
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977237
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.1, Problem 16.64P
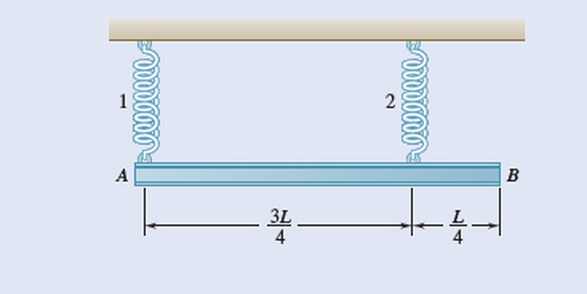
A beam AB with a mass m and of uniform cross-section is suspended from two springs as shown. If spring 2 breaks, determine at that instant (a) the angular acceleration of the beam, (b) the acceleration of point A, (c) the acceleration of point B.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Quiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size
for weld w1 is h1=6mm, for w2 h2 5mm, and for w3 is h3 -5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds.
F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx).
140
101.15
REDMI NOTE 8 PRO
AI QUAD CAMERA
F
Quiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size
for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2 = 6mm, and for w3 is h3 -6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds.
F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx).
BES FOR P
163 mm
133 mm
140 mm
Example
-4s
F(s) =
=
(s²+4)²
As + B Cs+D
+
(s²+4) (s²+4)²
(s²+4)
(H.W)
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two solid cylinders, A and B, have the same mass m...Ch. 16.1 - A 6-ft board is placed in a truck with one end...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.F2PCh. 16.1 - Two uniform disks and two cylinders are assembled...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.F4PCh. 16.1 - A 60-Ib uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - Knowing that the coefficient of static friction...
Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.4PCh. 16.1 - A uniform rod BC of mass 4 kg is connected to a...Ch. 16.1 - A 2000-kg truck is being used to lift a 400-kg...Ch. 16.1 - The support bracket shown is used to transport a...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.8PCh. 16.1 - A 20-kg cabinet is mounted on casters that allow...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.10PCh. 16.1 - A completely filled barrel and its contents have a...Ch. 16.1 - A 40-kg vase has a 200-mm-diameter base and is...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.13PCh. 16.1 - Bars AB and BE, each with a mass of 4 kg, are...Ch. 16.1 - At the instant shown, the tensions in the vertical...Ch. 16.1 - Three bars, each of mass 3 kg, are welded together...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.17PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.18PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.19PCh. 16.1 - The coefficients of friction between the 30-lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.21PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.22PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.23PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.24PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.25PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.26PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.27PCh. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.27, assuming that the initial...Ch. 16.1 - The 100-mm-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 180-mm-radius disk is at rest when it is...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.30, assuming that the direction of...Ch. 16.1 - In order to determine the mass moment of inertia...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.33PCh. 16.1 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a mass moment...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.35PCh. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.35, assuming that the couple M is...Ch. 16.1 - Gear A weighs 1 lb and has a radius of gyration of...Ch. 16.1 - The 25-lb double pulley shown is at rest and in...Ch. 16.1 - A belt of negligible mass passes between cylinders...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.39 for P=2.00lb .Ch. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass of 6 kg and an initial angular...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.42PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.43PCh. 16.1 - Disk B is at rest when it is brought into contact...Ch. 16.1 - Cylinder A has an initial angular velocity of 720...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.46PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.47PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.48PCh. 16.1 - (a) In Prob. 16.48, determine the point of the rod...Ch. 16.1 - A force P with a magnitude of 3 N is applied to a...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.51PCh. 16.1 - A 250-lb satellite has a radius of gyration of 24...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.53PCh. 16.1 - A uniform semicircular plate with a mass of 6 kg...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.55PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.56PCh. 16.1 - The 12-lb uniform disk shown has a radius of r=3.2...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.58PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.59PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.60PCh. 16.1 - The 400-lb crate shown is lowered by means of two...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.62PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.63PCh. 16.1 - A beam AB with a mass m and of uniform...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.65PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.66PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.67PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.68PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.69PCh. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.69, assuming that the sphere is...Ch. 16.1 - A bowler projects an 8-in.-diameter ball weighing...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.71, assuming that the bowler...Ch. 16.1 - A uniform sphere of radius r and mass m is placed...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m has a linear...Ch. 16.2 - A cord is attached to a spool when a force P is...Ch. 16.2 - A cord is attached to a spool when a force P is...Ch. 16.2 - A front-wheel-drive car starts from rest and...Ch. 16.2 - A front-wheel-drive car starts from rest and...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.F5PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.F6PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.F7PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.F8PCh. 16.2 - Show that the couple I of Fig. 16.15 can be...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.76PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.77PCh. 16.2 - A uniform slender rod of length L=36 in. and...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.79PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.80PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.81PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.82PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.83PCh. 16.2 - A uniform rod of length L and mass m is supported...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.85PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.86PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.87PCh. 16.2 - Two identical 4-lb slender rods AB and BC are...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.89PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.90PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.91PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.92PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.93PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.94PCh. 16.2 - A homogeneous sphere S, a uniform cylinder C, and...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.96PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.97PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.98PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.99PCh. 16.2 - A drum of 80-mm radius is attached to a disk of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.101PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.102PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.103PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.104PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.105PCh. 16.2 - A 12-in.-radius cylinder of weight 16 lb rests on...Ch. 16.2 - A 12-in.-radius cylinder of weight 16 lb rests on...Ch. 16.2 - Gear C has a mass of 5 kg and a centroidal radius...Ch. 16.2 - Two uniform disks A and B, each with a mass of 2...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.110PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.111PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.112PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.113PCh. 16.2 - A small clamp of mass mBis attached at B to a hoop...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.115PCh. 16.2 - A 4-lb bar is attached to a 10-lb uniform cylinder...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform rod AB with a mass m and a length of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.118PCh. 16.2 - A 40-lb ladder rests against a wall when the...Ch. 16.2 - A beam AB of length L and mass m is supported by...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.122PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.123PCh. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform rod ABD is attached to the crank...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.126PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.127PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.128PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.129PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.130PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.131PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.132PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.133PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.134PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.135PCh. 16.2 - The 6-kg rod BC connects a 10-kg disk centered at...Ch. 16.2 - In the engine system shown, l=250 mm and b=100 mm....Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.137 when =90 .Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.140PCh. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.142PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.143PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.144PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.145PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.146PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.147PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.148PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.149PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.150PCh. 16.2 - (a) Determine the magnitude and the location of...Ch. 16.2 - Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the...Ch. 16 - A cyclist is riding a bicycle at a speed of 20 mph...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.154RPCh. 16 - The total mass of the Baja car and driver,...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.156RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.157RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.158RPCh. 16 - A bar of mass m=5 kg is held as shown between four...Ch. 16 - A uniform plate of mass m is suspended in each of...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.161RPCh. 16 - Two 3-kg uniform bars are connected to form the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.163RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.164RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q1/ Find L[t et sin t] Q2/ Find The Laplace Transform f(t) = [sint [sint 0arrow_forwardb) The 50 mm diameter rod is placed in a hole, lubricated walls. There is no clearance between the rod and the sides of the hole. Determine the change in length of the rod if an 8 kN load is applied. Take E(brass) = 80 GPa; v = 0.55 [10] 50 mmm 300 rat 3arrow_forwardThe Mach number NM for flow of a perfect gas in a pipe depends upon the specific-heat ratio k (dimensionless), the pressure p, the density ρ, and the velocity V. Obtain by dimensional reasoning the form of the Mach number expression. (Buckingham pi)Answer: NM = f(V/sqrt(p/ρ), k)arrow_forwardoyfr 3. The figure shows a frame under the influence of an external loading made up of five forces and two moments. Use the scalar method to calculate moments. a. Write the resultant force of the external loading in Cartesian vector form. b. Determine the & direction of the resultant moment of the external loading about A. 15 cm 18 cm 2.2 N-m B 50 N 45° 10 cm 48 N.m 250 N 60 N 20 21 50 N 25 cm 100 N A 118, 27cm 5, 4:1arrow_forwardAssume the Link AO is the input and revolves 360°, determine a. the coordinates of limit positions of point B, b. the angles (AOC) corresponding to the limit positionsarrow_forwardoyfr 3. The figure shows a frame under the influence of an external loading made up of five forces and two moments. Use the scalar method to calculate moments. a. Write the resultant force of the external loading in Cartesian vector form. b. Determine the & direction of the resultant moment of the external loading about A. 15 cm 18 cm 2.2 N-m B 50 N 45° 10 cm 48 N.m 250 N 60 N 20 21 50 N 25 cm 100 N A 118, 27cm 5, 4:1arrow_forwardThe 2-mass system shown below depicts a disk which rotates about its center and has rotational moment of inertia Jo and radius r. The angular displacement of the disk is given by 0. The spring with constant k₂ is attached to the disk at a distance from the center. The mass m has linear displacement & and is subject to an external force u. When the system is at equilibrium, the spring forces due to k₁ and k₂ are zero. Neglect gravity and aerodynamic drag in this problem. You may assume the small angle approximation which implies (i) that the springs and dampers remain in their horizontal / vertical configurations and (ii) that the linear displacement d of a point on the edge of the disk can be approximated by d≈re. Ө K2 www m 4 Cz 777777 Jo Make the following assumptions when analyzing the forces and torques: тв 2 0>0, 0>0, x> > 0, >0 Derive the differential equations of motion for this dynamic system. Start by sketching LARGE and carefully drawn free-body-diagrams for the disk and the…arrow_forwardA linear system is one that satisfies the principle of superposition. In other words, if an input u₁ yields the output y₁, and an input u2 yields the output y2, the system is said to be linear if a com- bination of the inputs u = u₁ + u2 yield the sum of the outputs y = y1 + y2. Using this fact, determine the output y(t) of the following linear system: given the input: P(s) = = Y(s) U(s) = s+1 s+10 u(t) = e−2+ sin(t) =earrow_forwardThe manometer fluid in the figure given below is mercury where D = 3 in and h = 1 in. Estimate the volume flow in the tube (ft3/s) if the flowing fluid is gasoline at 20°C and 1 atm. The density of mercury and gasoline are 26.34 slug/ft3 and 1.32 slug/ft3 respectively. The gravitational force is 32.2 ft/s2.arrow_forwardUsing the Bernoulli equation to find the general solution. If an initial condition is given, find the particular solution. y' + xy = xy¯¹, y(0) = 3arrow_forwardTest for exactness. If exact, solve. If not, use an integrating factor as given or obtained by inspection or by the theorems in the text. a. 2xydx+x²dy = 0 b. (x2+y2)dx-2xydy = 0 c. 6xydx+5(y + x2)dy = 0arrow_forwardNewton's law of cooling. A thermometer, reading 5°C, is brought into a room whose temperature is 22°C. One minute later the thermometer reading is 12°C. How long does it take until the reading is practically 22°C, say, 21.9°C?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY