
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781259639272
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.1, Problem 16.3CQ
Two solid cylinders, A and B, have the same mass m and the radii 2r and r, respectively. Each is accelerated from rest with a force applied as shown. In order to impart identical angular accelerations to both cylinders, what is the relationship between F1 and F2?
a. F1 = 0.5F2
b. F1 = F2
c. F1 = 2F2
d. F1 = 4F2
e. F1 = 8F2
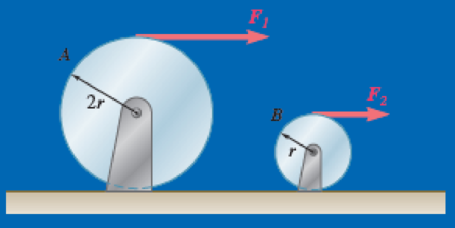
Fig. P16.CQ3
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
reading is 0.4 mas SHOWN.
Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m.
(a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury?
(b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline?
(c) Do you know the specific weight of oil?
(a) YHg
=
133,000
(b) Ygas
= 6867
(c) Yoil =
8829
eTextbook and Media
Part 2
N/m³
N/m³
N/m³
A+
Gasoline
t
+B
Oil
-Mercury
Attempts: unlimited
Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight?
Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes?
Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations?
Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground?
Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference.
Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid.
(a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB)
(b) What is…
Find the solution of the following Differential Equations
1)
"-4y+3y=0
3) "+16y=0
2) y"-16y=0
4) y"-y-6y=0
5) y"+2y=0
7) y"+y=0, (#0)
9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4
11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1,
13)
y'(0) = -5
"+2y+2y=0
15) y"-9y=0
17) y"-4y=0
6) y"-2y+2y=0
8)
"+4y+5y=0
10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0
12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1,
y'(0) = 0
14) 4y+4y+y=0
16) "+6y+12y=0
18) 4y+4y+17y=0
Access Pearson
Mastering Engineering
Back to my courses
Course Home
Course Home
Scores
Chapter 16 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two solid cylinders, A and B, have the same mass m...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.1FBPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.2FBPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.3FBPCh. 16.1 - The 400-lb crate shown is lowered by means of two...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - 16.3 Knowing that the coefficient of static...
Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.4PCh. 16.1 - A uniform rod BC of mass 4 kg is connected to a...Ch. 16.1 - A 2000-kg truck is being used to lift a 400-kg...Ch. 16.1 - The support bracket shown is used to transport a...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.8PCh. 16.1 - A 20-kg cabinet is mounted on casters that allow...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.9, assuming that the casters are...Ch. 16.1 - 16.11 A completely filled barrel and its contents...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.12PCh. 16.1 - The retractable shelf shown is supported by two...Ch. 16.1 - Bars AB and BE, each with a mass of 4 kg, are...Ch. 16.1 - At the instant shown, the tensions in the vertical...Ch. 16.1 - Three bars, each of mass 3 kg, are welded together...Ch. 16.1 - Members ACE and DCB are each 600 mm long and are...Ch. 16.1 - 16.18 A prototype rotating bicycle rack is...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.19PCh. 16.1 - The coefficients of friction between the 30-lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.21PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.22PCh. 16.1 - For a rigid body in translation, show that the...Ch. 16.1 - For a rigid body in centroidal rotation, show that...Ch. 16.1 - It takes 10 min for a 2.4-Mg flywheel to coast to...Ch. 16.1 - The rotor of an electric motor has an angular...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.27PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.28PCh. 16.1 - The 100-mm-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 180-mm-radius disk is at rest when it is...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.30, assuming that the direction of...Ch. 16.1 - In order to determine the mass moment of inertia...Ch. 16.1 - The flywheel shown has a radius of 20 in., a...Ch. 16.1 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a mass moment...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.35PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.36PCh. 16.1 - Gear A weighs 1 lb and has a radius of gyration of...Ch. 16.1 - The 25-lb double pulley shown is at rest and in...Ch. 16.1 - A belt of negligible mass passes between cylinders...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.40PCh. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass of 6 kg and an initial angular...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.42PCh. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass mA = 4 kg, a radius rA = 300 mm,...Ch. 16.1 - Disk B is at rest when it is brought into contact...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.45PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.46PCh. 16.1 - For a rigid body in plane motion, show that the...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.48PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.49PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.50PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.51PCh. 16.1 - A 250-lb satellite has a radius of gyration of 24...Ch. 16.1 - A rectangular plate of mass 5 kg is suspended from...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.54PCh. 16.1 - A drum with a 200-mm radius is attached to a disk...Ch. 16.1 - A drum with a 200-mm radius is attached to a disk...Ch. 16.1 - The 12-lb uniform disk shown has a radius of r =...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.58PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.59PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.60PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.61PCh. 16.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W = 14 lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.63PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.64PCh. 16.1 - A uniform slender bar AB with a mass m is...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.66PCh. 16.1 - 16.66 through 16.68A thin plate of the shape...Ch. 16.1 - 16.66 through 16.68A thin plate of the shape...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is projected along...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.69, assuming that the sphere is...Ch. 16.1 - A bowler projects an 8-in.-diameter ball weighing...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.72PCh. 16.1 - A uniform sphere of radius r and mass m is placed...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m has a linear...Ch. 16.2 - A cord is attached to a spool when a force P is...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.5CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.6CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.7CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.5FBPCh. 16.2 - Two identical 4-lb slender rods AB and BC are...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.7FBPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.8FBPCh. 16.2 - Show that the couple I of Fig. 16.15 can be...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.76PCh. 16.2 - 16.77 In Prob. 16.76, determine (a) the distance r...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender rod of length L = 36 in. and...Ch. 16.2 - In Prob. 16.78, determine (a) the distance h for...Ch. 16.2 - An athlete performs a leg extension on a machine...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.81PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.82PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.83PCh. 16.2 - A uniform rod of length L and mass m is supported...Ch. 16.2 - 16.84 and 16.85 A uniform rod of length L and mass...Ch. 16.2 - An adapted launcher uses a torsional spring about...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.87PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.88PCh. 16.2 - The object ABC consists of two slender rods welded...Ch. 16.2 - A 3.5-kg slender rod AB and a 2-kg slender rod BC...Ch. 16.2 - A 9-kg uniform disk is attached to the 5-kg...Ch. 16.2 - Derive the equation MC=IC for the rolling disk of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.93PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.94PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.95PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.96PCh. 16.2 - A 40-kg flywheel of radius R = 0.5 m is rigidly...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.98PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.99PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.100PCh. 16.2 - 16.98 through 16.101 A drum of 60-mm radius is...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.102PCh. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105 A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.104PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.105PCh. 16.2 - 16.106 and 16.107A 12-in.-radius cylinder of...Ch. 16.2 - 16.106 and 16.107A 12-in.-radius cylinder of...Ch. 16.2 - Gear C has a mass of 5 kg and a centroidal radius...Ch. 16.2 - Two uniform disks A and B, each with a mass of 2...Ch. 16.2 - A single-axis personal transport device starts...Ch. 16.2 - A hemisphere of weight W and radius r is released...Ch. 16.2 - A hemisphere of weight W and radius r is released...Ch. 16.2 - The center of gravity G of a 1.5-kg unbalanced...Ch. 16.2 - A small clamp of mass mB is attached at B to a...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.115PCh. 16.2 - A 4-lb bar is attached to a 10-lb uniform cylinder...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform rod AB with a mass m and a length of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.118PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.119PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.120PCh. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 8-kg uniform rod AB is attached to a...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform rod ABD is attached to the crank...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - The test rig shown was developed to perform...Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.127 for = 90. 16.127The test rig...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform slender bar BD is attached to bar...Ch. 16.2 - The motion of the uniform slender rod of length L...Ch. 16.2 - At the instant shown, the 20-ft-long, uniform...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.132PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.133PCh. 16.2 - The hatchback of a car is positioned as shown to...Ch. 16.2 - The 6-kg rod BC connects a 10-kg disk centered at...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.136PCh. 16.2 - In the engine system shown, l = 250 mm and b = 100...Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.137 when = 90. 16.137In the engine...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Two disks, each with a mass m and a radius r, are...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender bar AB of mass m is suspended as...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform rod AB, of mass 15 kg and length 1 m, is...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform slender 2-kg bar BD is attached to the...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.147PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.148PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.149PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.150PCh. 16.2 - (a) Determine the magnitude and the location of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.152PCh. 16 - A cyclist is riding a bicycle at a speed of 20 mph...Ch. 16 - 16.154 The forklift truck shown weighs 2250 lb and...Ch. 16 - The total mass of the Baja car and driver,...Ch. 16 - Identical cylinders of mass m and radius r are...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.157RPCh. 16 - The uniform rod AB of weight W is released from...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.159RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.160RPCh. 16 - A cylinder with a circular hole is rolling without...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.162RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.163RPCh. 16 - The Geneva mechanism shown is used to provide an...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Using your text editor, enter (that is, type in) the C++ program shown in Display 1.8. Be certain to type the f...
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Consider the adage Never ask a question for which you do not want the answer. a. Is following that adage ethica...
Experiencing MIS
Computers process data under the control of sets of instructions called
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Access Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardCan you answer this question?arrow_forwardA gear has a gear wheel with 16 teeth. The gear should be dimensioned for the highest and lowest gear ratio. Looking for output power, torque, speed?nin= 2000 rpmmin = 30Nmn=0,9a max= 450 mmModule 4Gear limitsz1 z213 13-1614 14-2615 15-4516 16-10117 17-131418 18-…..I have calculate but I can’t get the right answers…..√16 =459x60/56x57=1.1 lowest59x60/13x13=20,94 highestnut=2000/1.1= 1818rpmnut=2000/20.94=95.5 rpmMut=1.1x30=33 NmMut=20.94x30=628,2 Nm(Right answer)LowestZ=13, M=24,4Nm, n=2462 rpmHighestZ=92, M=172,5Nm, n=347,8 rpmP=5655W on botharrow_forwardPlease see attached pic.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Work, Energy, and Power: Crash Course Physics #9; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w4QFJb9a8vo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Different Forms Of Energy | Physics; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XiNx7YBnM-s;License: Standard Youtube License