
Concept explainers
Disk A has a mass mA = 4 kg, a radius rA = 300 mm, and an initial angular velocity ω0 = 300 rpm clockwise. Disk B has a mass mB = 1.6 kg, a radius rB = 180 mm, and is at rest when it is brought into contact with disk A. Knowing that μk = 0.35 between the disks and neglecting bearing friction, determine (a) the angular acceleration of each disk, (b) the reaction at the support C.
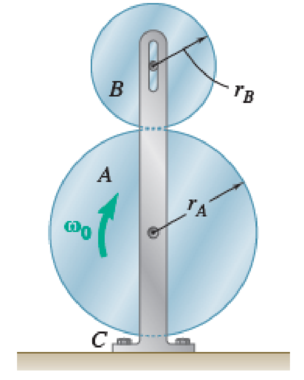
Fig. P16.43 and P16.44
(a)
Find the angular acceleration of each disk
Answer to Problem 16.43P
The angular acceleration of each disk
Explanation of Solution
The mass of the disk A
The mass of the disk B
The initial angular velocity of the disk A
The coefficient of the kinetic friction
The radius of the disk A
The radius of the disk B
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity (g) as
Convert the unit of the radius of the disk A
Convert the unit of the radius of the disk B
Calculate the mass moment of inertia of the disk A
Substitute
Calculate the mass moment of inertia of the disk B
Substitute
Calculate the load of the disk A
Substitute
Calculate the load of the disk B
Substitute
Show the free body diagram of the disk B as in Figure 1.
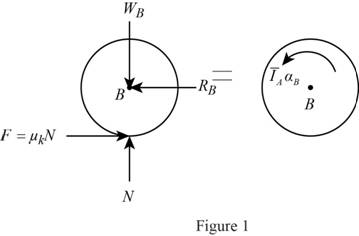
Here,
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the vertical forces by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Sum of vertical forces is equal to 0.
Substitute
Calculate the magnitude of the friction force
Substitute
Calculate the horizontal forces by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Sum of horizontal forces is equal to 0.
Substitute
Calculate the angular acceleration of the disk B
Calculate the moment about point B by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Substitute
Show the free body diagram of the disk A as in Figure 2.
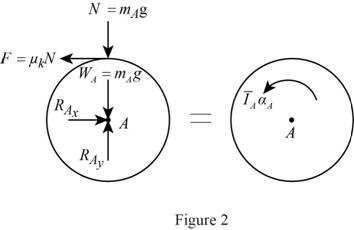
Here,
Refer to Figure 2.
Calculate the horizontal forces by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Sum of horizontal forces is equal to 0.
Substitute
Calculate the vertical forces by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Sum of vertical forces is equal to 0.
Substitute
Calculate the angular acceleration of the disk A
Calculate the moment about point A by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Substitute
Hence, the angular acceleration of each disk
(b)
Find the reaction at the support C
Answer to Problem 16.43P
The reaction at the support C
Explanation of Solution
The mass of the disk A
The mass of the disk B
The initial angular velocity of the disk A
The coefficient of the kinetic friction
The radius of the disk A
The radius of the disk B
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
Show the free body diagram of the support C as in Figure 3.
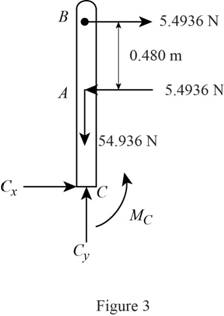
Here,
Refer to Figure 3.
Calculate the horizontal forces by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Sum of horizontal forces is equal to 0.
Calculate the vertical forces by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Sum of vertical forces is equal to 0.
Calculate the moment about point C by applying the equation of equilibrium:
Sum of moments about point C is equal to 0.
