
Concept explainers
A 250-lb satellite has a radius of gyration of 24 in. with respect to the y axis and is symmetrical with respect to the zx plane. Its orientation is changed by firing four small rockets—A, B, C, and D—each of which produces a 4-lb thrust T directed as shown. Determine the angular acceleration of the satellite and the acceleration of its mass center G (a) when all four rockets are fired, (b) when all rockets except D are fired.
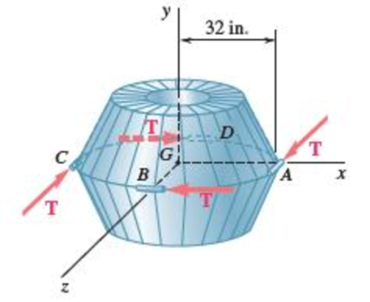
Fig. P16.52
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Heating Ventilating and Air Conditioning: Analysis and Design
- Dynamicsarrow_forwardA torque T of 100 N-m is applied to a wheel D having a mass of 50 kg. a diame- ter of 600 mm, and a radius of gyration of 280 mm. The wheel D is attached by a light member AB to a slider C having a mass of 30 kg. If the system is at rest at the instant shown, what is the acceleration of slider C? What is the axial force in member AB? Neglect friction everywhere, and neglect the inertia of the memberAB. (Draw FBDs)arrow_forwardIn the helicopter shown; a vertical tail propeller is used to pre- vent rotation of the cab as the speed of the main blades is changed. Assuming that the tail propeller is not operating determine the final angular velocity of the cab after the speed of the main blades has been changed from I80 to 240 rpm. (The speed of the main blades is measured relative to the cab, and the cab has a centroidal moment of inertia of 650 lb.ft.s2. Each of the four main blades is assumed to be a slender rod 14 ft weighing 55 lb.)arrow_forward
- Problem (1) Gears A and B each have a mass of 4 kg and a radius of gyration of 75 mm about their centers, while gear C has a mass of 15 kg and a radius of gyration of 180 mm about its center. A couple moment M = (0.20) N-m is applied to gear C. Determine the number of revolutions gears A and B experience if gear C increases its angular velocity from 25 rpm to 500 rpm. B 80 mm S0 mm 200 mmarrow_forward6. The uniform ring of mass m = 10 kg and radius r= 0.5 m is hinged at O and can rotate freely in the vertical plane. If the ring is released with a clockwise angular velocity o = 4 rad/s from the position shown where OC is horizontal, determine the magnitude of the reaction at pin O the instant the disk is released. toarrow_forwardA turbine rotor is found to be out of balance to the extent of 1.5 kg at 0.45 m radius in the plane AA and 2kg at 0.6 m radius in the plane BB, the relative angular positions being given in the end view. It is desired to balance these masses by a mass in each of the planes XX and YY at radii of 0.525m and 0.45m respectively. Determine the magnitude and positions of these masses and show their positions in an end view. (Answer: X, 1.42kg, 209.27 degrees from A; y, 2.12KG, 329.1 degrees from A)arrow_forward
- Gear A has a mass of 1 kg and a radius of gyration of 30 mm; gear B has a mass of 4 kg and a radius of gyration of 75 mm; gear C has a mass of 9 kg and a radius of gyration of 100 mm. The system is at rest when a couple M0 of constant magnitude 4 N.m is applied to gear C . Assuming that no slipping occurs between the gears, determine the number of revolutions required for disk A to reach an angular velocity of 300 rpm.arrow_forward4. (20 pts) A concrete block is lifted by a hoisting mechanism in which the cables are securely wrapped around their respective drums. The drums are fastened together and rotate as a single unit at their center of mass O. Combined mass of drum is 150 kg, and radius of gyration at O is 450 mm. A constant tension of 1.8 kN is maintained in the cable by the power unit at A. Determine the vertical acceleration of the block and the resultant force on the bearing at O. 600 mm 300 mm P = 1.8 kN m = 150 kg ko = 450 mm %3D 45° 300 kgarrow_forwardGive me right solution with clear calculationsarrow_forward
- If the earth were a sphere, the gravitational attraction of the sun, moon, and planets would at all times be equivalent to a single force R acting at the mass center of the earth. However, the earth is actually an oblate spheroid and the gravitational system acting on the earth is equivalent to a force R and a couple M. Knowing that the effect of the couple M is to cause the axis of the earth to precess about the axis GA at the rate of one revolution in 25 800 years, determine the average magnitude of the couple M applied to the earth. Assume that the average density of the earth is 5.51 g/cm 3 , that the average radius of the earth is 6370 km, and that ( Note: This forced precession is known as the precession of the equinoxes and is not to be confused with the free precession discussed in Prob. 18.123.)arrow_forwardA homogeneous disk of mass m = 4 kg rotates at the constant rate wi = 12 rad/s with respect to arm OA, which itself rotates at the constant rate wz = 4 rad/s about the y- axis, determine: 1. Angular momentum of the disk about point A. 2. Angular momentum of the disk about point O. 3. The force-couple system representing the dynamic reactions at the support. Neglect the mass of of arm OA. 320 min 200 mm T = 100 mmarrow_forwardThe mass of gear A is 25 kg and its centroidal radius of gyration is 105 mm. The mass of gear B is 13 kg and its centroidal radius of gyration is 85 mm. Calculate the angular acceleration of gear B when a torque of 16 N·m is applied to the shaft of gear A. Neglect friction. The angular acceleration is positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise..arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





