
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977251
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.1, Problem 16.35P
Two disks A and B, of mass mA = 2 kg and mB = 4 kg, are connected by a belt as shown. Assuming no slipping between the belt and the disks, determine the angular acceleration of each disk if a 2.70-N·m counterclockwise couple M is applied to disk A.
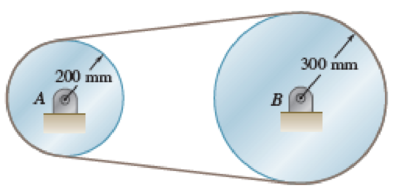
Fig. P16.35 and P16.36
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A metal plate of thickness 200 mm with thermal diffusivity 5.6 x10-6 m²/s and thermal
conductivity 20 W/mK is initially at a uniform temperature of 325°C. Suddenly, the 2 sides of
the plate are exposed to a coolant at 15°C for which the convection heat transfer coefficient is
100 W/m²K. Determine temperatures at the surface of the plate after 3 min using
(a) Lumped system analysis
(b) Analytical one term approximation
(c) One dimensional Semi infinite solid
Analyze and discuss the results
Problem 3
This problem maps back to learning
objectives 1-4 & 8.
Consider the particle attached to a spring shown below. The particle
has a mass m and the spring has a spring constant k. The mass-spring
system makes an angle of 0 with respect to the vertical and the
distance between point 0 and the particle can be defined as r. The
spring is unstretched when r = l.
Ꮎ
g
m
a) How many degrees of freedom is this system and what are
they?
b) Derive the equation(s) of motion that govern the movement of
this system.
Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY...
Scores
■Review
Determine the maximum constant speed at which the pilot can travel, so that he experiences a maximum acceleration
an = 8g = 78.5 m/s².
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
μΑ
v =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
?
Determine the normal force he exerts on the seat of the airplane when the plane is traveling at this speed and is at its lowest
point.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
о
HÅ
N =
Value
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
?
Units
Next >
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two solid cylinders, A and B, have the same mass m...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.1FBPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.2FBPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.3FBPCh. 16.1 - The 400-lb crate shown is lowered by means of two...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - A loading car is at rest on a track forming an...
Ch. 16.1 - A 2100-lb rear-wheel-drive tractor carries a 900...Ch. 16.1 - A uniform rod BC of mass 4 kg is connected to a...Ch. 16.1 - A 2000-kg truck is being used to lift a 400-kg...Ch. 16.1 - The support bracket shown is used to transport a...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.8PCh. 16.1 - A 20-kg cabinet is mounted on casters that allow...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.9, assuming that the casters are...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.11PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.12PCh. 16.1 - The retractable shelf shown is supported by two...Ch. 16.1 - Bars AB and BE, each with a mass of 4 kg, are...Ch. 16.1 - At the instant shown, the tensions in the vertical...Ch. 16.1 - Three bars, each of mass 3 kg, are welded together...Ch. 16.1 - Members ACE and DCB are each 600 mm long and are...Ch. 16.1 - A prototype rotating bicycle rack is designed to...Ch. 16.1 - The control rod AC is guided by two pins that...Ch. 16.1 - The coefficients of friction between the 30-lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.21PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.22PCh. 16.1 - For a rigid body in translation, show that the...Ch. 16.1 - For a rigid body in centroidal rotation, show that...Ch. 16.1 - It takes 10 min for a 2.4-Mg flywheel to coast to...Ch. 16.1 - The rotor of an electric motor has an angular...Ch. 16.1 - The 10-in.-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 10-in.-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 100-mm-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 180-mm-radius disk is at rest when it is...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.30, assuming that the direction of...Ch. 16.1 - In order to determine the mass moment of inertia...Ch. 16.1 - The flywheel shown has a radius of 20 in., a...Ch. 16.1 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a mass moment...Ch. 16.1 - Two disks A and B, of mass mA = 2 kg and mB = 4...Ch. 16.1 - Two disks A and B, of mass mA = 2 kg and mB = 4...Ch. 16.1 - Gear A weighs 1 lb and has a radius of gyration of...Ch. 16.1 - The 25-lb double pulley shown is at rest and in...Ch. 16.1 - A belt of negligible mass passes between cylinders...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.40PCh. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass of 6 kg and an initial angular...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.42PCh. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass mA = 4 kg, a radius rA = 300 mm,...Ch. 16.1 - Disk B is at rest when it is brought into contact...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.45PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.46PCh. 16.1 - For a rigid body in plane motion, show that the...Ch. 16.1 - A uniform slender rod AB rests on a frictionless...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.49PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.50PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.51PCh. 16.1 - A 250-lb satellite has a radius of gyration of 24...Ch. 16.1 - A rectangular plate of mass 5 kg is suspended from...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.54PCh. 16.1 - A drum with a 200-mm radius is attached to a disk...Ch. 16.1 - A drum with a 200-mm radius is attached to a disk...Ch. 16.1 - The 12-lb uniform disk shown has a radius of r =...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.58PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.59PCh. 16.1 - 16.60 and 16.61The 400-lb crate shown is lowered...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.61PCh. 16.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W = 14 lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.63PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.64PCh. 16.1 - A uniform slender bar AB with a mass m is...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.66PCh. 16.1 - 16.66 through 16.68A thin plate of the shape...Ch. 16.1 - 16.66 through 16.68A thin plate of the shape...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is projected along...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.69, assuming that the sphere is...Ch. 16.1 - A bowler projects an 8-in.-diameter ball weighing...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.72PCh. 16.1 - A uniform sphere of radius r and mass m is placed...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m has a linear...Ch. 16.2 - A cord is attached to a spool when a force P is...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.5CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.6CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.7CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.5FBPCh. 16.2 - Two identical 4-lb slender rods AB and BC are...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.7FBPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.8FBPCh. 16.2 - Show that the couple I of Fig. 16.15 can be...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender rod of length L = 900 mm and...Ch. 16.2 - A crate of mass 80 kg is held in the position...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender rod of length L = 36 in. and...Ch. 16.2 - In Prob. 16.78, determine (a) the distance h for...Ch. 16.2 - An athlete performs a leg extension on a machine...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.81PCh. 16.2 - A turbine disk weighing 50 lb rotates at a...Ch. 16.2 - The 80-lb tailgate of a car is supported by the...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform rod of length L and mass m is supported...Ch. 16.2 - Three stage lights are mounted on a pipe fixture...Ch. 16.2 - An adapted launcher uses a torsional spring about...Ch. 16.2 - A 4-kg slender rod is welded to the edge of a 3-kg...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.88PCh. 16.2 - The object ABC consists of two slender rods welded...Ch. 16.2 - A 3.5-kg slender rod AB and a 2-kg slender rod BC...Ch. 16.2 - A 9-kg uniform disk is attached to the 5-kg...Ch. 16.2 - Derive the equation MC=IC for the rolling disk of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.93PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.94PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.95PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.96PCh. 16.2 - A 40-kg flywheel of radius R = 0.5 m is rigidly...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.98PCh. 16.2 - 16.98 through 16.101A drum of 80-mm radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.98 through 16.101A drum of 80-mm radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.98 through 16.101A drum of 80-mm radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.106 and 16.107A 12-in.-radius cylinder of...Ch. 16.2 - 16.106 and 16.107A 12-in.-radius cylinder of...Ch. 16.2 - Gear C has a mass of 5 kg and a centroidal radius...Ch. 16.2 - Two uniform disks A and B, each with a mass of 2...Ch. 16.2 - A single-axis personal transport device starts...Ch. 16.2 - A hemisphere of weight W and radius r is released...Ch. 16.2 - A hemisphere of weight W and radius r is released...Ch. 16.2 - The center of gravity G of a 1.5-kg unbalanced...Ch. 16.2 - A small clamp of mass mB is attached at B to a...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.115PCh. 16.2 - A 4-lb bar is attached to a 10-lb uniform cylinder...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform rod AB with a mass m and a length of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.118PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.119PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.120PCh. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 8-kg uniform rod AB is attached to a...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform rod ABD is attached to the crank...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - The test rig shown was developed to perform...Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.127 for = 90. 16.127The test rig...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform slender bar BD is attached to bar...Ch. 16.2 - The motion of the uniform slender rod of length L...Ch. 16.2 - At the instant shown, the 20-ft-long, uniform...Ch. 16.2 - A driver starts his car with the door on the...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.133PCh. 16.2 - The hatchback of a car is positioned as shown to...Ch. 16.2 - The 6-kg rod BC connects a 10-kg disk centered at...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.136PCh. 16.2 - In the engine system shown, l = 250 mm and b = 100...Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.137 when = 90. 16.137In the engine...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Two disks, each with a mass m and a radius r, are...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender bar AB of mass m is suspended as...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform rod AB, of mass 15 kg and length 1 m, is...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform slender 2-kg bar BD is attached to the...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.147PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.148PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.149PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.150PCh. 16.2 - (a) Determine the magnitude and the location of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.152PCh. 16 - A cyclist is riding a bicycle at a speed of 20 mph...Ch. 16 - The forklift truck shown weighs 3200 lb and is...Ch. 16 - The total mass of the Baja car and driver,...Ch. 16 - Identical cylinders of mass m and radius r are...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.157RPCh. 16 - The uniform rod AB of weight W is released from...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.159RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.160RPCh. 16 - A cylinder with a circular hole is rolling without...Ch. 16 - Two 3-kg uniform bars are connected to form the...Ch. 16 - A crate of mass 80 kg is held in the position...Ch. 16 - The Geneva mechanism shown is used to provide an...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words.
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
The following C++ program will not compile because the lines have been mixed up. cout Success\n; cout Success...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I want to know the Milankovich orbital element constraint equation. Is it e*cos(i) = cos(argp), where e is eccentricity, i is inclination, and argp is arguement of periapsisarrow_forwardThe following data were taken during a one-hour trial run on a single cylinder, single acting, four-stroke diesel engine of cylinder diameter of 175 mm and stroke 225 mm , the speed being constant at 1000 rpm : Indicated mep: 5.5 barsDiam. of rope brake: 1066 mmLoad on brake: 400 NReading of balance: 27 NFuel consumed: 5.7 kgCalorific value: 44.2 MJ/kg Calculate the indicated power, brake power, specific fuel consumption per indicated kWh and per brake kWh , mechanical efficiency, indicated thermal and brake thermal efficiency.arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Document Sharing P Pearson MyLab and Mastering User Settings Part A P Course Home b Success Confirmation of Question Submission | bartleby A particle moves along an Archimedean spiral r = (80) ft, where 0 is given in radians. (Figure 1) If ė = = 4 rad/s and € = 5 rad/s², determine the radial component of the particle's velocity at the instant Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure y r = Α ? Vr = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the transverse component of the particle's velocity. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. о MÅ ve = Value Submit Request Answer Part C Units ? 1 of 1 Determine the radial component of the particle's acceleration. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Ar = (80) ft о ΜΑ Value Units ? = π/2 rad.arrow_forward
- Can you help me with a matlab code? I am trying to plot the keplerian orbital elements over time. I would usually find the orbit using cartesian system and then transform into keplerian orbital elements. Is there a way to directly integrate keplerian orbital elements?arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardK mylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Scores Course Homearrow_forwardK mylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Scores Course Homearrow_forwardChapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Scoresarrow_forwardIn a single cylinder, four stroke, single acting gas engine, the cylinder diameter is 180 mm and the stroke is 350 mm . When running at 250 rpm , the mean area of the indicator diagram taken off the engine is 355 mm² , length of diagram 75 mm , scale of the indicator spring 90 kN/m sq per mm , and the number of explosions was counted to be 114 per minute. Calculate the indicated power. so i have already asked this question and got a good answer, however on step 4, i dont understand how they reached 18.43 KW. When i do the math provided, i get the answer 7195.566. Where am i going wrong? thanks StepsTo clarify how we determined the Indicated Power, I'll go over each step in detail. Step 1: Comprehending the Provided Information - Cylinder diameter (in meters) = 180 mm = 0.18 m - Stroke length (in meters) = 350 mm = 0.35 m - Engine speed = 250 rpm -Indicator diagram mean area = 355 mm² The diagram's length is 75 mm; its spring scale is 90 kN/m² per mm, or 90,000 N/m² per mm; and…arrow_forwardIn MATLAB, can you help me simulate an orbit under earth J2 perturbation with the Milankovich orbital elements? Also, can you check to see if they fit the Milankovich constraint equaiton?arrow_forward8. All of the members in the Warren truss of Figure 8 are of length 10 ft. Use the method of sections to determine the forces in the members BD,CD,CE. B A C D E F G 2000 lb 3000 lb 5000 lb Figure 8 Harrow_forwardAn acrobat is walking on a tightrope of length L =20.1 m attached to supports A and B at a distance of 20.0 m apart. The combined weight of the acrobat and his balancing pole is 900 N, and the friction between his shoes and the rope is large enough to prevent him from slipping. Neglecting the weight of the rope and any elastic deformation, determine the deflection (y) and the tension in portion AC and BC of the rope for values of x from 0.5 m to 10 m using 0.5 m increments. 1. Determine the maximum deflection (y) in the rope. 2. Plot tension of AC and BC vs. x (on the same plot with x on the x-axis). Turn in the plot and the table of x, TAC, and TBC (clearly label each). A C 20.0 m Barrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
BEARINGS BASICS and Bearing Life for Mechanical Design in 10 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aU4CVZo3wgk;License: Standard Youtube License