Substitute
Calculate the time required for the disk to come to rest (t):
Substitute
Calculate the final angular velocity of the disk A
Substitute
Calculate the final angular velocity of the disk B
Substitute
Hence, the reaction at the support C
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Modern Database Management
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- متوسعة الفرج بو عمامة المستوى رم الواجب المنزلي رقم 04 تمرین الوان حسب يتمعن العبارات الأتية : A= (+2)+(-45) B=(+13)- C = (+17)-(+13)-(-20)+(-19 D= [(-15)-(+15)]-[(+20) + هست قیم مدرج مبدؤه النقطة ة الطول :tcm A(-2,5): B(+ 2,5) ≤ C (+5) المسافتين : BAD ين الثاني لمستوي مبدؤه 8 وحدتهarrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on AI, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer!!!!! You can borrow ideas from AI, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! ( If you write by hand or don't use AI, I'll give you a big thumbs up ) Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forwardA thin uniform rod of mass m and length 2r rests in a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius r. A moment M = mgr horizontal plane. is applied to the rod. Assume that the bowl is fixed and its rim is in the HINT: It will help you to find the length l of that portion of the rod that remains outside the bowl. M 2r Ꮎ a) How many degrees of freedom does this system have? b) Write an equation for the virtual work in terms of the angle 0 and the motion of the center of mass (TF) c) Derive an equation for the variation in the position of the center of mass (i.e., Sŕƒ) a. HINT: Use the center of the bowl as the coordinate system origin for the problem. d) In the case of no applied moment (i.e., M = 0), derive an equation that can be used to solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation e) In the case of an applied moment (i.e., M: = mgr 4 -) derive an equation that can be used to solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation. f) Can the angle 0 and…arrow_forward
- Please do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forward= The frame shown is fitted with three 50 cm diameter frictionless pulleys. A force of F = 630 N is applied to the rope at an angle ◊ 43°. Member ABCD is attached to the wall by a fixed support at A. Find the forces indicated below. Note: The rope is tangent to the pully (D) and not secured at the 3 o'clock position. a b •C *су G E e d BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 81 cm b 50 cm с 59 cm d 155 cm For all answers, take x as positive to the right and positive upward. At point A, the fixed support exerts a force of: A = + ĴN and a reaction couple of: →> ΜΑ Member CG is in Select an answer magnitude У as k N-m. and carries a force of N.arrow_forwardThe lower jaw AB [Purple 1] and the upper jaw-handle AD [Yellow 2] exert vertical clamping forces on the object at R. The hand squeezes the upper jaw-handle AD [2] and the lower handle BC [Orane 4] with forces F. (Member CD [Red 3] acts as if it is pinned at D, but, in a real vise-grips, its position is actually adjustable.) The clamping force, R, depends on the geometry and on the squeezing force F applied to the handles. Determine the proportionality between the clamping force, R, and the squeezing force F for the dimensions given. d3 d4 R 1 B d1 2 d2 D... d5 F 4 F Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value d1 65 mm d2 156 mm d3 50 mm 45 d4 d5 113 mm 30 mm R = Farrow_forward
- A triangular distributed load of max intensity w =460 N/m acts on beam AB. The beam is supported by a pin at A and member CD, which is connected by pins at C and D respectively. Determine the reaction forces at A and C. Enter your answers in Cartesian components. Assume the masses of both beam AB and member CD are negligible. cc 040 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl W A C D -a- B Ул -b- x Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value α 5.4 m b 8.64 m C 3.24 m The reaction at A is A = i+ ĴN. λ = i+ Ĵ N. The reaction at C is C =arrow_forward56 Clamps like the one shown are commonly used in woodworking applications. This clamp has the dimensions given in the table below the figure, and its jaws are mm thick (in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the picture). a.) The screws of the clamp are adjusted so that there is a uniform pressure of P = 150 kPa being applied to the workpieces by the jaws. Determine the force carried in each screw. Hint: the uniform pressure can be modeled in 2-D as a uniform distributed load with intensity w = Pt (units of N/m) acting over the length of contact between the jaw and the workpiece. b.) Determine the minimum vertical force (parallel to the jaws) required to pull either one of the workpieces out of the clamp jaws. Use a coefficient of static friction between all contacting surfaces of μs = 0.56 and the same clamping pressure given for part (a). 2013 Michael Swanbom A B C a Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale.…arrow_forwardDetermine the force in each member of the space truss given F=5 kN. Use positive to indicate tension and negative to indicate compression. F E Z -2 m. B 3 m C 5 m 3 m A -4 m. AB = KN FAC = FAD = KN KN KN FBC = KN FBD FBE = = KN Farrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





