₂ FeBr3 + Br₂ D a. The nucleophile in the reaction is: BODADES b. The Lewis acid catalyst in the reaction is: C. This reaction proceeds d. Draw the structure of product D. (faster or slower) than benzene.arrow_forwardPart 2. A solution of 6.00g of substance B in 100.0mL of aqueous solution is in equilibrium, at room temperature, wl a solution of B in diethyl ether (ethoxyethane) containing 25.0 g of B in 50.0 mL 9) what is the distribution coefficient of substance B b) what is the mass of B extracted by shaking 200 ml of an aqueous solution containing 10g of B with call at room temp): i) 100 mL of diethyl ether ii) 50ml of diethyl ether twice iii) 25ml of diethyl ether four timesarrow_forward
- - Rank the following groups of compounds from most acidic (1) to least acidic (4). Place the number corresponding to the compound's relative rank in the blank below the structure. a. NO₂ NO₂ CH2CH2CH2CH2OH CH3 CH3CH2CHOH CH3CH2CH2CH2OH NO₂ CH3CHCH2CH2OH b. OH OH CH₂OH CO₂H HC CN CN CNarrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry a. H MgBr 1. ether 2. H₂O* 4 COH b. 1. LIAIH, ether 2. H₂O Choose the best reagent(s) for carrying out the following conversions from the list provided below. Place the letter of the best choice in the blank to the left of the conversion. Reagents may be used more than once. a. 1. CH3MgBr, ether 2. H3O+ NaOH b. 1. PBr3 2. C. 2. 1. (CH3)3SiCl, (CH3CH2)3N CH3MgBr, ether 3. H₂O*+ 2. H3O+ e. 1. p-TosCl, pyridine f. نها g. 2. NaOH CrO3, H₂SO4, H₂O 1. NaBH4, ethanol 2. H30* h. PCC, CH2Cl2 Ovoldo-6 a. b. OH OH H OH O any organicarrow_forwardDetermine the rate law for sodium thiosulfate from the following data: [Na2S2O3] Time (s) 0.0318 230. 0.0636 57.5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
DIGESTER-35 | VITAMINS AND THEIR RELATED COENZYMES| GPAT | NIPER | PHARMACIST| DI; Author: GPAT DISCUSSION CENTER;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CGrdNYmho0s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY