
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the couple M.
(a)
Answer to Problem 16.136P
The couple M is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the rod BC is
The mass of the disk is
The mass of the rod CD is
The angular velocity is
The angular acceleration is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Calculate the velocity of disk AB
Substitute
Calculate the velocity of rod BC
The velocity of disk AB is equal to the velocity of rod BC.
Substitute
Calculate the angular velocity of rod CD
Substitute
Apply the acceleration analysis as shown below.
Calculate the acceleration for disk AB
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration for rod BC
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration for rod CD
Substitute
Equating the components of Equations (1) and (2) as shown below.
Along x component.
Along y component.
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of the mass centers as shown below.
Calculate the acceleration of mass center for disk AB
Calculate the acceleration of the mass center at P for rod BC
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of the mass center at Q for rod CD
Substitute
Calculate the inertial terms at mass centers as shown below.
The inertia terms at centers are
For disk AB.
For rod BC.
Substitute
For rod CD.
Substitute
Calculate the mass moment of inertia
For disk AB.
Substitute
For rod BC.
Substitute
For rod CD.
Substitute
Calculate the effective couples at mass centers as shown below.
The inertia terms at centers are
For disk AB.
For rod BC.
Substitute
For rod CD.
Substitute
Sketch the effective force and couples on the system as shown in Figure 1.
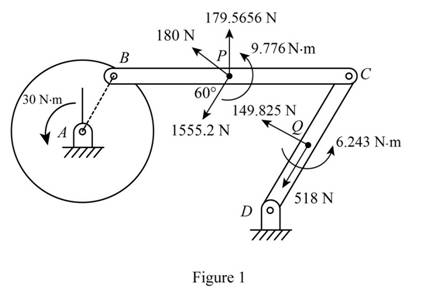
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the rod BC as shown in Figure 2.
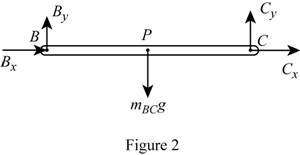
Refer to Figure 2.
Apply the Equilibrium of moment about B as shown below.
Substitute
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the rod CD as shown in Figure 3.
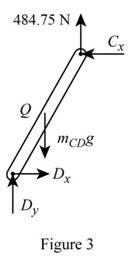
Refer to Figure 3.
Apply the Equilibrium of moment about D as shown below.
Substitute
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the rod AB and BC as shown in Figure 4.
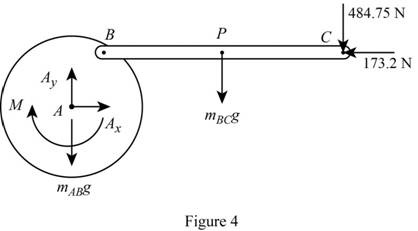
Refer to Figure 4.
Apply the Equilibrium of moment about A as shown below.
Substitute
Therefore, the couple M is
(b)
The components of force exerted at C on rod BC.
(b)
Answer to Problem 16.136P
The components of force exerted at C on rod BC is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the rod BC is
The mass of the disk is
The mass of the rod CD is
The angular velocity is
The angular acceleration is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The components of force exerted at C on rod BC along x direction is
The components of force exerted at C on rod BC along y direction is
Therefore, the components of force exerted at C on rod BC is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- A piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the change in the volume of the cylinder of the refrigerant-134a if the specific volume and enthalpy of R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and -10°C and at the final state of 90.4 kPa and 15°C are as follows: = 0.2418 m³/kg, h₁ = 247.77 kJ/kg 3 v2 = 0.2670 m³/kg, and h₂ = 268.18 kJ/kg The change in the volume of the cylinder is marrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the final pressure of the refrigerant-134a. The final pressure is kPa.arrow_forwardThe hydraulic cylinder BC exerts on member AB a force P directed along line BC. The force P must have a 560-N component perpendicular to member AB. A M 45° 30° C Determine the force component along line AB. The force component along line AB is N.arrow_forward
- ! Required information A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. The tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is given to be T₁ = 815 lb. A 15° 25° B T₂ Using trigonometry, determine the required tension T₂ in the right-hand portion if the resultant R of the forces exerted by the cable at A is to be vertical. The required tension is lb.arrow_forwardWhat are examples of at least three (3) applications of tolerance fitting analysis.arrow_forwardThe primary material used in the production of glass products is silica sand. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Which one of the following is the most common polymer type in fiber-reinforced polymer composites? thermosets thermoplastics elastomers none of the abovearrow_forwardA pattern for a product is larger than the actual finished part. True or Falsearrow_forwardIn the lost foam process, the pattern doesn’t need to be removed from the mold. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Tempering eliminates internal stresses in glass. True or Falsearrow_forwardThermoset polymers can be recycled with little to no degradation in properties. True or Falsearrow_forwardTwo forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DG a 터 Using trigonometry, determine the required angle a such that the resultant R of the two forces applied to the support will be horizontal. The value of a isarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





